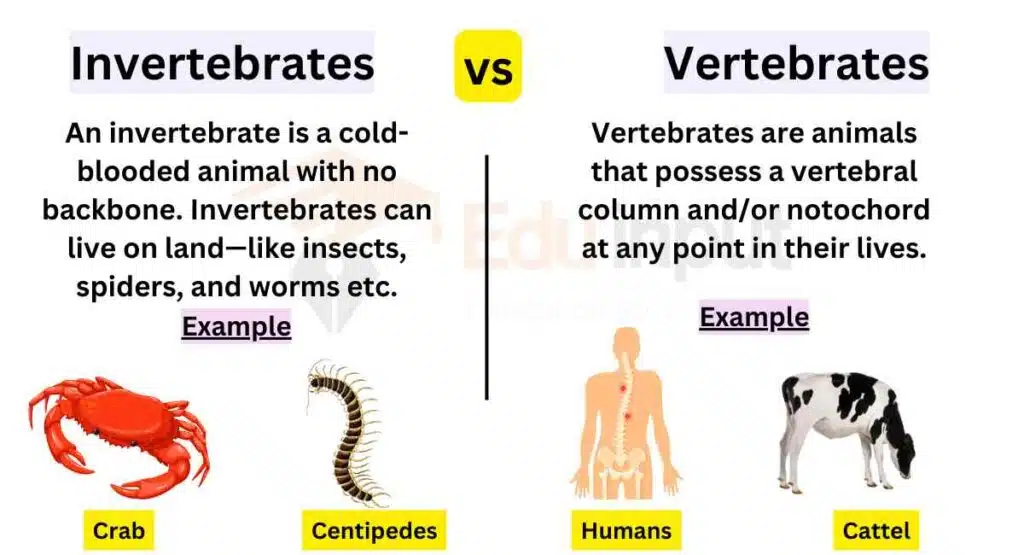
Invertebrates And Vertebrates- What’s the Difference?
vertebrates and invertebrates are two main animal groups. Vertebrates have a backbone, like humans, dogs, birds, and fish. Invertebrates don’t have a backbone, such as insects, spiders, and jellyfish. Vertebrates have an inner skeleton of bone or cartilage, while invertebrates often have no skeleton or an outer shell.
Most animals are invertebrates. They make up about 97% of all animal species. Vertebrates are usually bigger and more complex. But invertebrates come in many shapes and sizes, from tiny bugs to large octopuses.
Check out these 10 examples of invertebrates.
Invertebrates vs Vertebrates
Here are the main differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates:
| Aspect | Invertebrates | Vertebrates |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Animals without a backbone | Animals with a backbone |
| Diversity | Vast majority of animal species are invertebrates | Smaller number of species compared to invertebrates |
| Body Structure | Varied body structures and forms | More complex body structures and internal skeletons |
| Skeletal System | Lack a bony skeleton; may have exoskeletons, shells, or no hard structure | Possess an internal skeleton made of bones or cartilage |
| Nervous System | Diverse nervous system types, including nerve nets and ganglia | Possess a well-developed centralized nervous system, including a brain and spinal cord |
| Reproduction | Various modes of reproduction, including sexual and asexual | Mostly sexual reproduction, with internal fertilization being common |
| Size Range | Varies greatly in size, from microscopic to large sizes | Sizes range from small to very large |
| Habitat | Occupy diverse habitats, including terrestrial, aquatic, and aerial environments | Found in a wide range of habitats, including terrestrial, aquatic, and aerial environments |
| Exoskeleton | Have an exoskeleton | Do not possess an exoskeleton |
| Circulatory System | Majority have an open circulatory system | Possess a closed circulatory system |
| Eyes | Many have compound eyes | Do not have compound eyes |
| Body Symmetry | Includes radial or bilateral body symmetry | All have bilateral body symmetry |
| Mode of Nutrition | Autotrophic, parasitic, and heterotrophic | Usually heterotrophic |
| Species Distribution | 95% of animal species are invertebrates | 5% of animal species are vertebrates |
| Examples | Flatworms, arthropods, sponges, insects, worms, mollusks, jellyfish, sponges | Mammals, fish, reptiles, amphibians, birds |



Leave a Reply