Immunoglobin- Definition, Structure, and Types
Immunoglobulins are glycoprotein molecules produced by Leukocytes (white blood Cells). Immunoglobulins are commonly known as antibodies. They are typically found in blood and other bodily fluids.
Structure of Immunoglobins
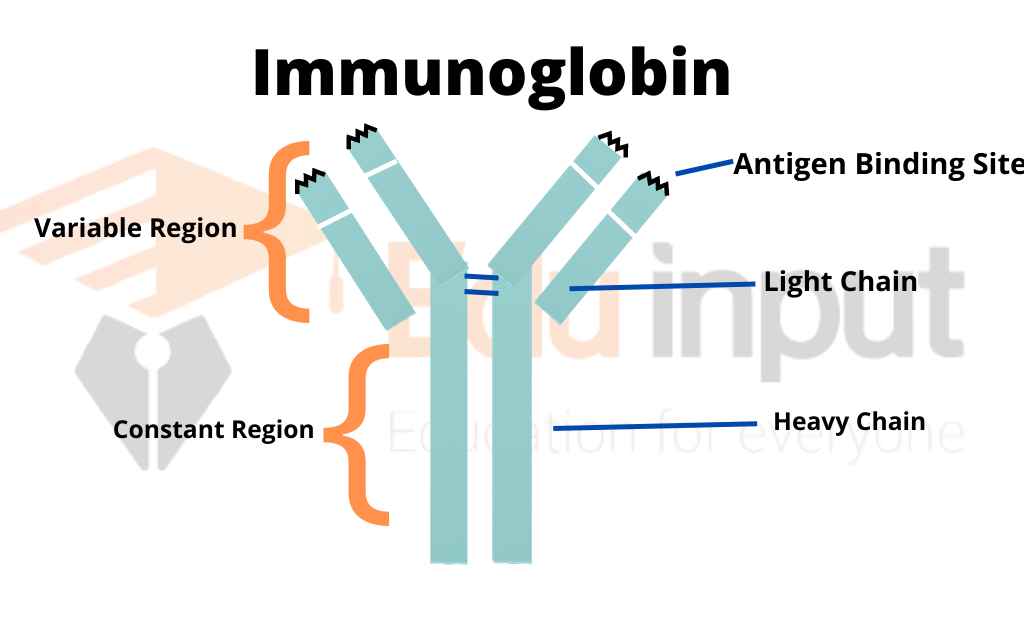
An antibody is a Y-shaped protein that is composed of four subunits. Two of these subunits are light chains, and the other two are heavy chains. The N-terminus of each heavy chain has an antigen-binding domain. This domain is what allows the antibody to bind to a specific antigen.
The C-terminus of the heavy chain forms the fragment crystallization domain. This domain helps the antibody interact with effector cells.
All four subunits are held together by disulfide and non-covalent bonds.
Types Of Immunoglobin
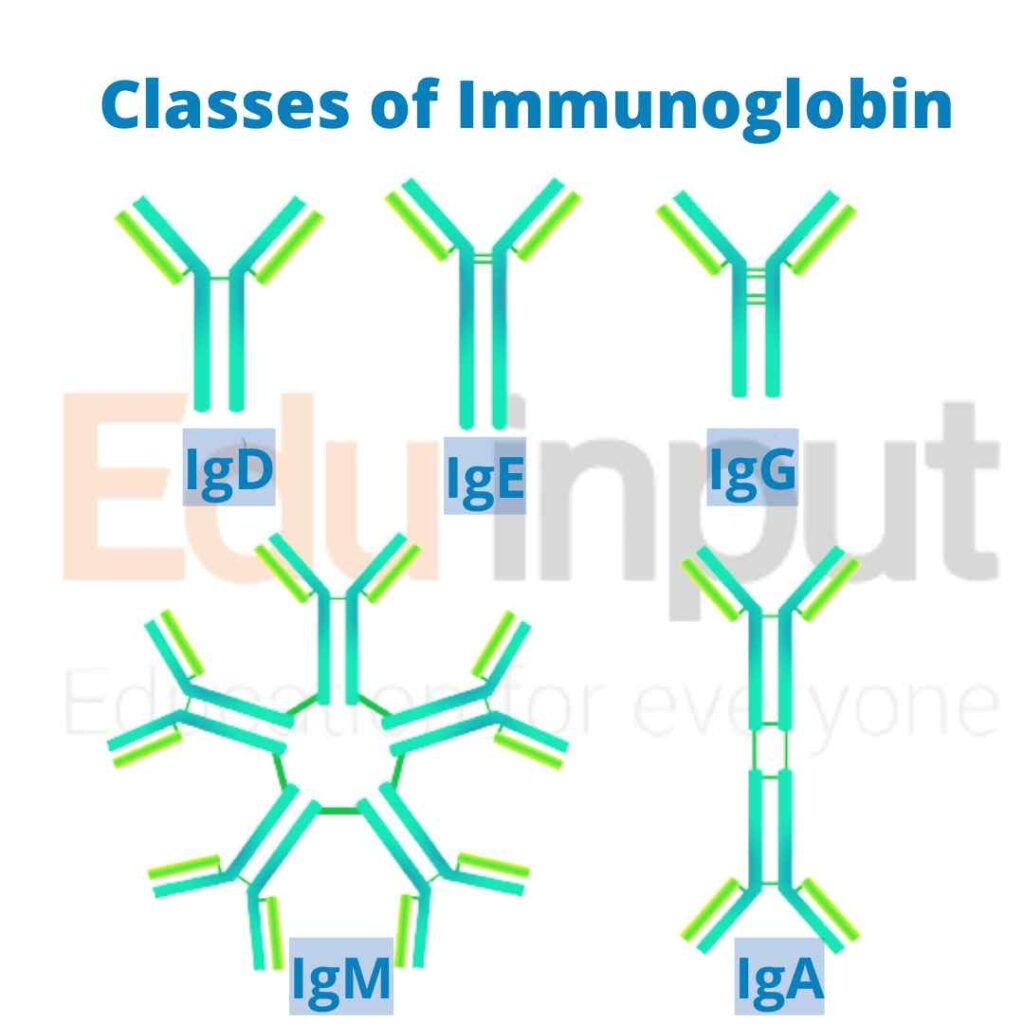
There are five classes of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM).
IgM
IgM is the first antibody that B cells produce when they come under attack from bacteria. It is typically the form of immunoglobulin that is present on the surface of B cells. When IgM is secreted from B cells, it exists as a pentamer molecule with 10 antigen-binding sites.
It constitutes 6% of the total antibody content.
IgG
IgG is a type of immunoglobulin that is commonly found in blood and tissue fluids. It is made up of two H chains and two identical L chains, and each chain has an antigen-binding site. It constitutes 80% of the total antibody content. IgG is important for providing immunity to the developing fetus.
IgA
IgA is the most common one found in secretions like tears, saliva, and colostrum. It’s produced by B cells and it’s mainly found in mucous membranes. Not a lot of IgA is present in serum. It constitutes 13% of the total antibody content.
IgE
only a small proportion of B cells produces IgE. Additionally, it is present within blood in low concentrations. Each IgE molecule is made up of one four-chain unit, and as a result has two antigen-binding sites – just like IgG molecules. It constitutes 0.02% of the total antibody content.
IgD
While IgD molecules are commonly found on the surface of B cells during their early development, not all B cells contain them. Additionally, very little IgD is ever released into blood circulation. It constitutes 1% of the total antibody content.
What are B-Cell?
B-cell is precursors, which are constantly generated in the bone marrow, and play an important role in lifelong immunity. When a B cell’s receptor recognizes an antigen, it binds to the antigen and becomes activated. The B cell then produces antibodies that help destroy the antigen.



Leave a Reply