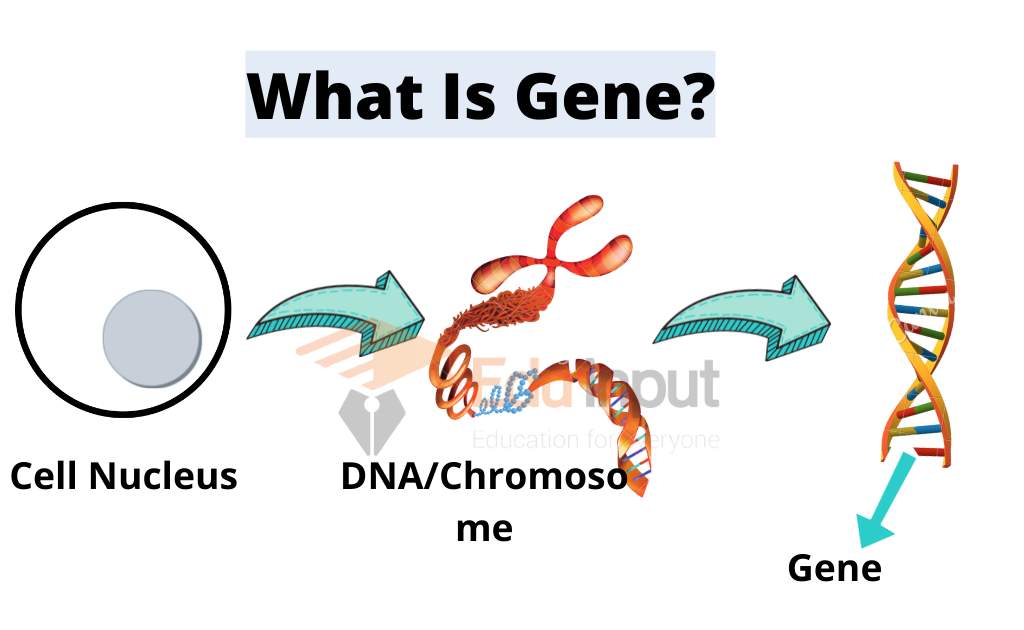
Synthesis of Protein | Translation of mRNA
The synthesis of protein at the ribosomes from mRNA is called translation.
Role of tRNA in Synthesis of Protein
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA that plays an important role in translation. It reads codes on the mRNA and brings different amino acids. Thus a polypeptide chain is formed.
The RNA has a complementary pairing of bases. But tRNA has some unusual bases. These bases disrupt the normal base pairing and form loops in the molecule.
The center loop is called the anticodon loop. It has a sequence of three unpaired bases called the anticodon.
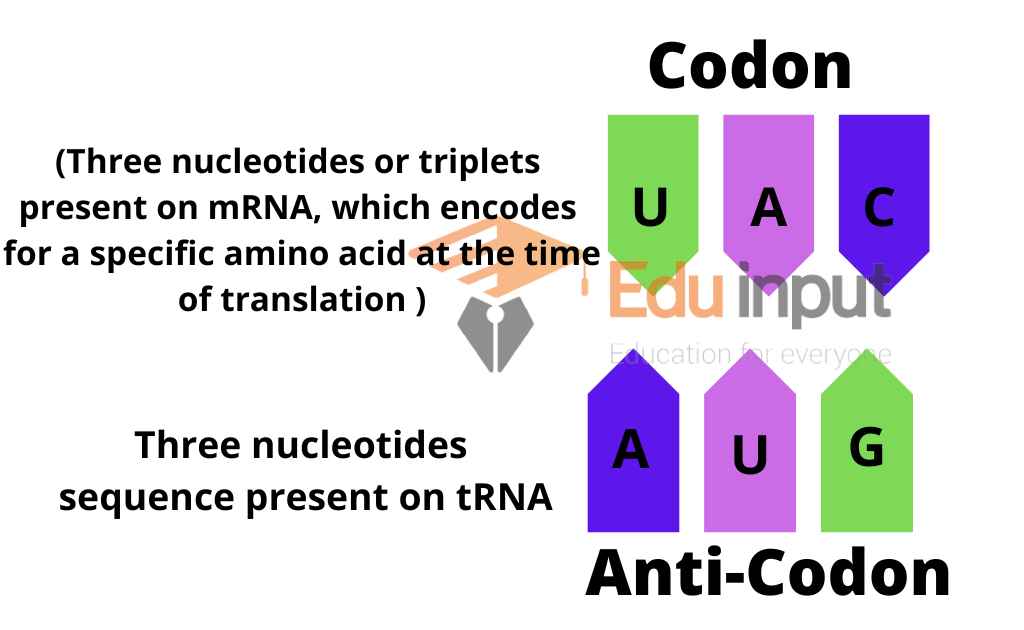
The mRNA codon forms pairing with its complementary anticodon of tRNA. The tRNA carries amino acids.
Role of ribosomes in protein synthesis
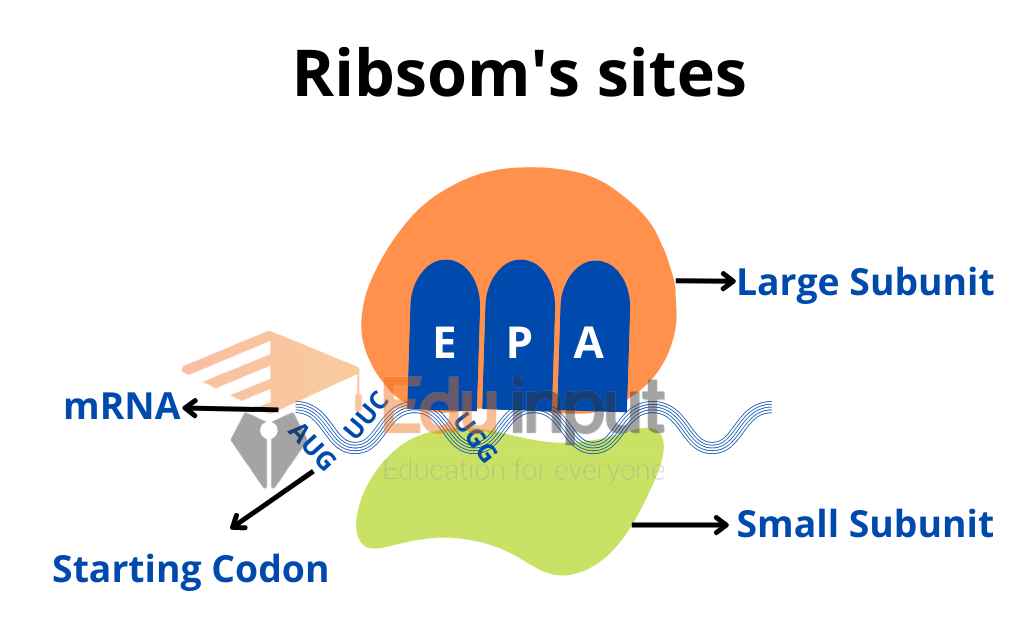
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. They consist of large and small subunits.
These subunits organize the pairing between the codon and the anticodon. The ribosome has several binding sites for mRNA and tRNA.
Ribosome Sites
The ribosome has three sites:
P site (peptidyl site): It is the site of the ribosome where peptide bonds are formed.
A site (aminoacyl site): This site contains successive (next) amino acids with its rRNA.
E site (exit site): It is a site of ribosome where empty tRNA is present.
Steps of Protein Synthesis
There are the following steps of protein synthesis:
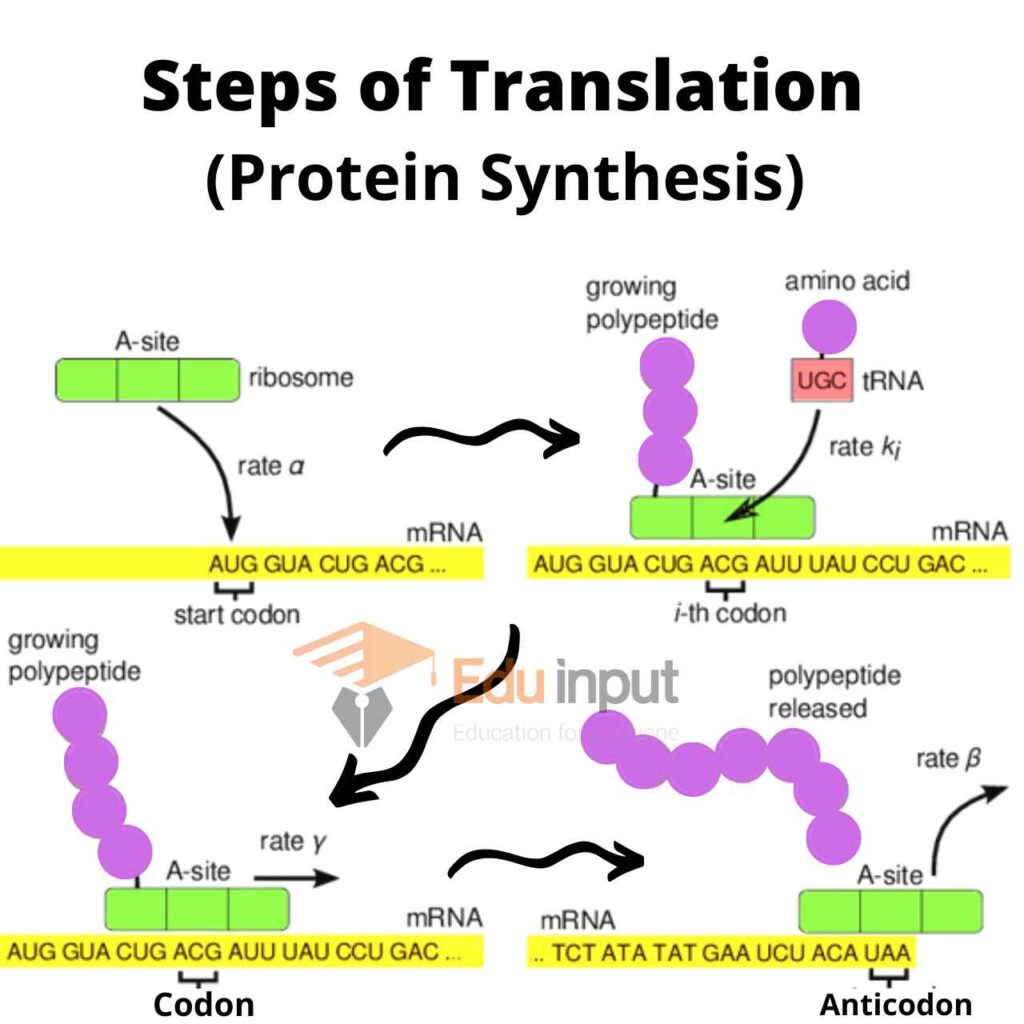
1- Initiation
The mRNA binds to a small ribosomal subunit. The initiation codon on mRNA is AUG. The initiation code of mRNA aligns with the P (peptidyl) site of the ribosome.
A tRNA with methionine binds to the mRNA on the initiation codon. The large subunit joins this complex. It forms a complete ribosome.
2- Elongation
The A (aminoacyl) site is present next to the P site. It has a second codon. A second tRNA attaches to this codon with its anticodon.
Two tRNA molecules with their amino acids are now side-by-side in A sites. This step requires enzymes and energy. Guanine triphosphate (GTP) provides energy to this step.
An enzyme peptidyl transferase breaks the bond between the amino acid and tRNA in the P site. It also catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between that amino acid and the amino acid in the A site.
The mRNA strand then moves along the ribosome. It exposes a new codon. The tRNA with their two amino acids moves to the P site. A third tRNA can now enter the exposed A site. This process continues and the entire mRNA has been translated.
3- Termination
The ribosome reaches the end of the mRNA. The polypeptide chain has been synthesized. Termination codon like UAA comes and translation ends.
4- Export of protein
Protein synthesis occurs on ribosomes. Most of the ribosomes are attached to the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
The newly synthesized protein moves into the ER. The protein then moves into the Golgi apparatus. It is packed into a secretory vesicle or a lysosome.
Related FAQs
What is Translation?
The synthesis of protein by ribosomes from mRNA is called translation.
What is the difference between Translation and Transcription?
Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA from DNA, while this mRNA is used to synthesis protein through translation.
What are the Steps of Protein Synthesis?
Steps of Protein Synthesis involve the following steps;
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Transport of Protein
Where are protein synthesized?
Proteins are synthesized at Ribosomes, which are also known as protein factories.
What is the process of protein synthesis called?
The process of protein synthesis is called translation, as the code on mRNA is translated into proteins.



Leave a Reply