What is Cell Cycle? | Phases of Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is the process in which a cell increases its size, replicates its DNA, prepares itself for division, and then divides into daughter cells. It includes Mitosis and Meiosis. Cell division occurs during the growth and repair processes of the body.
The cell cycle has the following basic stages:
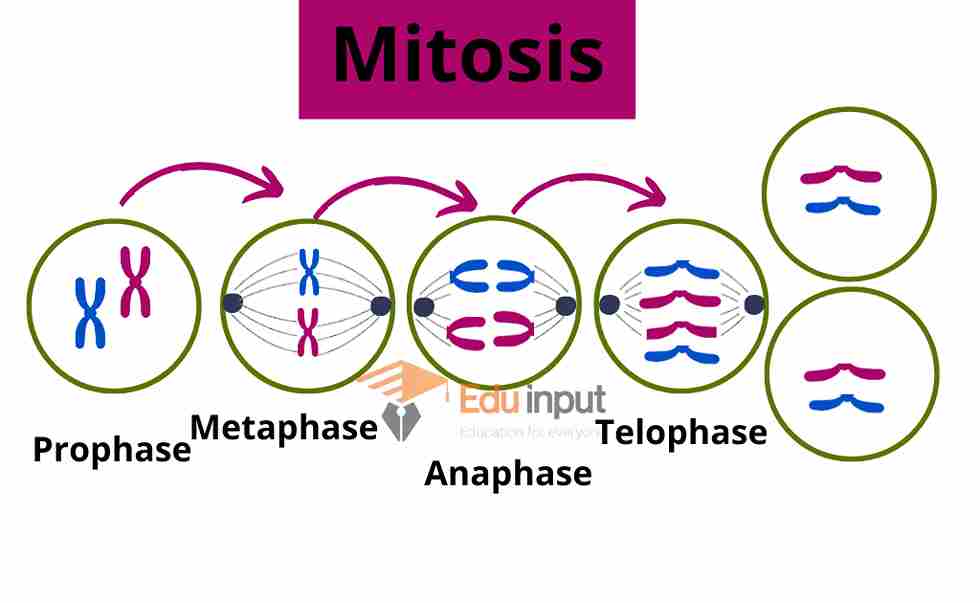
Mitosis
It is the division of the nucleus. The nucleus divides into two nuclei.
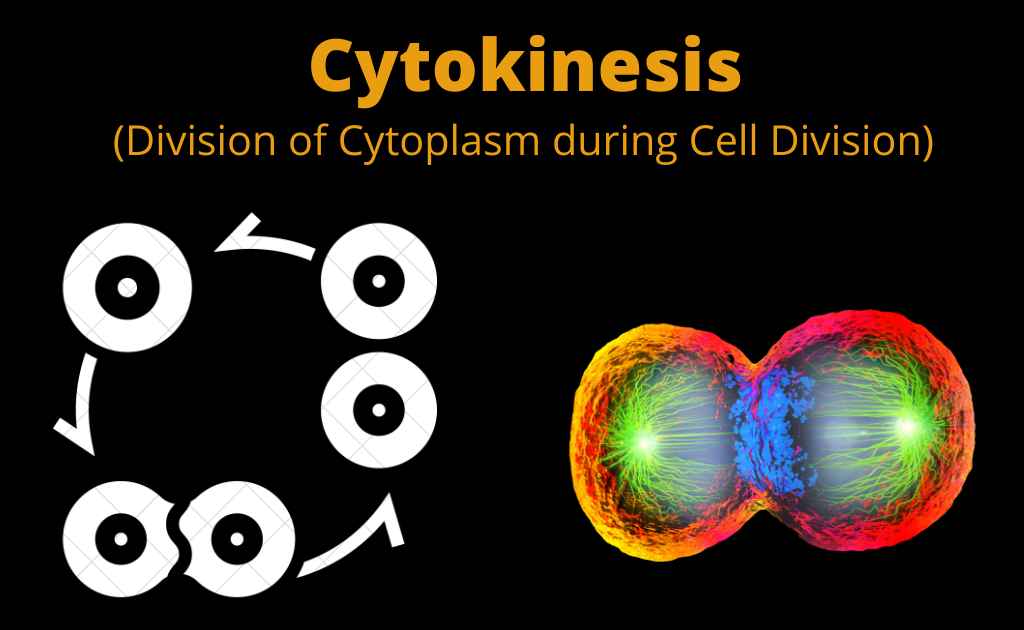
Cytokinesis
Division of Cytoplasm is known as cytokinesis. Cytoplasm divides to form daughter cells.
Interphase
The cell grows and carries out its various metabolic processes during the interphase.
Stages of Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is divided into the following stages:
The G phase (size increasing phase)
It is also known as the first growth phase. It is the early growth phase of the cell in which the cell increases in size.
S phase (synthesis phase)
During this phase, the growth continues. This phase involves DNA replication.
G₂ (second growth or gap)
This phase prepares the cell for division. It Includes replication of the mitochondria and other organelles and synthesis of Microtubules and protein. These microtubules and proteins will make up Mitotic spindle fibers, and chromosome condensation.
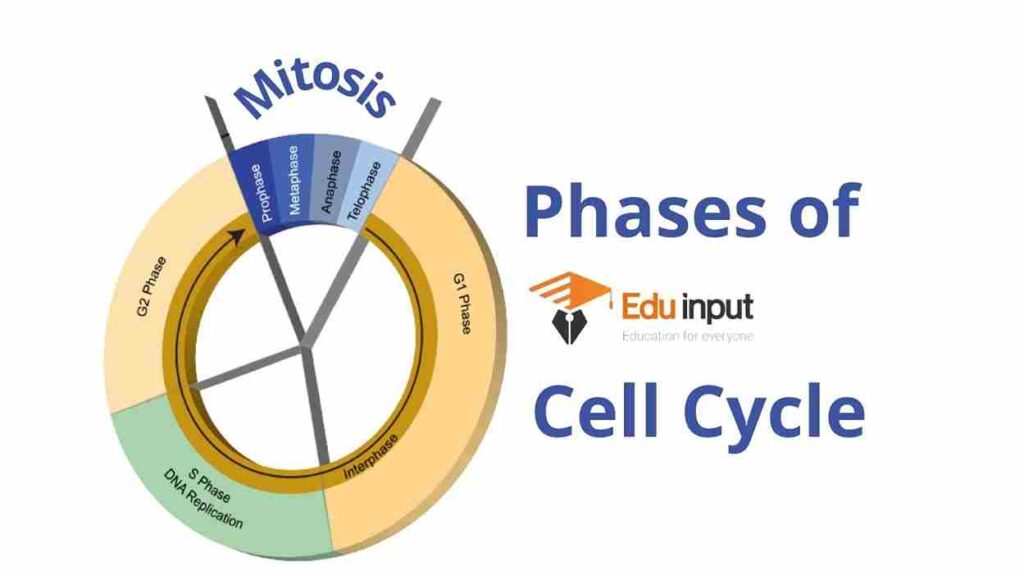
The M (Mitotic) phase
Partitioning of chromosomes and daughter cells takes place in the M phase.
Interphase
Interphase occupies 90% of the total cell cycle. It includes the G, S, and G phases. Normal activities of the cell take place during this phase.
During the S phase of interphase, DNA replication is complete. Thus Interphase also prepares the cell for division. Before cell division, An exact copy of DNA is formed. This process is called replication.
The double-stranded DNA makes a replica of itself. Each daughter cell receives the same genetic makeup as the parent cell. Therefore, replication is essential.
Thus a pair of sister chromatids is formed. A chromatid is a copy of a chromosome produced by replication.
Sister chromatids are attached by a centromere. The centromere is a specific DNA sequence, containing about 220 nucleotides.
The centromere has a specific location on any given chromosome. A disk of a protein called a kinetochore is attached to each centromere.
It forms an attachment site, for the microtubules of the mitotic spindle. The cell cycle moves into the G2 phase, and the condensation of chromosomes begins. The cell also begins to assemble different structures during the G₂ phase.
The cell later uses these structures to move the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. For example, centrioles replicate, and there is an extensive synthesis of the proteins that make up the microtubules.
Related FAQs
What is the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is the process in which a cell increases its size, replicates its DNA, prepares itself for division, and then divides into daughter cells. It includes Mitosis and Meiosis.
What are the basic stages of the cell cycle?
It involves;
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
Interphase (Meiosis)
What is the G phase in the cell cycle?
G phase is the growth phase of the cell cycle in which cell increases its size.
What is the S phase in the cell cycle?
The S phase is the synthesis phase in which a cell copies its DNA.



Leave a Reply