Biotic and Abiotic Components of an Ecosystem
Biotic means living organisms or life forms. Abiotic means nonliving things.
The term ‘Biotic’ refers to living organisms (plants, animals, fungi, bacteria) and their interactions with other living organisms. In contrast, ‘Abiotic’ is defined as non-living things such as rocks, minerals, water, air, etc.
Biotic Components
The living components are called biotic components. They are following biotic
Components;
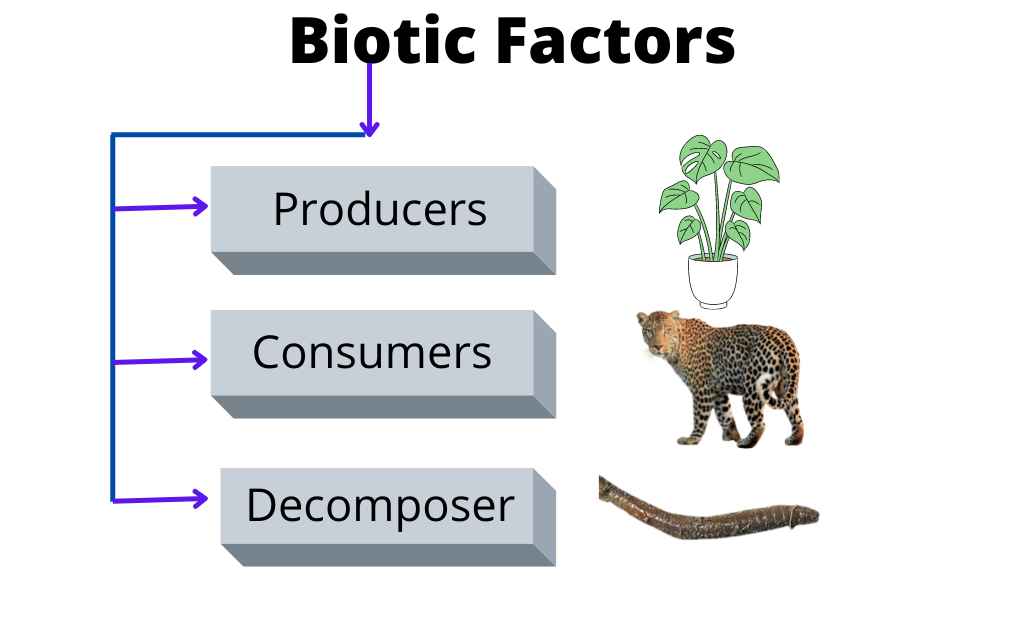
1. Producers
At the start of every food chain is a producer. And just like every other chain, there has to be something to get the whole process going. That’s where plants come in. They create their food and energy to grow, reproduce and continue living.
2. Consumer
Organisms that depend on other organisms for food are called consumers or heterotrophs.
They can’t make their food, so they have to eat other organisms to get energy. Animals and birds are the most well-known consumers, but there are also other less well-known ones, like fungi.
3. Decomposers
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organic matter into smaller pieces. They play a vital role in recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Decomposers are important because they recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, helping plants grow. In addition, decomposers also help prevent soil erosion and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Abiotic Components
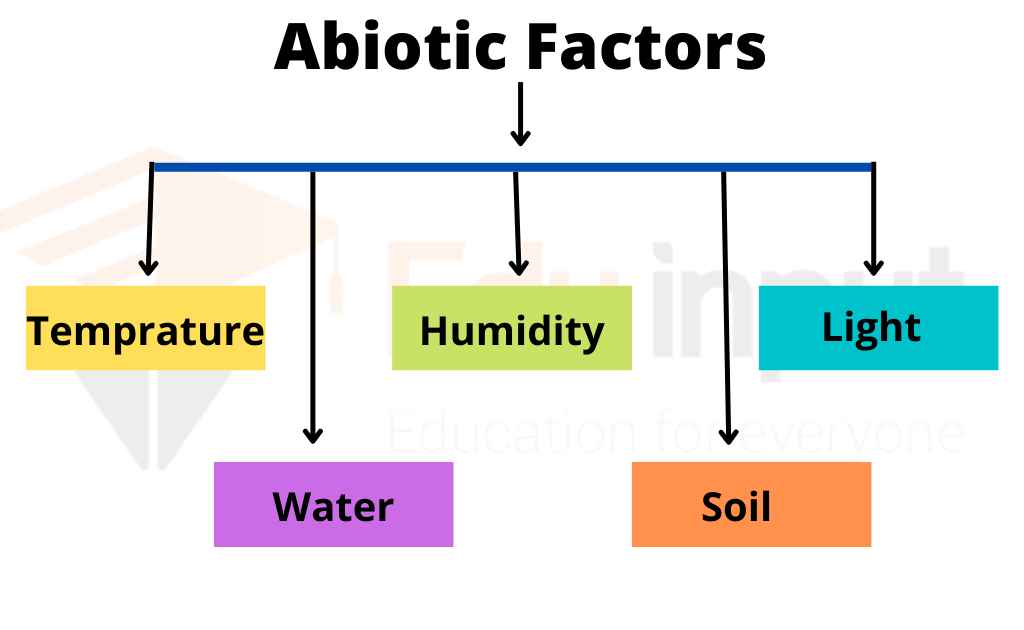
Abiotic components The non-living factors are called abiotic components. The nonliving factors include light, water, wind, soil, fire, temperature, etc.
Life is always changing and never stagnant. Each organism is constantly interacting with its environment, whether it’s getting food, shelter, or avoiding predators.
The roots of a tree absorb water and minerals from the soil, and the leaves take in carbon dioxide from the air. Chlorophyll is important because it helps with photosynthesis.
By absorbing sunlight, it drives the process of converting water and carbon dioxide into sugar and oxygen. The tree releases oxygen into the air, and its roots break up rocks into smaller particles.
In addition to that, roots also secrete acid and absorb minerals, which changes the soil. All of these interactions between organisms and their environment form an ecosystem.
• Temperature – Abiotic factors refer to environmental conditions outside of the organism. Temperature refers to the average temperature of a given area.
• Humidity – Abiotic factors refer specifically to the amount of moisture in the air.
• Light – Abiotic factors refer mainly to the quality of light.
• Water – Abiotic factors refer primarily to water content.
• Soil – Abiotic factors refer generally to the physical state of the soil.
• Air – Abiotic factors refer principally to the quality of air.

 written by
written by 




Leave a Reply