Difference Between Transdermal and Intradermal
Key Difference
Transdermal and intradermal are terms used to describe routes of medication administration through the skin, but they differ in their depth and purpose. Transdermal administration involves delivering medication through the skin to the bloodstream for systemic effect. It typically uses patches that release drugs slowly over time. Intradermal administration, on the other hand, involves injecting a small amount of medication just beneath the skin’s surface, primarily used for allergy testing and vaccinations.
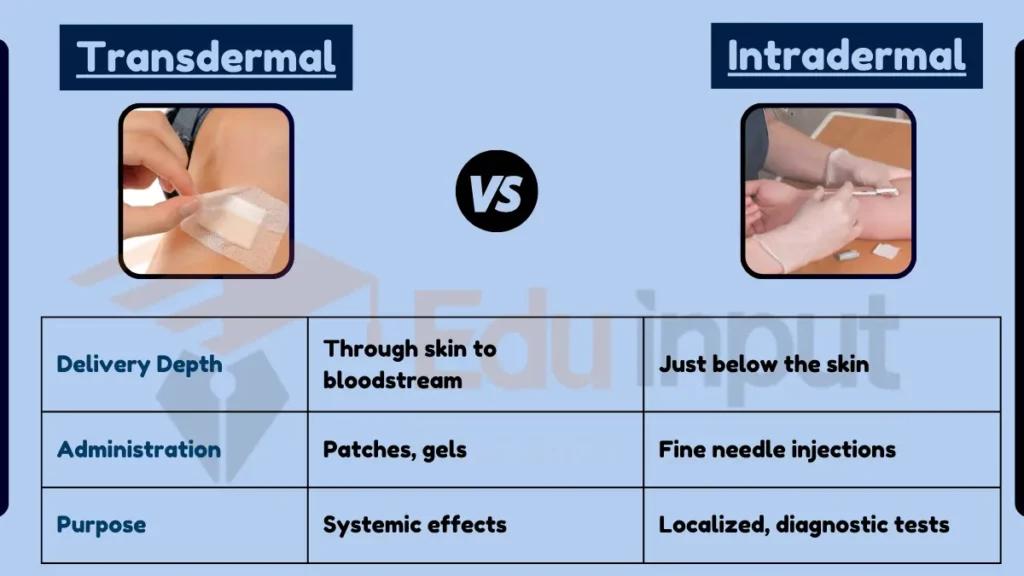
Comparative Analysis
- Depth of Delivery:
- Transdermal: Through the entire skin layer into the bloodstream.
- Intradermal: Just below the skin’s surface.
- Method of Administration:
- Transdermal: Patches or gels.
- Intradermal: Injections using a fine needle.
- Purpose and Effect:
- Transdermal: Systemic effects, such as pain relief or hormone delivery.
- Intradermal: Localized effect, used for diagnostic tests or vaccinations.
- Duration of Action:
- Transdermal: Designed for prolonged, consistent release.
- Intradermal: Typically for immediate, short-term response.
- Examples of Use:
- Transdermal: Nicotine patches, hormone therapy.
- Intradermal: Tuberculosis skin tests, allergy testing.
Table Summary
| Feature | Transdermal | Intradermal |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Depth | Through skin to bloodstream | Just below the skin |
| Administration | Patches, gels | Fine needle injections |
| Purpose | Systemic effects | Localized, diagnostic tests |
| Duration | Prolonged release | Immediate response |
| Examples | Nicotine patches, hormones | TB tests, vaccines |
Transdermal and intradermal routes are both used for delivering medication through the skin but differ in their depth of delivery, purpose, and duration of action, catering to various medical needs from systemic treatment to localized testing.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply