Electron Transport Chain | Step-by-Step guide to Process Of Electron Transport Chain
A group of 4 proteins is involved in a series of chemical reactions or Redox reactions. An Electrochemical gradient is created that is followed by the generation of ATP.
The pathway of electron movement is called the Electron transport chain.
ATP is an essential unit of the metabolic process. Electron donors transfer electrons to electron acceptors.
NADP+ is The final electron acceptor, which is later reduced to NADPH. H2O is the electron donor, that donates electrons during Light-dependent reactions.
Reactants of Electron transport chain
There are the following five main electron acceptors in the electron transport chain.
- NADH
- FADH2
- Oxygen
- ADP
- Protons
Products of the electron transport chain
- NAD+
- FAD
- Water
- ATP.
Process Of Electron Transport Chain
- During glycolysis, NADH, and FADH2 are produced. After the oxidation of NADH and FADH2, highly excited electrons are produced. Energy is produced during the transfer of electrons from NADH & FADH2.
- Those Electrons are transferred to molecular oxygen through many electron carriers, following a single path.
- The electron transport chain is also known as the Cytochrome oxidase system.
- Fe-S, co-enzyme, and different cytochromes are the main components of the Electron transport chain.
- The energy that was generated during electron transfer is used to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane from the matrix to the cytosol.
- After this, an electrochemical gradient is generated, which consists of a proton gradient and a membrane potential.
- The energy created by the formation of this gradient is then used to form ATP as the protons move down the gradient into the matrix through the ATP synthase channel.
- Energy generated by the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain to O2 is used in the production of ATP, the overall process is known as cyclic phosphorylation.
- Thus, electron transport and ATP production occur simultaneously.
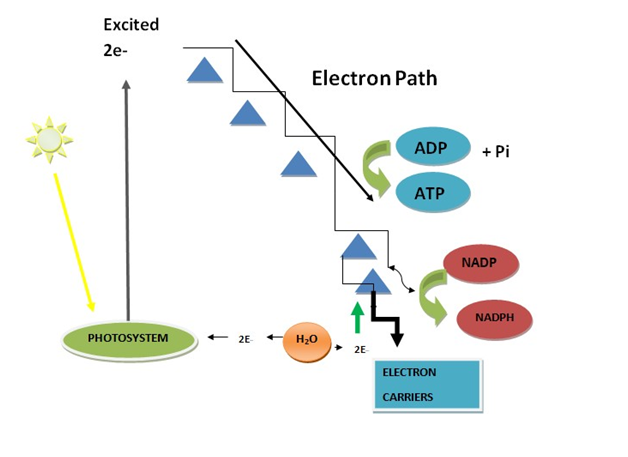
Overview
The 6 predominant steps of the electron transport chain are:
- Excitation of electron
- Photolysis of water to release H+, O2, and electrons.
- Passage of electrons through Electron transport chain.
- Photophosphorylation (Light reaction)
- Synthesis of NADP+.
- Reduction of NADP+ and synthesis of ATP.
Electron Transport Chain Quiz
Test your knowledge of the Electron Transport Chain by attempting our 13-mark quiz. However, If you do not know this topic or want to revise it, read our detailed guide on the Electron Transport Chain.
Let us start our quiz on the Electron Transport Chain with answers.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What is the electron transport chain?
Electrons are transferred from one carrier to another, and they release energy while going through the pathway. This pathway of electrons is called Electron Transport Chain.
Which statement describes the electron transport chain?
The oxidation of NADH and FADH2 produces highly excited electrons. These electrons are then transferred to molecular Oxygen, and NADPH & FADH are produced as the end product.
How many ATPs are produced in Electron Transport Chain?
The electron transport chain produces approximately 30-32 ATP molecules. As one NADPH and FADH respectively produce 3 and 2 molecules of ATP.
How many NADPH are produced during Electron Transport Chain?
8 NADH are produced during Electron Transport Chain.
How many FADH are produced in Electron Transport Chain?
2 molecules of FADH2 are produced.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply