15 Examples of Catabolism
Catabolism is a metabolic process that involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones. It releases energy in the process.
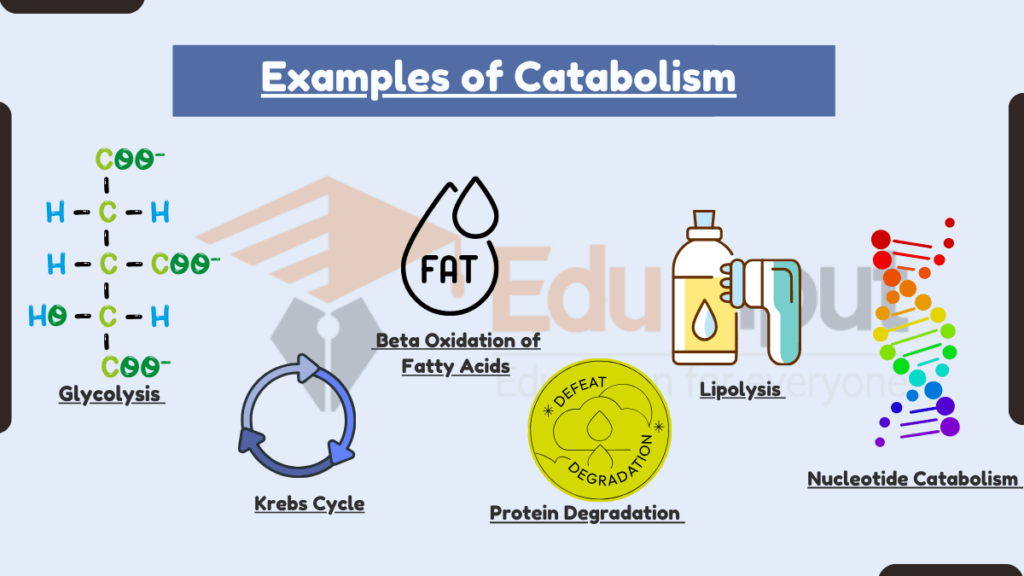
Examples of Catabolism
Here are 10 examples of catabolism:
1: Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a catabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. This process occurs in the cytoplasm and generates a small amount of ATP and NADH.
2: Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is also an example of catabolic process. It is a series of catabolic reactions that occur in the mitochondria. It oxidizes acetyl-CoA, producing ATP, NADH, FADH2, and carbon dioxide.
3: Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids
Beta oxidation is a catabolic process that breaks down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA molecules. This process takes place in the mitochondria and is important for energy production from fats.
4: Protein Degradation
Proteins can be catabolized into their constituent amino acids through processes like proteolysis. These amino acids can then enter various metabolic pathways for energy production or biosynthesis.
5: Lipolysis
Lipolysis is the breakdown of triglycerides (fat molecules) into glycerol and fatty acids. This process occurs in adipose tissue and provides a source of energy during periods of fasting or high energy demand.
6: Nucleotide Catabolism
Nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA and RNA, can be catabolized into nucleosides and phosphate groups. These products can then be further broken down into simpler molecules.
7: Amino Acid Catabolism
Amino acid catabolism involves the breakdown of amino acids into various intermediates, including ammonia, which can be excreted, and carbon skeletons that can enter metabolic pathways for energy production or biosynthesis.
8: Glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the process of breaking down glycogen, a storage form of glucose, into glucose-1-phosphate. This provides a rapid source of glucose for energy during times of need.
9: Urea Cycle
The urea cycle is an important example of catabolism that is responsible for converting toxic ammonia into urea, which can be safely excreted by the body. This process involves the catabolism of amino acids.
10: Cell Respiration
Cell respiration consists of a series of catabolic reactions, including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, which together generate the majority of ATP used by cells.

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply