Gram Staining Technique | Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
A gram stain is a laboratory test that helps to identify different types of bacteria. This test can be performed on a sample of tissue from the site of an infection or on a sample of bodily fluid.
Gram Staining Technique
This technique was discovered by Christian gram. There are two dyes used in the gram staining technique:
- Crystal violet (purple) is the primary dye
- Red dye (Safranine or Eosin) is the secondary dye.
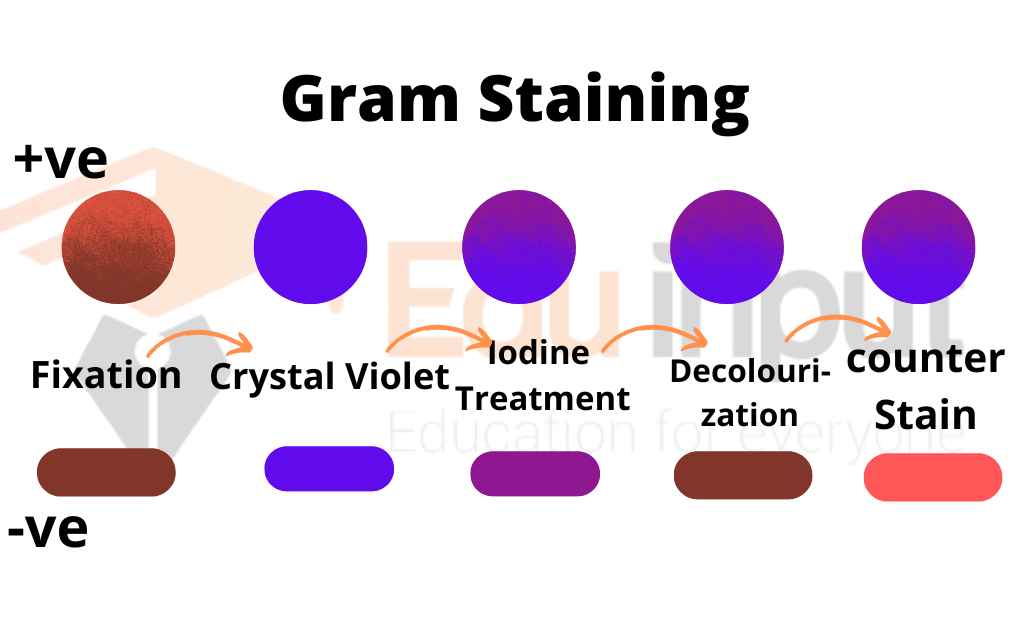
Different bacteria show different responses to the gram stain procedure. So bacteria are divided into two groups based on this response.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
They are stained purple with this staining technique. They form a crystal Violet complex and retain the primary dye color. Gram-positive bacteria have simple cell walls. It has a large amount of Peptidoglycan. They have a lesser amount of lipopolysaccharides.
Examples of Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Staphylococcus,
- Bacillus
- Corynebacterium
Characteristics Of Gram-Positive Bacteria
The gram-positive bacterium usually shows the following characteristics:
1. They have a cytoplasmic lipid membrane.
2. Gram-positive bacteria have a single membrane layer.
3. They have a thick layer of Peptidoglycan. Teichoic acids and lipoids are present.
3. They form Lipoteichoic acids. It acts as a chelating agent.
4. Capsule is made up of polysaccharides (only in some species)
5. Flagellum (only in some species) if present, contains two rings for support.
Gram-Negative Bacteria
They are stained pink with this staining technique. They retain the color of the secondary dye.
Gram-negative bacteria have a lesser amount of Peptidoglycan. It has a more complex structure. An outer membrane of Lipopolysaccharides is present outside the Peptidoglycan layer.
Their species are more dangerous than Gram-Positive Bacteria. The Lipopolysaccharide layer is often toxic. This layer protects bacteria from the immune system of the host. Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics.
Its example is pseudomonas.
Characteristics Of Gram-Negative Bacteria
characteristics of gram-negative bacteria are enlisted below:
1. They also have a cytoplasmic membrane.
2. They have a thin Peptidoglycan layer (much thinner than in gram-positive bacteria).
3. Outer membrane containing a Lipopolysaccharide outside the Peptidoglycan layer.
4. Porins are present in the outer membrane. It acts like pores for particular molecules.
5. There is a space between both the layers (Peptidoglycans and the secondary cell membrane). It is called periplasmic space.
6. The s-layer is directly attached to the outer membrane.
7. If present, the flagella have four support rings instead of two.
8. Teichoic acids or Lipoteichoic acids are absent.
9. Lipoproteins are attached to the polysaccharide.
Related FAQs
What is gram staining?
A gram stain is a laboratory test that helps to identify different types of bacteria. This test can be performed on a sample of tissue from the site of an infection or on a sample of bodily fluid. This technique is called the gram staining technique.
What are Gram-Positive Bacteria?
Bacteria that show positive results to gram staining technique and retain violet color are called Gram-Positive Bacteria. Example: Staphylococci
What are Gram-Negative Bacteria?
Bacteria that show negative results to the gram staining technique and do not retain the violet color are called Gram Negative Bacteria.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply