Phagocytosis and Phagocytes – Discovery and Types
Unicellular organisms rely on phagocytosis for nutrition, and this process is also present in almost all cells of multicellular organisms. In phagocytosis, a cell engulfs solid particles by extending its plasma membrane around the particle, forming a vacuole that encloses it.
In phagocytosis, cells ingest and eliminate particles larger than 0.5 μm in diameter. This process is essential for tissue homeostasis and is found in many types of cells.
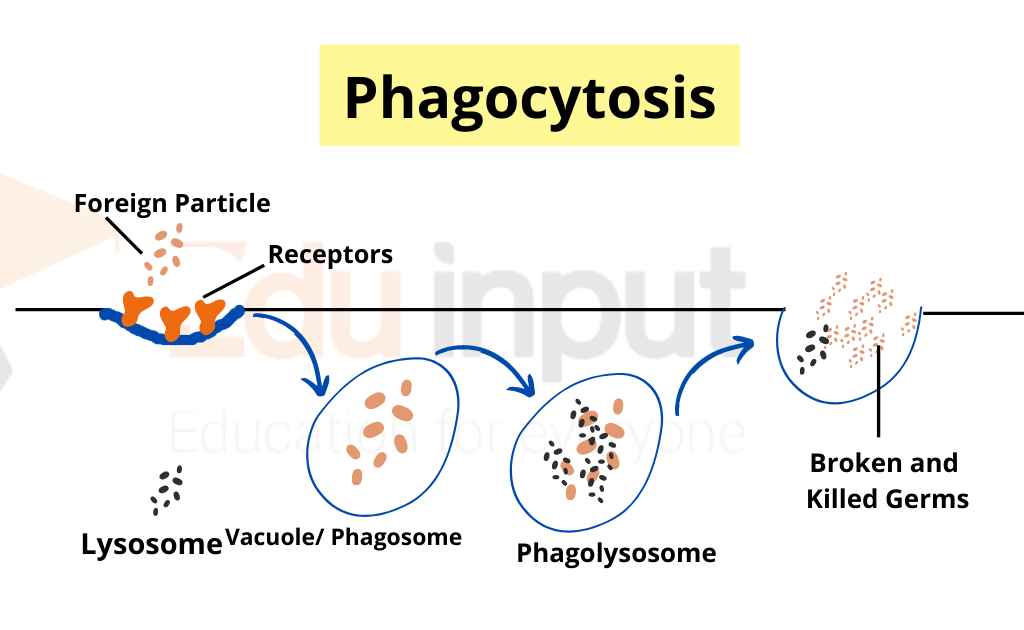
It ingests:
- Microorganisms
- Foreign particles
- Apoptotic cells
Discovery of Phagocytosis and Phagocytes
Elie Metchnikoff discovered phagocytes and phagocytosis during his late 1800s studies of bacteria and infection. He identified two types of phagocytic cells- macrophages and microphages- during his research.
Phagocytes
Phagocytes are a type of cell that can engulf and sometimes digest foreign particles such as bacteria, carbon, dust, or dye. They do this by extending cytoplasm into pseudopods, which are like feet. The foreign particle is surrounded by the cytoplasm and a vacuole is formed.
These are a type of immune cells that are good at finding and destroying bacteria, viruses, and dead or damaged cells in the body.
Types Of Phagocytes
There are three main types of phagocytes,
- The Granulocyte
- The Macrophage
- The Dendrite Cell
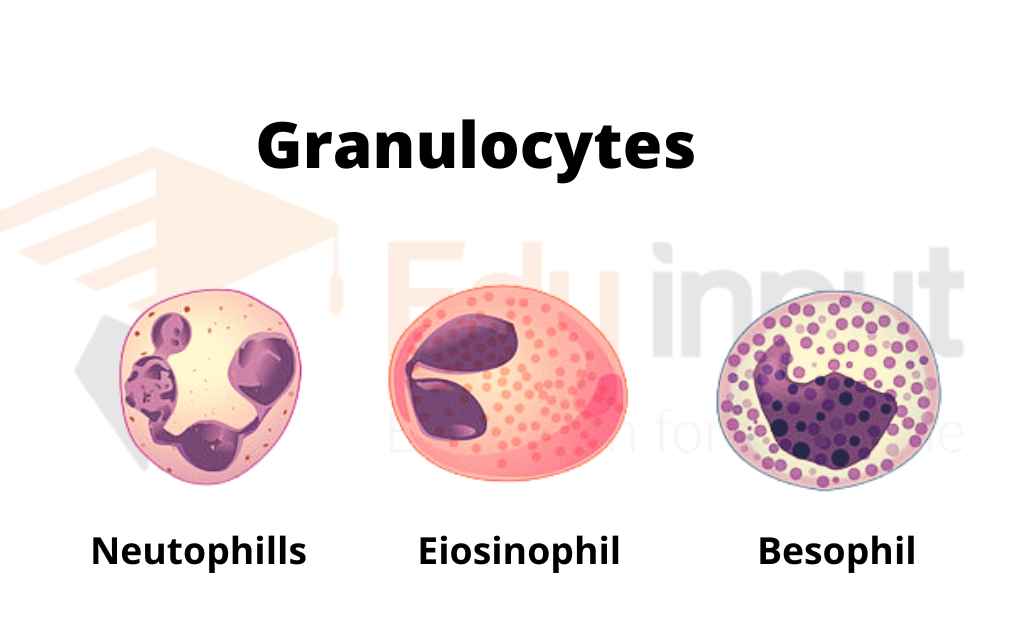
Granulocytes
Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell that helps protect the body against infections. They can kill and remove invading bacteria and other foreign substances from the body. Granulocytes are a key part of the immune system and are usually the first line of defense against infection.
The pus in an infected wound is made mostly of dead granulocytes. A small number of granulocytes have a special job of attacking larger parasites, such as worms.
Macrophages
Macrophages, also known as big eaters, are a type of white blood cell. They are slower to respond to invaders than granulocytes, but they are larger, live longer, and have a greater capacity to fight.
Macrophages also play an important role in alerting the rest of the body of invaders. Macrophages start as white blood cells called monocytes. Monocytes that leave the bloodstream to turn into macrophages.
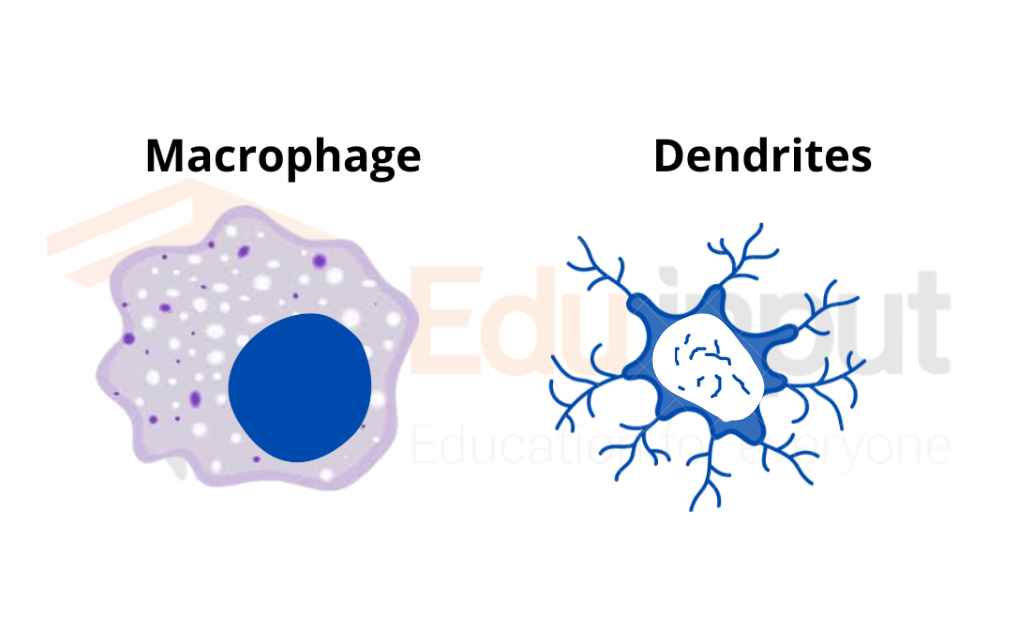
Dendrite Cell
Dendritic cells are special because they are able to eat other cells, like granulocytes and macrophages. Dendritic cells help to activate the Immune system and they also have the ability to cleanse the body of foreign particles and organisms.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply