Phospholipids- Structure, Classes and Functions
Phospholipids are complex or compound lipids containing phosphoric acid, in addition to fatty acids, nitrogenous bases, and alcohol.
Phospholipids are essential components of cell membranes. They play a role in maintaining membrane fluidity and permeability, and they also act as signaling molecules. In addition, phospholipids are precursors to important bioactive compounds such as hormones and neurotransmitters.
Phospholipids have become a hot topic in recent years because of their potential therapeutic applications. This article provides an overview of phospholipids.
Classes of Phospholipids
There are two classes of phospholipids:
Glycerophospholipids (or phosphoglycerides)
They contain glycerol as alcohol.
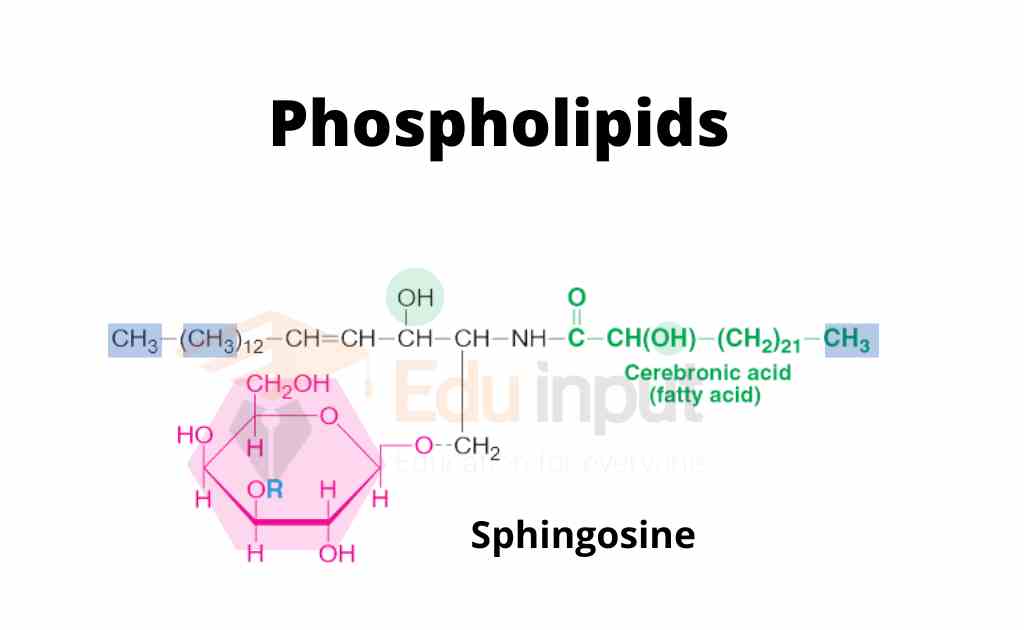
Sphingophospholipids (or sphingomyelins).
They contain sphingosine as alcohol.
Glycerophospholipids
Glycerophospholipid is the major lipid that occurs in biological membranes. They consist of glycerol 3-phosphate. It is esterified at its C-1 and C-2 with fatty acids.
Usually, C1 contains a saturated fatty acid. Meanwhile, C2 contains an unsaturated fatty acid, which are
- Phosphatidic acid
- Lecithins
- Phosphatidylinositol
- Phosphatidylserine
- Plasmalogens
- Cardiolipin
Structures Of Phospholipid
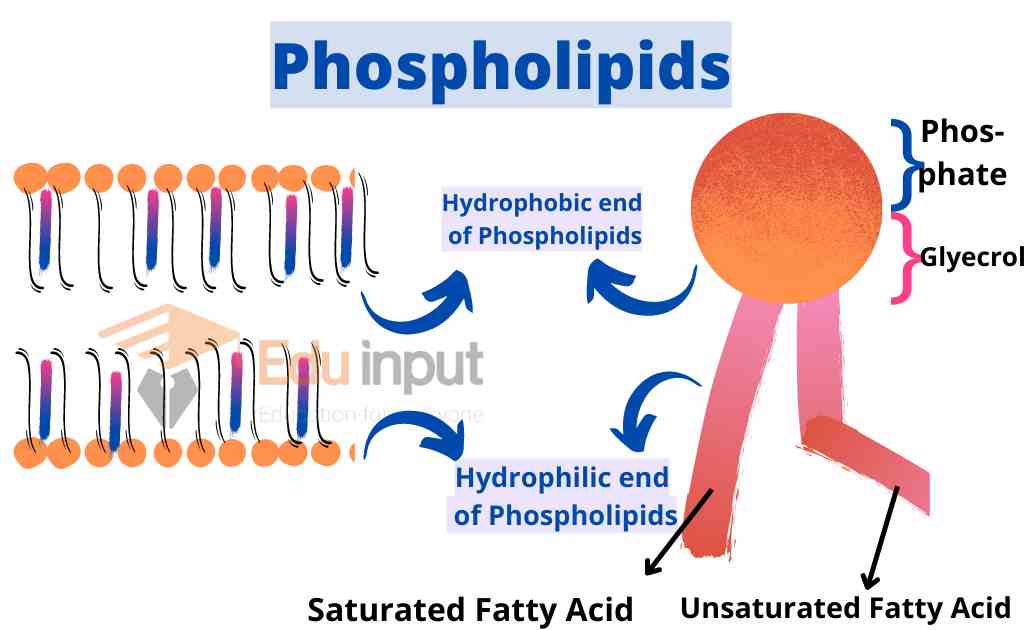
Phospholipids consist of
• A glycerol molecule,
• Two fatty acids
• A phosphate group that is modified by alcohol. The phosphate group is the negatively charged polar head. thus it is hydrophilic. The fatty acid chains are the uncharged and nonpolar tails. so they are known as the hydrophobic end.
Functions Of Phospholipis
Phospholipids constitute an important group of compound lipids that perform a wide variety of functions
- Phospholipids (lecithin, cephalin, and cardiolipin) in the mitochondria maintain the conformation of components of the electron transport chain.
- Phospholipids form the structural components of cell membranes and help to regulate membrane permeability.
- Phospholipids facilitate to absorption of fat from the intestine.
- Phospholipids participate in reverse cholesterol transport and thus help in the removal of cholesterol from the body.
- Phosphatidylinositol is the source of second messengers, inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol, that are involved in the action of some hormones.
- They are essential for the synthesis of different lipoproteins, and also help in lipids transport.
- Accumulation of fat can be prevented by phospholipids, hence they are regarded as lipotropic factors.
- Phospholipids act as an agent to lower surface tension.
- Cephalins are an important group of phospholipids, that participate in the clotting of blood.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply