Mutations- Definition, Types, and Examples
A spontaneous change in a gene is called a mutation.
The cells of eukaryotes contain a large amount of DNA. If the DNA in all of the cells of an adult human is lined up end to end. They will stretch nearly 100 billion kilometers. This distance is 60 times the distance from the earth to Jupiter. Changes in the DNA occur due to mistakes in replication.
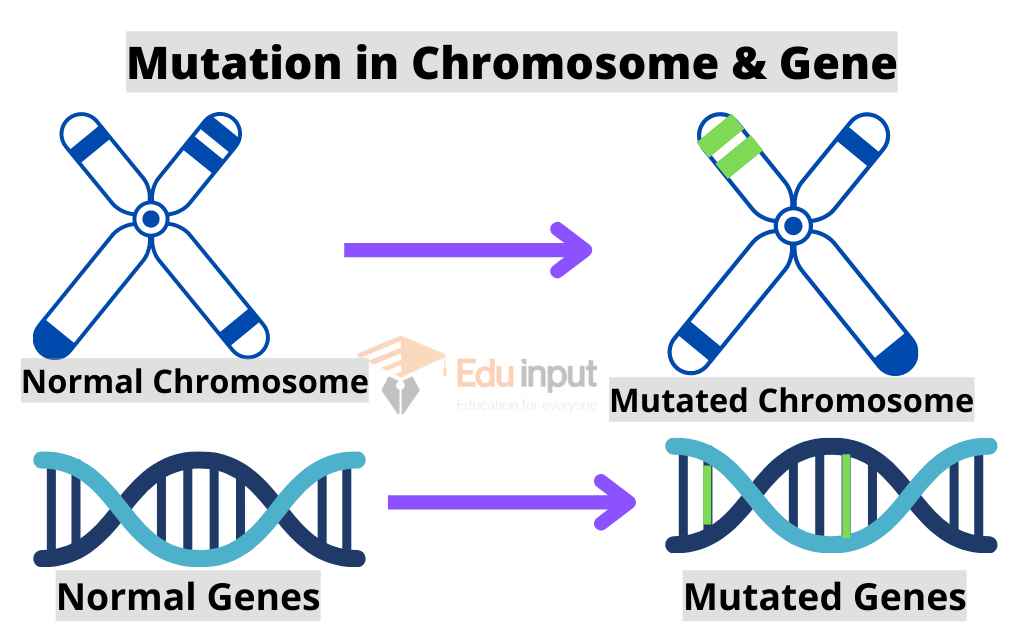
DNA may also be damaged by genetic mutations causing agents. The mutations in somatic cells do not pass to offspring. So these mutations, have no evolution importance.
Types of Mutation
The mutation in germ cells is transferred to new generations. So it provides the raw material for natural selection.
This natural selection produces evolutionary change. mutations can be classified as:
Chromosomal aberration
Chromosomal aberrations are mega changes. Such chromosomal aberrations cause syndromes like down’s syndrome, Klinefelter’s syndrome, etc.
There are the following types of chromosomal aberration:
- Presence of an extra chromosome or loss of a chromosome from the diploid number of chromosomes.
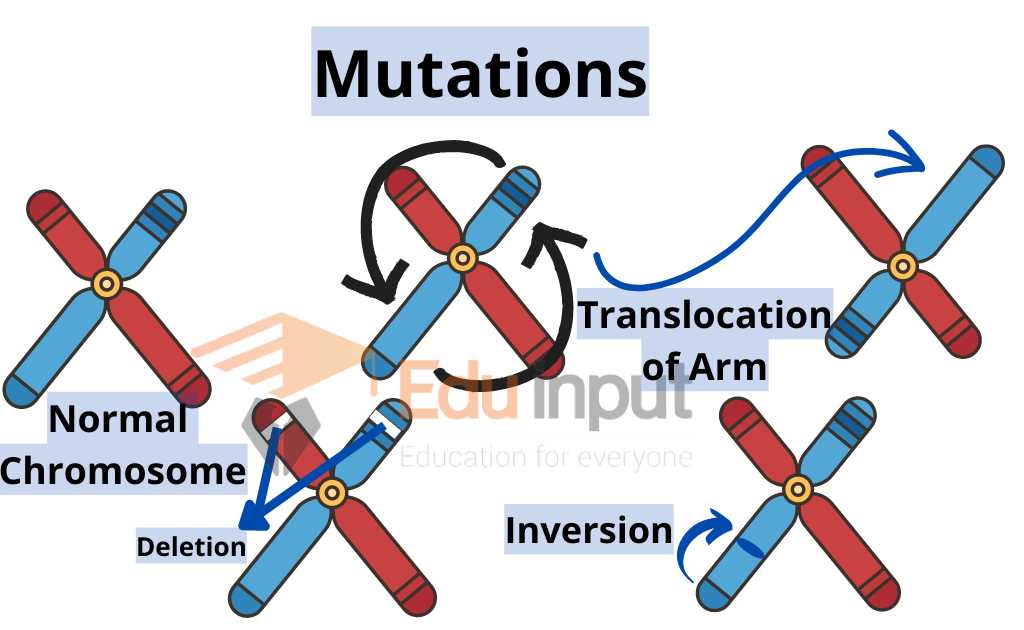
- There may be some changes in the part chromosomes like deletions, insertions, Inversions, etc.
Point mutation
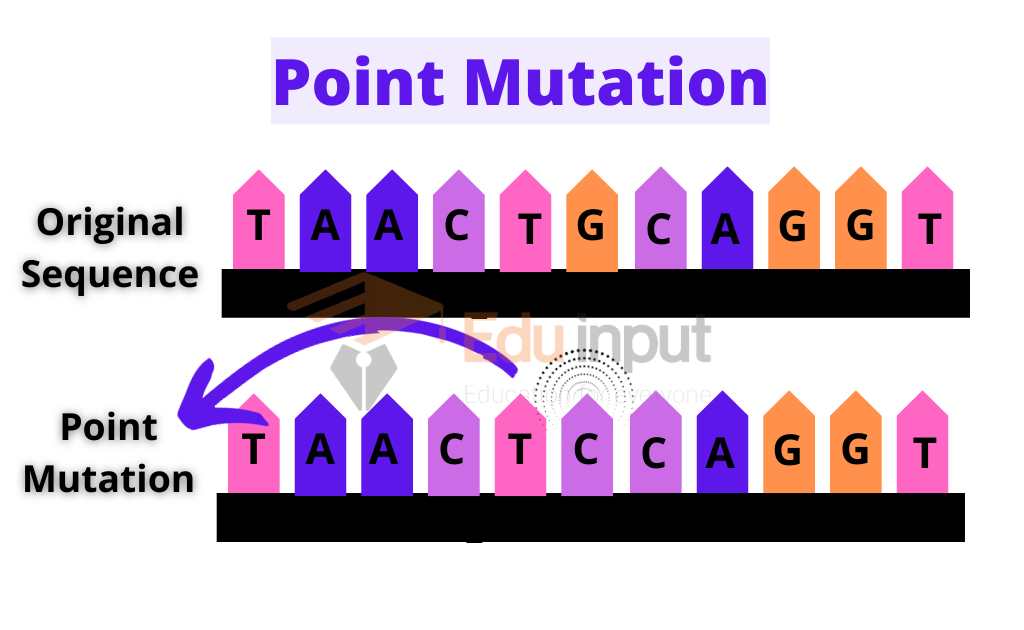
There are two causes of the point mutations:
- Some point mutations occur due to spontaneous pairing errors. These errors occur during DNA replication.
- Some are the result of damage to the DNA. These damages are caused by mutagens.
mutagens
The mutagens are radiations or chemicals. Chemical mutagens have particular Practical importance. The modern industrial units release many chemical Mutagens into the environment.
Examples of Point Mutation
Sickle cell anemia and Phenylketonuria are examples of point mutation.
Sickle cell Anemia
Point mutation occurs in sickle cell anemia. It changes amino acid glutamic acid into valine at position 6 from the N terminal end in the hemoglobin chain. It alters the tertiary structure of the hemoglobin molecule. This mutation reduces the ability of Hemoglobin to carry oxygen.

Phenylketonuria
This disorder is also caused due to point mutation. In this case, defective enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase is produced. It cannot degrade phenylalanine. Thus phenylalanine accumulates in the cells. It causes mental retardation. So brain fails to develop in infants.
Related FAQs
What is Mutation?
A spontaneous change in a gene or chromosome is called a mutation.
What are Mutagens?
The mutagens are radiations or chemicals. Chemical mutagens have particular Practical importance. The modern industrial units release many chemical Mutagens into the environment.
What are the types of mutations?
There are four types of mutations:
Deletion
Insertions
Inversions
Translocation

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply