Difference Between Synthetic Biology and Genetic Engineering
Synthetic Biology is the design and construction of new biological systems, while genetic engineering is the modification of existing biological systems. Both are fields of Biotechnology.
What is Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering is a more traditional approach that involves the transfer of genes from one organism to another.
This is done using a variety of techniques, such as recombinant DNA technology. It allows scientists to isolate genes from different organisms together.
What is Synthetic Biology?
Synthetic biology is a new field that takes a more engineering-based approach to the manipulation of genes.
In synthetic biology, scientists design and build new biological systems from scratch, using standardized genetic parts. It allows them to create organisms with unique properties that do not exist naturally.
For example, synthetic biologists have created bacteria that can produce biofuels, or yeast that can produce plastics.
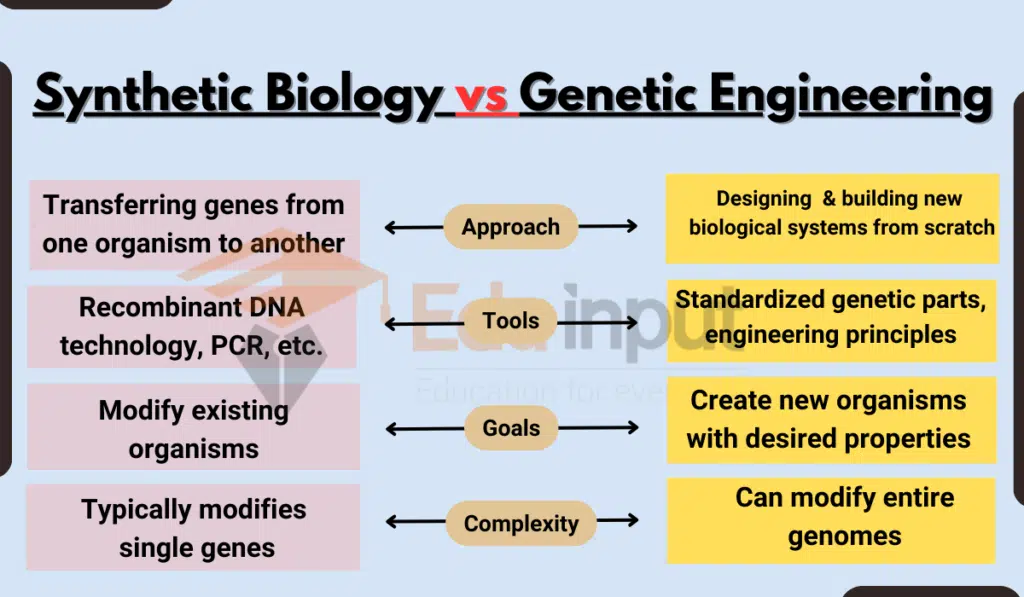
Synthetic biology vs Genetic Engineering
Here are the main differences between Synthetic biology and Genetic Engineering:
| Feature | Genetic engineering | Synthetic biology |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Transferring genes from one organism to another | Designing and building new biological systems from scratch |
| Tools | Recombinant DNA technology, PCR, etc. | Standardized genetic parts, engineering principles |
| Goals | Modify existing organisms | Create new organisms with desired properties |
| Complexity | Typically modifies single genes | Can modify entire genomes |
| Risks | Relatively well-understood | Still being studied |
| Regulation | Regulated by many countries | Not yet as widely regulated |
| Potential applications | Genetically modified crops, bacteria that produce human insulin, vaccines | Biofuels, plastics, medicines, etc. |





Leave a Reply