Difference Between Male and Female Clavicle
Key Difference
The male and female clavicles, commonly known as collarbones, differ in various anatomical aspects due to sexual dimorphism. Typically, male clavicles are longer, stronger, and more robust in comparison to female clavicles. Female clavicles are usually shorter, thinner, and less curved. These differences are part of the broader variations in skeletal structure between males and females, influenced by hormonal and genetic factors.
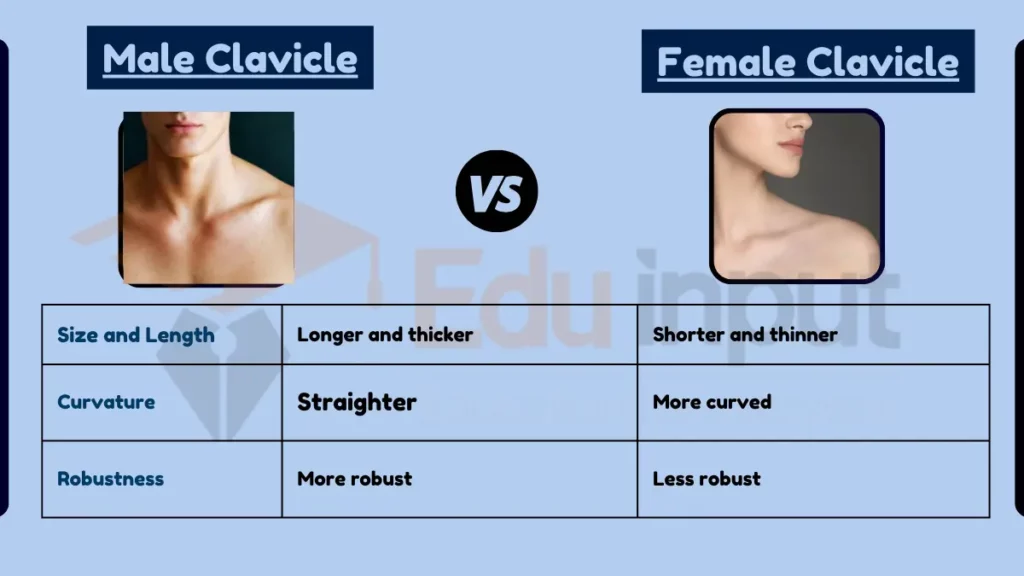
Comparative Analysis
- Size and Length:
- Male Clavicle: Generally longer and thicker.
- Female Clavicle: Shorter and more slender.
- Curvature and Shape:
- Male Clavicle: Tends to be straighter with less curvature.
- Female Clavicle: Often exhibits a more pronounced curvature.
- Robustness and Strength:
- Male Clavicle: More robust, reflecting greater muscle mass.
- Female Clavicle: Comparatively less robust.
- Anatomical Variations:
- Male Clavicle: Wider shoulder width correlates with broader clavicles.
- Female Clavicle: Adapted to different shoulder width and thoracic shape.
- Function and Implications:
- Both: Serve as support for the shoulder and as an attachment for muscles; variations do not typically affect function.
Table Summary
| Feature | Male Clavicle | Female Clavicle |
|---|---|---|
| Size and Length | Longer and thicker | Shorter and thinner |
| Curvature | Straighter | More curved |
| Robustness | More robust | Less robust |
| Anatomical Variations | Wider shoulders | Narrower shoulders |
| Function | Support and muscle attachment | Same as male |
The differences in the clavicles between males and females are part of the sexual dimorphism seen in human anatomy. These variations, while subtle, reflect the differences in overall body structure and muscle distribution between the sexes, although they do not typically affect the functional role of the clavicle in supporting the shoulder and facilitating muscle attachment.





Leave a Reply