Cougar – Complete Guide | Puma Concolor
October 23, 2023
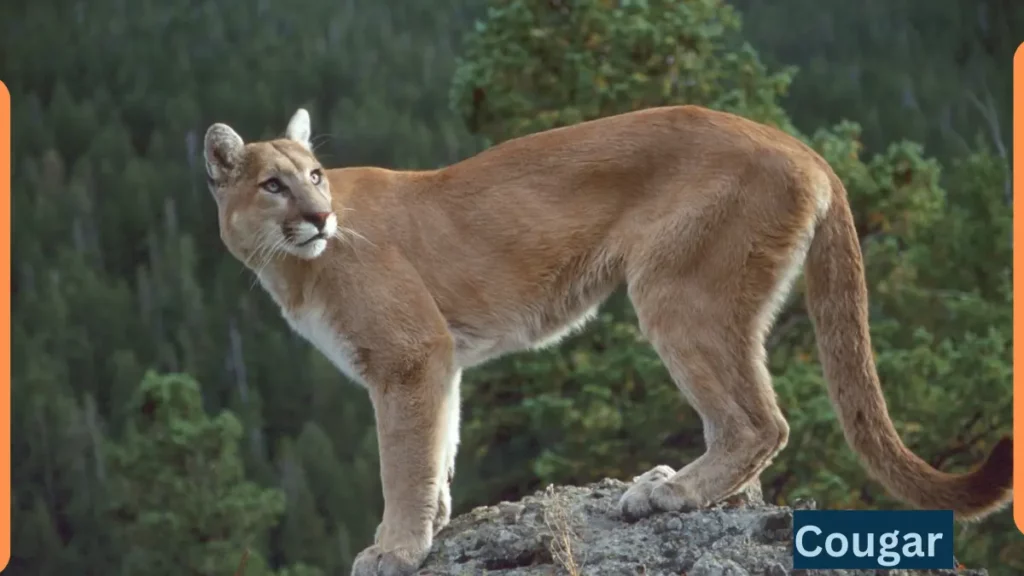
The Cougar, also known as the mountain lion or puma, is a large and powerful big cat found in the Americas.

Cougar
Here’s some information about the Cougar:
| Scientific Classification | Kingdom: Animalia |
| Phylum: Chordata | |
| Class: Mammalia | |
| Order: Carnivora | |
| Family: Felidae | |
| Genus: Puma | |
| Species: Puma concolor | |
| Physical Appearance | Size: Cougars are one of the largest wildcats in the Americas. They typically measure 3.25 to 5.25 feet (1 to 1.6 meters) in length, not including their long tail, and stand about 24 to 35 inches (60 to 90 centimeters) tall at the shoulder. |
| Coloration: Their fur is usually tan or tawny, with a white underbelly. Cougars may also have black markings on their face, ears, and tail. | |
| Range and Habitat | Cougars are highly adaptable and can be found throughout the Americas. They inhabit a wide range of ecosystems, including forests, mountains, deserts, and swamps. |
| Behavior and Lifestyle | Solitary Predators: Cougars are solitary animals and are known for their stealth and hunting prowess. They are primarily crepuscular, being most active during dawn and dusk. |
| Territorial: They establish territories that vary in size, with males having larger ranges than females. | |
| Reproduction and Life Cycles | Breeding: Cougars do not have a specific breeding season. Females give birth to a litter of typically 1 to 4 kittens after a gestation period of about 90 days. |
| Kittens: The kittens are born with spots that fade as they mature. They are weaned at around 2 months and begin hunting with their mother at about 6 months. | |
| Diet and Prey | Cougars are carnivorous and primarily prey on deer, though they may also hunt smaller mammals like rabbits and rodents. They are known for their stealthy hunting techniques. |
| Predators and Threats | Cougars are apex predators and do not have natural predators in their habitats. However, they face threats from habitat loss, hunting, and vehicle collisions. |
| Interesting Facts and Features | Wide Range: Cougars have one of the largest geographical distributions of any terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere. |
| Quiet Predators: They are often referred to as “ghost cats” due to their quiet nature and ability to stalk prey undetected. | |
| Relationship with Humans | Cougars generally avoid contact with humans and are known for their elusive behavior. They are occasionally encountered in wilderness areas and may pose a risk if they feel threatened. |
| Conservation Status and Life Today | The conservation status of Cougars varies by region. In some areas, they are considered a species of least concern, while in others, they may be listed as endangered or threatened. Conservation efforts aim to protect their populations. |
File Under:






Leave a Reply