Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
May 30, 2023
The main difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration is that aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen, produces carbon dioxide and water as end products, while anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen and produces alcohol as the end product.
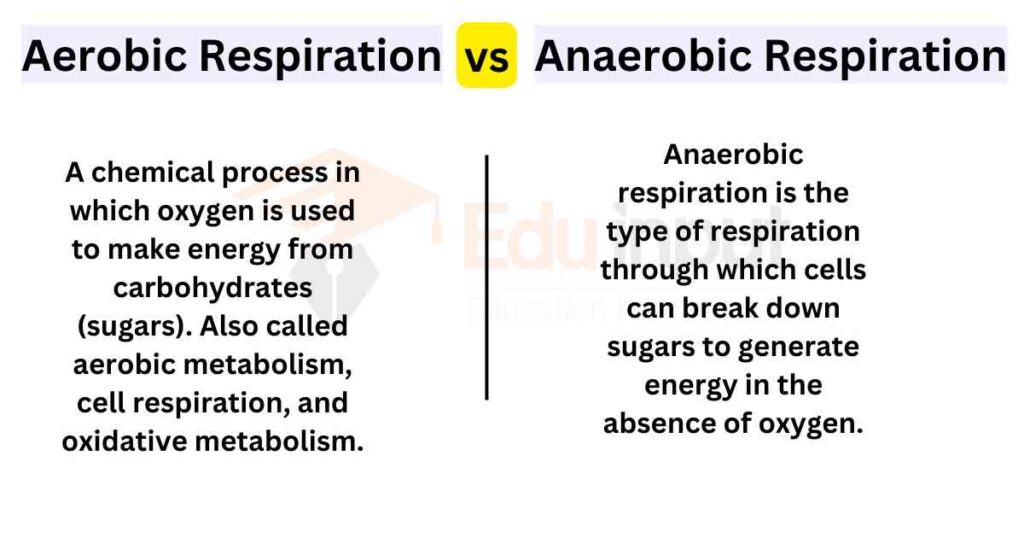
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
| Factors | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of cellular respiration that requires oxygen for the breakdown of glucose to produce energy | Process of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen, using alternative electron acceptors for energy production |
| Oxygen Requirement | Requires oxygen as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain | Does not require oxygen as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain |
| ATP Production | Produces a large amount of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation | Produces a limited amount of ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation |
| Efficiency | More efficient in terms of ATP production per glucose molecule | Less efficient in terms of ATP production per glucose molecule |
| End Products | Carbon dioxide and water | Various end products such as lactic acid, ethanol, or other organic compounds |
| Duration of Energy Production | Sustained energy production over a longer duration | Short bursts of energy production |
| Examples | Human muscle cells performing aerobic respiration during exercise | Yeast cells undergoing anaerobic respiration to produce ethanol during fermentation |
| Presence in Organisms | Found in aerobic organisms, including humans and many other animals and plants | Found in various organisms, including certain bacteria, yeast, and some muscle cells in animals |
| Stages | Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle), Electron Transport Chain | Glycolysis, Fermentation |
| Site of Reaction | Cytoplasm (Glycolysis), Mitochondria (Citric Acid Cycle, Electron Transport Chain) | Cytoplasm (Glycolysis), Cytoplasm or specialized organelles (Fermentation) |
| Products | ATP, Carbon dioxide, Water | ATP, Lactic acid, Ethanol, or other organic compounds |
File Under:

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply