Difference Between Blood Sugar and Urine Sugar
January 2, 2024
Key Difference
Blood sugar and urine sugar are two different indicators used in the monitoring and diagnosis of diabetes and other metabolic conditions. Blood sugar refers to the concentration of glucose present in the blood, a critical measure for the management of diabetes. Urine sugar, on the other hand, is the presence of glucose in the urine, which typically indicates that blood sugar levels are high enough that glucose is being excreted by the kidneys.
Comparative Analysis
- Indicator of Metabolic State:
- Blood Sugar: Shows current glucose levels in the bloodstream.
- Urine Sugar: Indicates that blood glucose levels have been high over a period.
- Measurement:
- Blood Sugar: Measured through blood tests; can be monitored at home with glucometers.
- Urine Sugar: Detected in urine samples; less commonly used for daily monitoring.
- Normal vs. Abnormal Levels:
- Blood Sugar: Has well-established normal ranges; variations indicate metabolic changes.
- Urine Sugar: Normally absent in urine; presence indicates elevated blood sugar levels.
- Role in Diabetes Management:
- Blood Sugar: Key focus for daily diabetes management.
- Urine Sugar: Used as a secondary indicator, more common in severe cases.
- Temporal Representation:
- Blood Sugar: Immediate, real-time glucose levels.
- Urine Sugar: Reflects past blood glucose levels, not immediate state.
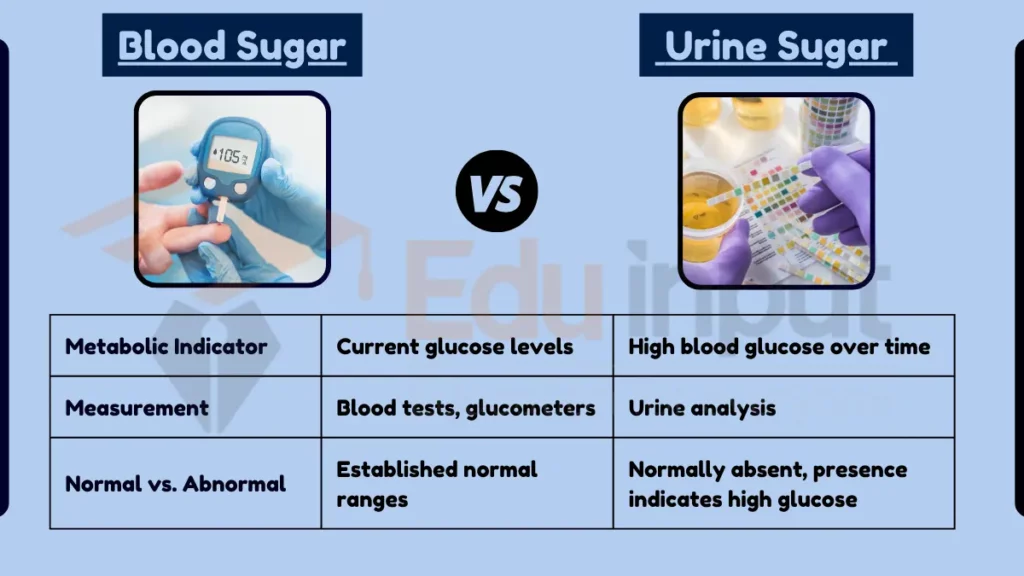
Table Summary
| Feature | Blood Sugar | Urine Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Indicator | Current glucose levels | High blood glucose over time |
| Measurement | Blood tests, glucometers | Urine analysis |
| Normal vs. Abnormal | Established normal ranges | Normally absent, presence indicates high glucose |
| Diabetes Management | Primary monitoring tool | Secondary, for severe cases |
| Temporal Aspect | Real-time levels | Reflects past glucose levels |
Also Read:
File Under:

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply