Difference Between Duodenum and Jejunum
Key Difference
The duodenum and jejunum are both parts of the small intestine, but they have distinct anatomical and functional characteristics. The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine, immediately following the stomach. It is primarily responsible for the initial phase of digestion, receiving chyme from the stomach along with bile and pancreatic juices, which aid in the breakdown of food.
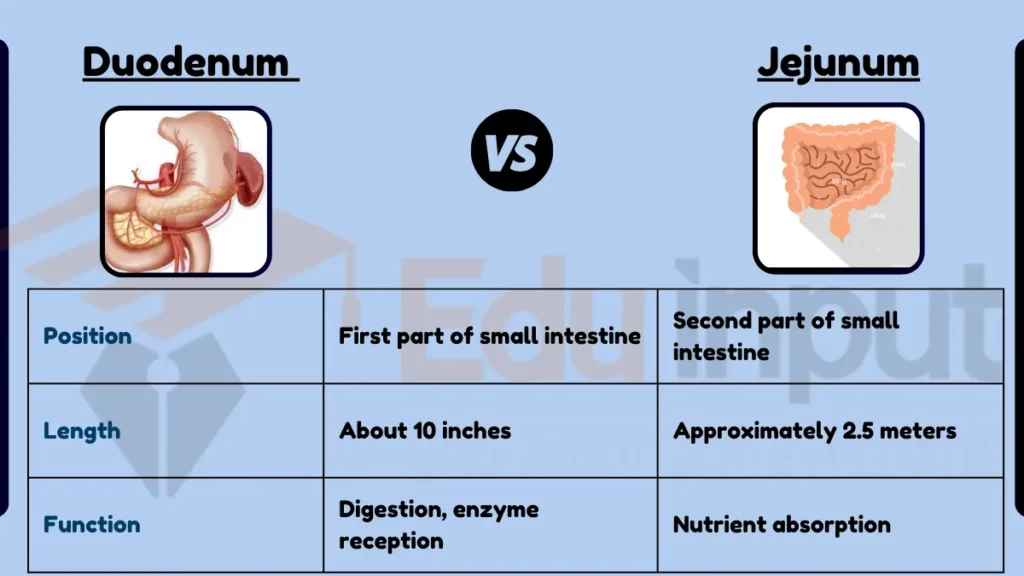
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine, following the duodenum. Its primary function is the absorption of nutrients and minerals from the food that has been partially digested in the duodenum.
Comparative Analysis
- Position in the Digestive System:
- Duodenum: First part of the small intestine, connected to the stomach.
- Jejunum: Second part, follows the duodenum.
- Length and Structure:
- Duodenum: Shortest part, about 10 inches, C-shaped.
- Jejunum: Longer than the duodenum, approximately 2.5 meters in length.
- Function:
- Duodenum: Digestion, receives digestive enzymes and bile.
- Jejunum: Absorption of nutrients and minerals.
- pH Environment:
- Duodenum: Neutralizes the acidic chyme from the stomach.
- Jejunum: Maintains a more neutral environment suitable for nutrient absorption.
- Pathological Conditions:
- Duodenum: Common site for ulcers and blockages.
- Jejunum: Less prone to ulcers, can be affected by conditions like celiac disease.
Table Summary
| Feature | Duodenum | Jejunum |
|---|---|---|
| Position | First part of small intestine | Second part of small intestine |
| Length | About 10 inches | Approximately 2.5 meters |
| Function | Digestion, enzyme reception | Nutrient absorption |
| pH Environment | Neutralizes stomach acid | Neutral for absorption |
| Pathology | Ulcers, blockages | Celiac disease, absorption issues |
Also Read:




Leave a Reply