Difference between hypoxia and hypercapnia
December 28, 2023
Table of Contents
Key Difference
Hypoxia and hypercapnia are both medical conditions related to respiratory dysfunction, but they differ in their specific nature and effects on the body. Hypoxia refers to a deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the body’s tissues, which can affect cellular function and survival. Hypercapnia, on the other hand, is characterized by an excess of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream, typically resulting from inadequate respiration.
Comparative Analysis
- Primary Condition:
- Hypoxia: Low oxygen levels in tissues.
- Hypercapnia: High carbon dioxide levels in blood.
- Causes:
- Hypoxia: Respiratory failure, high altitude, circulatory issues.
- Hypercapnia: Respiratory disorders, hypoventilation.
- Symptoms:
- Hypoxia: Shortness of breath, cyanosis, confusion.
- Hypercapnia: Drowsiness, headache, flushed skin.
- Physiological Effect:
- Hypoxia: Affects cellular metabolism and function.
- Hypercapnia: Leads to respiratory acidosis, affecting blood pH.
- Measurement and Diagnosis:
- Hypoxia: Measured by blood oxygen levels (SpO2).
- Hypercapnia: Detected by elevated blood CO2 levels, arterial blood gas analysis.
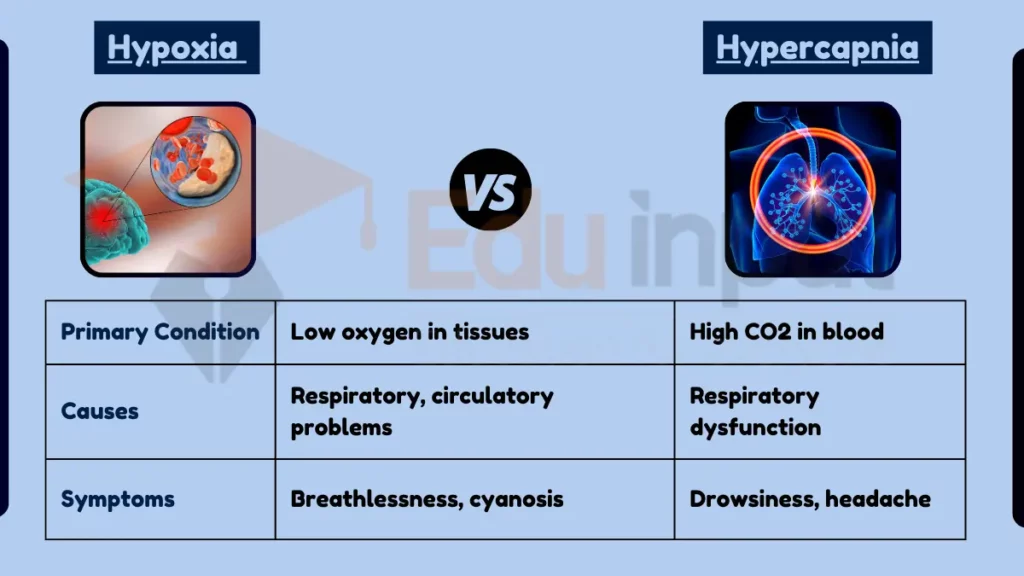
Table Summary
| Feature | Hypoxia | Hypercapnia |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Condition | Low oxygen in tissues | High CO2 in blood |
| Causes | Respiratory, circulatory problems | Respiratory dysfunction |
| Symptoms | Breathlessness, cyanosis | Drowsiness, headache |
| Physiological Effect | Cellular impact | Respiratory acidosis |
| Diagnosis | Blood oxygen levels | Blood CO2 levels, blood gas analysis |
Also Read:
File Under:




Leave a Reply