Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
July 22, 2022
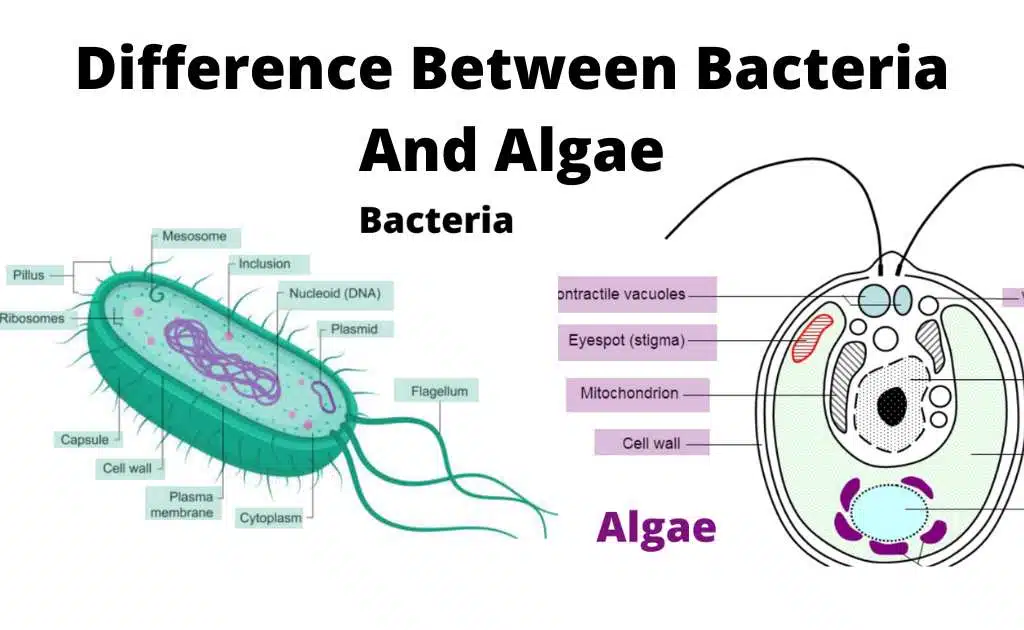
The key difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the presence or absence of a distinct nucleus and membrane-bound organelles within their cells.
Table of Contents
Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Here are the main differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
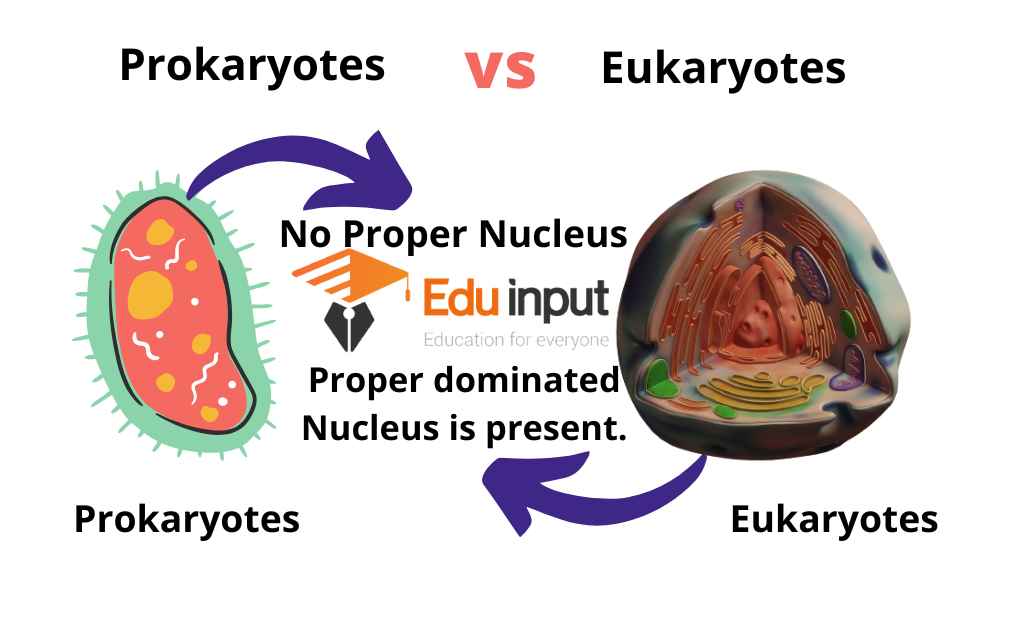
1. Presence of Nucleus
| Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
| Nucleus is Absent. | Nucleus is Present in Eukaryotic cell. |
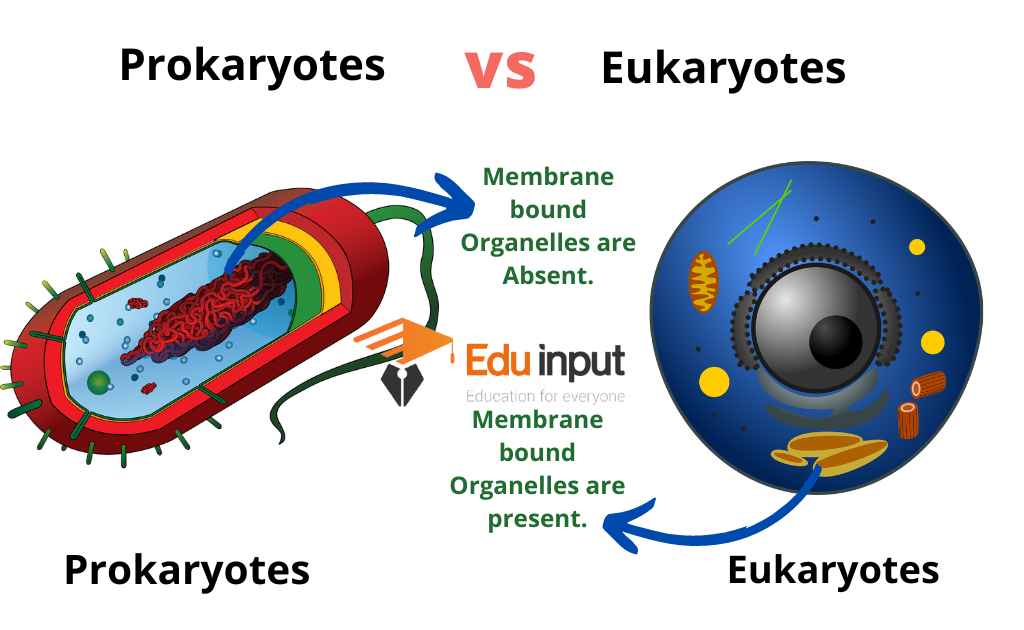
2. Presence of Membrane-bound organelles
| Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
| Membrane-bound organelles are Absent. | Membrane-bound organelles are Present. |
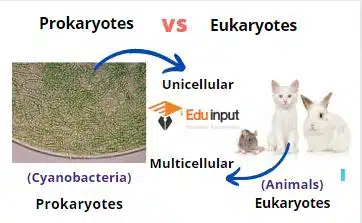
3. Cell Structure
| Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
| They are Unicellular. | Mostly eukaryotes are multicellular. Some are unicellular. |
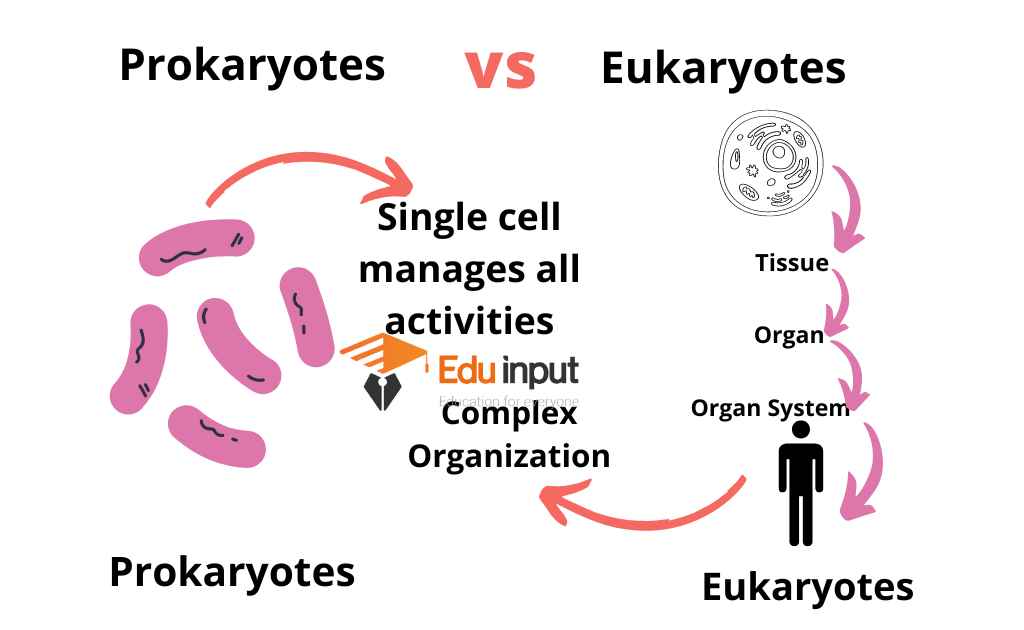
4. Complexity Of Cell
| Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
| Their body organization is Simpler. | Their body organization is more complex. |
5. Cell Size
| Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
| Cell size of prokaryotes is Smaller. It ranges from 0.1-5 μm. | Cell size of eukaryotes is larger. It ranges from 10-100 μm. |
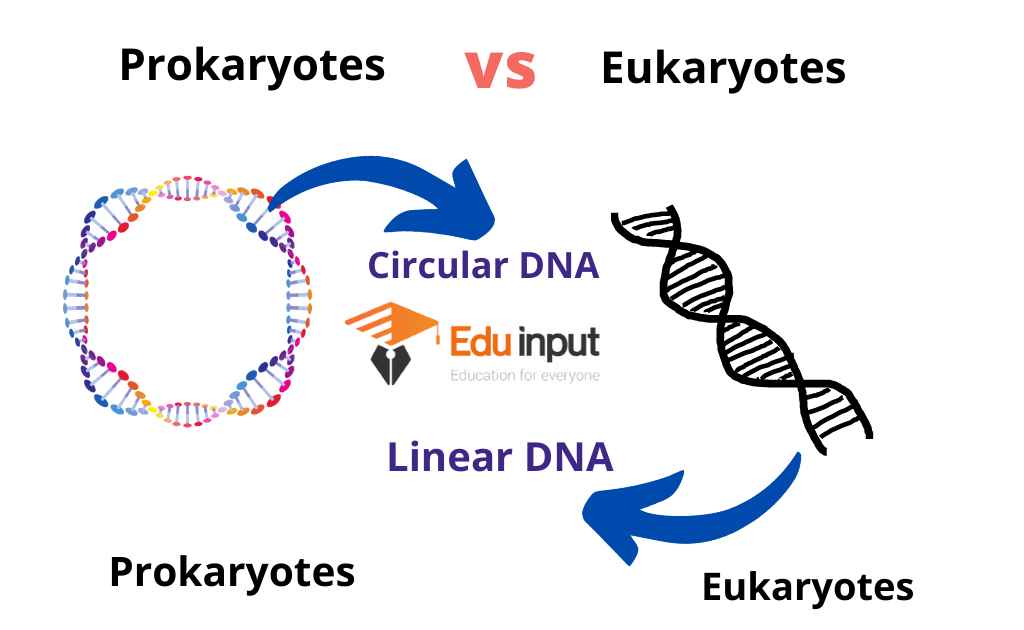
6. DNA Type
| Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
| Their DNA is in Circular. | Their DNA is linear. |
Detailed Overview of Difference Between Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ in several key features that reflect their distinct evolutionary paths.
- Cell Type – Prokaryotes have simple, single-celled organisms without a nucleus, while Eukaryotes have complex, multi-cellular organisms with a nucleus enclosed within a membrane.
- Size – Prokaryotes are typically smaller, ranging from 0.1 – 5.0 μm in diameter, while Eukaryotes are typically larger, ranging from 10 – 100 μm in diameter.
- Genetic Material – Prokaryotes have a single, circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm, while Eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes contained within a nucleus.
- Organelles – Prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, while Eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles that perform specialized cellular functions.
- Cell Wall – Prokaryotes have a cell wall composed of peptidoglycan, while Eukaryotes lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
- Ribosomes – Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes, while Eukaryotes have 80S ribosomes.
- Reproduction – Prokaryotes reproduce asexually by binary fission, while Eukaryotes can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
- Evolution – Prokaryotes are thought to be the early ancestors of eukaryotic cells, while Eukaryotes are believed to have evolved from early prokaryotic organisms.
File Under:



Leave a Reply