Difference Between Voice-over and Dubbing
Key Difference
Voice-over and dubbing are both techniques used in audio and video productions to replace or supplement spoken dialogue, but they serve different purposes and are executed differently. Voice-over involves a narrator or commentator speaking over the original audio track, often used in documentaries, news reports, and instructional videos.
The original audio is usually still audible beneath the voice-over. Dubbing, on the other hand, is the process of replacing the original dialogue in a film or television show with dialogue in another language. It involves careful synchronization of the new audio with the actors’ lip movements and expressions to maintain the original performance’s authenticity.
Comparative Analysis
- Purpose:
- Voice-over: To provide additional information, narration, or commentary.
- Dubbing: To replace original dialogue with a new language.
- Synchronization with Video:
- Voice-over: No need for precise lip-syncing.
- Dubbing: Requires precise synchronization with lip movements.
- Presence of Original Audio:
- Voice-over: Original audio usually remains audible.
- Dubbing: Original audio is replaced entirely.
- Usage:
- Voice-over: Documentaries, news, commercials.
- Dubbing: Movies, TV shows, video games.
- Viewer Experience:
- Voice-over: Adds to or complements the original content.
- Dubbing: Transforms the content for a different language audience.
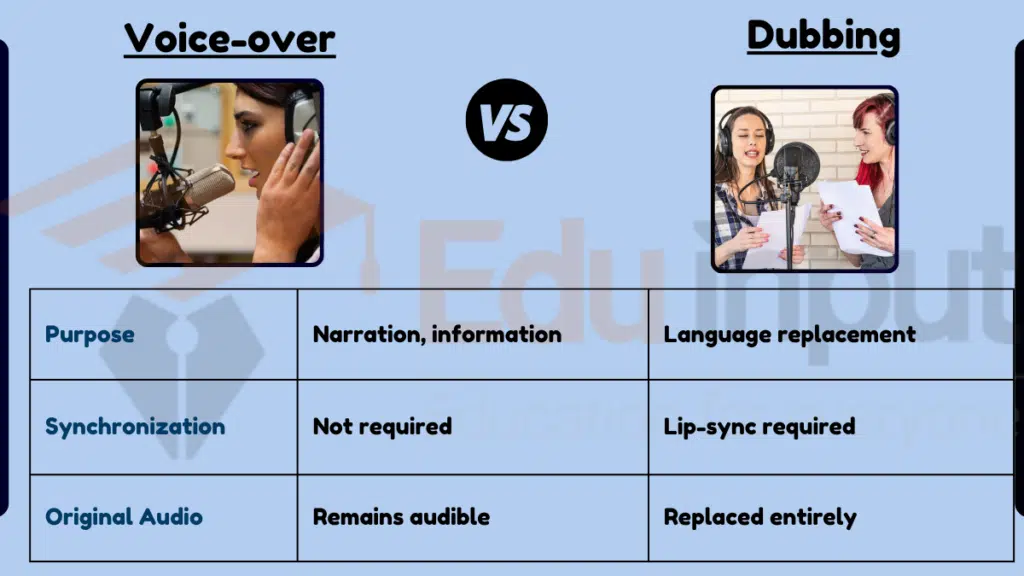
Table Summary of Voice-over vs Dubbing
| Feature | Voice-over | Dubbing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Narration, information | Language replacement |
| Synchronization | Not required | Lip-sync required |
| Original Audio | Remains audible | Replaced entirely |
| Usage | Documentaries, news | Movies, TV shows |
| Experience | Complementary | Transformative |



Leave a Reply