Difference between Whole Genome Sequencing and Whole Exome Sequencing
November 3, 2024
The main difference between Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) and Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) is on the basis of their sequencing regions.
The genome consists of the complete genetic information of an organism, including both coding and noncoding areas. At the same time, Exome consists of all exons that are coding parts of the genome. Likewise, Whole genome sequencing is the order of all nucleotides of the genome. At the same time, Whole Exome sequencing includes only the order of exons.
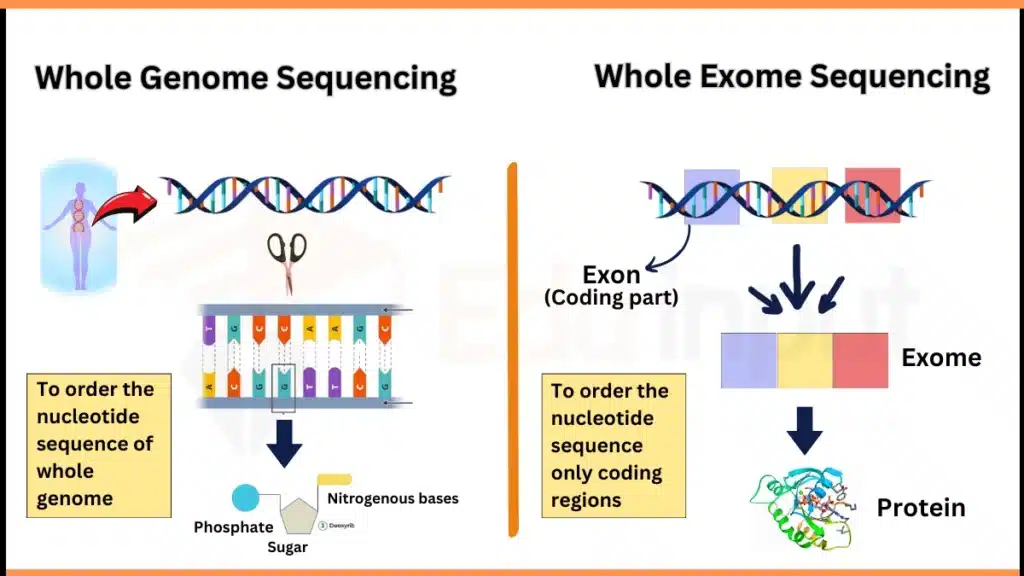
Whole Genome Sequencing VS Whole Exome Sequencing
Here are the some key differences between whole genome and exome sequencing:
| Character | Whole genome sequencing | Exome Sequencing |
| Definition | “To determine the whole DNA sequence of an organism.” It includes the order of nucleotides in DNA. | “To determine the sequence of only coding regions of DNA.” |
| Sequence regions | All the coding & non-coding regions. Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA in plants too. | Only the coding regions |
| Sequencing depth | Lower depth, due to large size of genome | Higher depth, as fewer regions are sequenced, |
| Cost | More expensive due to large data | Less expensive |
| Time | Takes more time | Takes less time |
| Applications | Suitable for studying complex genetic conditions. | To study diseases associated with specific genes |
| Clinical use | Less use due to higher cost and volume of data, but valuable for research | High use in clinics and labs; to check changes in genes |
| Limitations | More expensive and complicated; may find unrelated data. | Only shows coding parts of the genome; changes in noncoding regions are missed. |
File Under:



Leave a Reply