Differences Between Variation And Mutation
May 27, 2023
The main difference between mutation and variation is that mutation refers to an alteration in the nucleotide sequence of a gene, whereas variation is any difference observed among individuals of the same species.
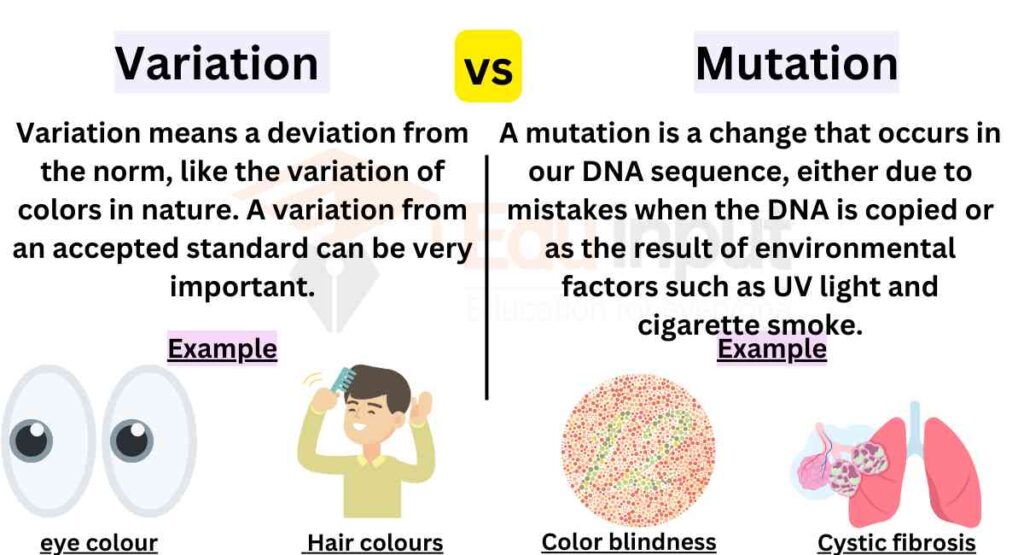
Variation vs. Mutation
Here are the main differences between variation and mutation:
| Aspect | Genetic Variation | Genetic Mutation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The diversity of genetic traits within a population or species | A permanent alteration or change in the DNA sequence of an organism |
| Source | Arises from processes such as genetic recombination, gene flow, and genetic drift | Primarily caused by spontaneous changes in DNA or exposure to mutagens |
| Scope | Can involve a range of genetic differences, including alleles, gene copy number variations, and chromosomal rearrangements | Refers specifically to changes at the DNA sequence level |
| Occurrence | Common and naturally occurring in populations, contributing to biodiversity | Relatively rare events, occurring randomly or due to specific factors |
| Impact | Contributes to the phenotypic diversity and adaptation of individuals and populations | Can have various effects, including neutral, beneficial, or harmful impacts on an organism |
| Mechanisms | Generated through sexual reproduction, genetic recombination during meiosis, and genetic exchange | Result from errors in DNA replication, repair, or recombination |
| Types | Includes polymorphisms, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and structural variations | Encompasses point mutations (substitutions, insertions, deletions), chromosomal mutations, and gene mutations |
| Inheritance | Can be inherited and passed down to offspring, contributing to hereditary traits | Can be inherited if it occurs in germ cells, potentially leading to genetic disorders |
| Importance | Provides the raw material for natural selection and evolutionary processes | Can introduce new genetic traits, cause diseases, or have implications in evolutionary biology and medicine |
| Examples | Allelic variations in eye color, blood type, or height within a population | Mutations causing genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, or BRCA gene mutations |
File Under:

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply