10 Examples of Vectors In Biology
In Biology, a vector is an organism that transmits a disease-causing agent from one host to another. Arthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and flies are some common examples of vectors.
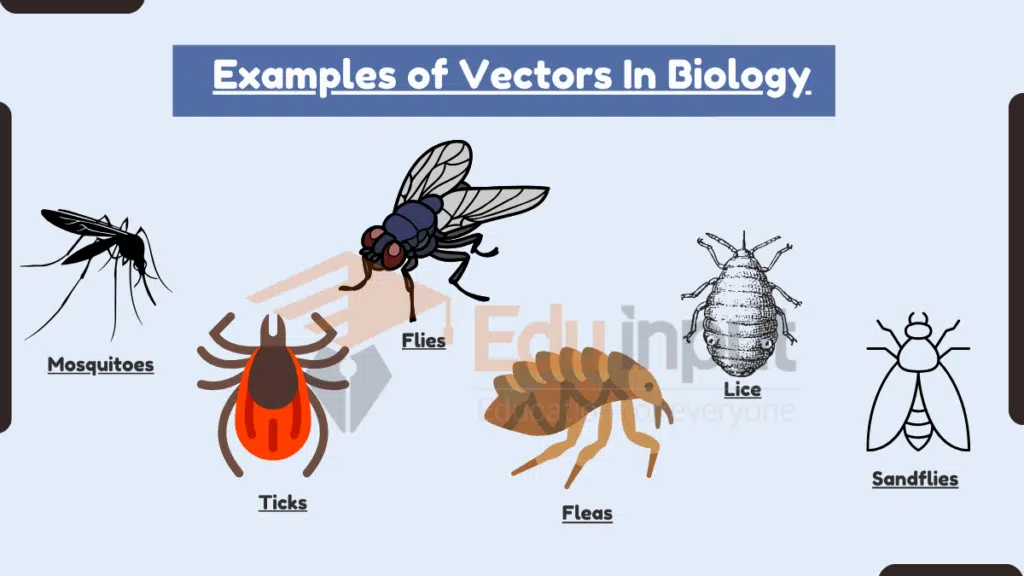
Examples of Vectors In Biology
Here are 10 examples of vectors in biology:
1. Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are the most important example of vectors of human disease worldwide. They can transmit a variety of diseases, including malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus infection, yellow fever, and West Nile virus.
Mosquitoes transmit diseases by biting infected hosts and then injecting the pathogen into the blood of a new host.
2. Ticks
Ticks are another important example of vectors. They can transmit a variety of diseases, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and ehrlichiosis.
Ticks transmit diseases by attaching to their hosts and feeding on their blood. As the tick feeds, it can inject the pathogen into the host’s bloodstream.
3. Flies
Flies can also transmit diseases, although they are not as important as mosquitoes and ticks. Some of the diseases that can be transmitted by flies include typhoid fever, cholera, and shigellosis.
Flies transmit diseases by contaminating food and water with their feces and saliva.
4. Fleas
Fleas can transmit diseases to humans and animals, including bubonic plague and typhus.
Fleas transmit diseases by biting infected hosts and then injecting the pathogen into the blood of a new host.
5. Lice
Lice are small, wingless insects that live on the hair and skin of humans and other animals.
Lice can transmit diseases, such as typhus and relapsing fever, by biting their hosts and then injecting the pathogen into their bloodstream.
6. Sandflies
Sandflies are small, biting insects that live in tropical and subtropical regions.
Sandflies can transmit diseases, such as leishmaniasis and bartonellosis, by biting their hosts and then injecting the pathogen into their bloodstream.
7. Blackflies
Blackflies are small, biting insects that live in rivers and streams. Blackflies can transmit diseases, such as onchocerciasis (river blindness) and tularemia, by biting their hosts and then injecting the pathogen into their bloodstream.
8. Kissing bugs
Kissing bugs are large, blood-sucking insects that live in Central and South America. Kissing bugs can transmit diseases, such as Chagas disease, by biting their hosts and then injecting the pathogen into their bloodstream.
9. Triatomine bugs
Triatomine bugs are large, blood-sucking insects that live in Central and South America. Triatomine bugs can transmit diseases, such as Chagas disease, by biting their hosts and then defecating on them.
The pathogen can enter the host’s body through the bite wound or through the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, or mouth.
10. Tsetse flies
Tsetse flies are large, biting insects that live in Africa. Tsetse flies can transmit diseases, such as African sleeping sickness and nagana, by biting their hosts and then injecting the pathogen into their bloodstream.




Leave a Reply