Factors Affecting The Speed Of Nerve Impulse
Action potentials are like electrical currents that help relay messages throughout the body. These signals travel along nerve fibers in response to a stimulus, whether that be a change in temperature, pressure, or any sort of outside stimuli.
Once the action potential reaches the correct receptor, it then serves as either a record of sensation or instruction to act. The term “action potential” comes from the fact that this signal can create an action. Action membrane potential occurs when a neuron sends a message to another neuron. When it is not sending any message, it is called the rest membrane potential.
Factors Affecting Nerve Impuls’s Speed
Following factors affect the speed of nerve impulse:
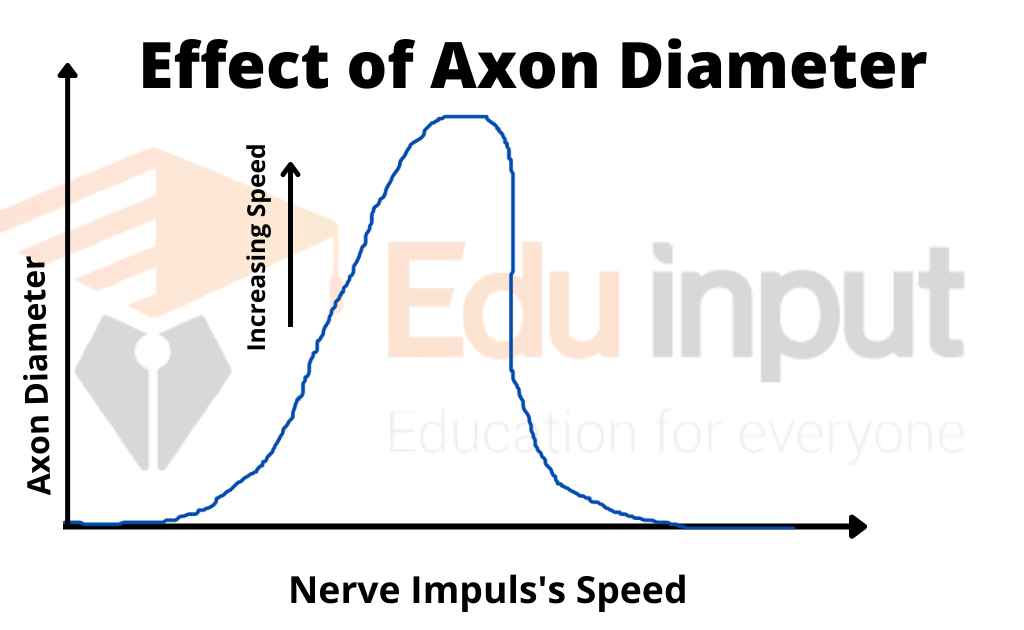
1. Diameter of Axons
An increase in the diameter of the axon increases the speed of nerve impulses. Axons with a large diameter can transmit impulses faster than those with smaller diameters. This is common among many invertebrates, such as crayfishes and earthworms.
The squids have the largest diameter. The diameter of its axon is over 1 mm. The axons have a conduction velocity greater than 36 m/second. The giant squid’s axons can easily escape from predators.
A single action potential causes maximum contraction of the mantle muscle in squids. Mantle contraction rapidly expels water like a jet. Thus the squid moves away from the predator. Most vertebrate axons have a diameter of less than 10 pm.
Some fishes and amphibians have large unmyelinated axons. Their diameter is 50 pm. They extend from the brain. They pass down the spinal cord and activate skeletal muscles.
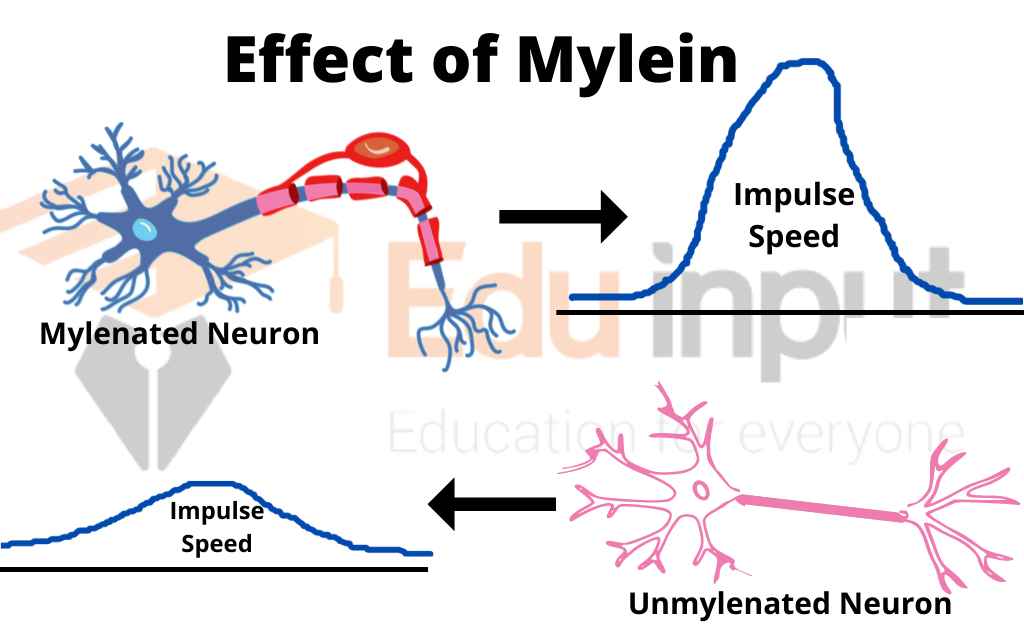
2. Addition of myelin
The addition of sheath also increases the speed of conduction of a nerve impulse. Myelin is a material that helps to insulate against electrical impulses. Thus it stops the movement of ions across it. Therefore, it increases the rate of conduction of nerve impulses.
Action potentials are generated only at the neurofibril nodes. This action potential “jumps” from one node to the next node. Therefore, conduction along myelinated fibers is known as salutatory conduction. It takes less time for the conduction of the nerve.
Myelin sheath allows rapid conduction in small neurons. Thus the evolution of the nervous system in animals took place. It does not occupy large spaces.

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply