Invertebrates-Classification, Types, and Examples
Invertebrates are animals that don’t have a backbone. This doesn’t mean they lack skeletons altogether. Many invertebrates have other structures that provide support and protection, such as exoskeletons, hydrostatic skeletons, or spicules.
Read How Invertebrate are Different From Vertebrates
That means more than 90% of all animal species are invertebrates. Invertebrates can be found all over the world, in all sorts of different habitats. Some invertebrates, like worms and snails, live in the ground. Other invertebrates, like jellyfish and squid, live in the ocean. There are even invertebrates that live in trees.
Check Common Invertebrate Examples
Classification of Invertebrates
There are a variety of invertebrates, which can be classified by Phylum, Claases and families. The main four types are listed below.
| Phylum | Class | Family |
| Porifera | Demospongiae | |
| Cnidaria | Scyphozoa | |
| Anthozoa | ||
| Platyhelminthes | Turbellaria | |
| Cestoda | ||
| Trematoda | ||
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | |
| Enoplea | ||
| Annelida | Clitellata | |
| Polychaeta | ||
| Hirudinea | ||
| Echinodermata | Asteroidea | Asteriidae |
| Echinoidea | Echinidae | |
| Clypeasteridae | ||
| Holothuroidea | Holothuriidae | |
| Mollusca | Gastropoda | Helicidae |
| Turbinidae | ||
| Bivalvia | Mytilidae | |
| Ostreidae | ||
| Cephalopoda | Octopodidae | |
| Loliginidae | ||
| Arthropoda | Insecta | Coleoptera |
| Lepidoptera | ||
| Arachnida | Araneae | |
| Scorpiones | ||
| Crustacea | Decapoda | |
| Chilopoda |
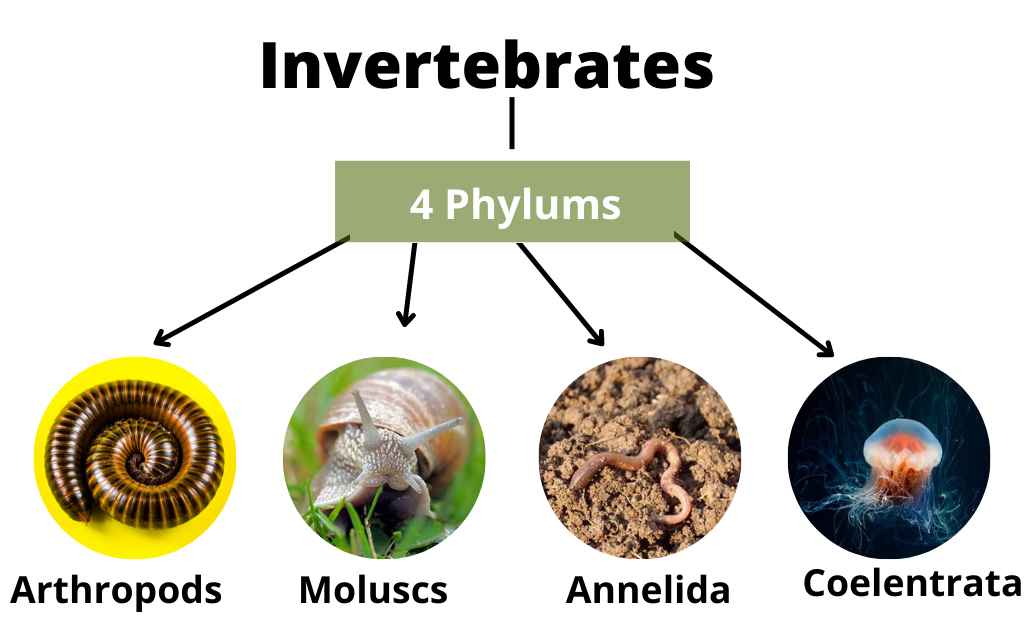
Types of Invertebrates
Different groups of Invertebrates exhibit a wide range of body plans, physiological adaptations, and ecological roles.
Here are the major invertebrate groups :
Porifera (Sponges)
Sponges are simple, multicellular animals that lack true tissues and organs. They have a porous body structure and are sessile (attached to a surface).
Here are a few examples:
- Bath sponges (Spongia spp.)
- Red beard sponge (Microciona prolifera)
- Purse sponge (Isodictya spp.)
Cnidaria (Jellyfish, Corals, Sea Anemones)
Cnidarians are radially symmetrical animals characterized by the presence of stinging cells called cnidocytes. They have a saclike body with a single opening surrounded by tentacles.
Here are some examples of Cnidarians:
- Moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita)
- Sea anemones (Actiniaria)
- Brain coral (Diploria spp.)
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
Flatworms Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic (three germ layers), and acoelomate (no body cavity) animals. They are dorsoventrally flattened and have no specialized circulatory or respiratory systems.
Some of the Platyhelminthes are:
- Planarians (Turbellaria)
- Tapeworms (Cestoda)
- Liver flukes (Fasciola spp.)
Nematoda (Roundworms)
Nematodes are unsegmented, cylindrical worms with a digestive system and a pseudocoelom (a fluid-filled body cavity). They have a tough, flexible cuticle and a muscular body.
Invertebrate Nematodes include:
- Hookworms (Ancylostoma spp.)
- Pinworms (Enterobius vermicularis)
- Vinegar eels (Turbatrix aceti)
Annelida (Segmented Worms)
Annelids are Segmented worms with a true coelom (a fluid-filled body cavity) and a closed circulatory system. They have a well-developed digestive system and a nervous system.
Annelids include:
- Earthworms (Lumbricus spp.)
- Leeches (Hirudinea)
- Sandworms (Nereididae)
Mollusca (Mollusks)
Mollusks are Soft-bodied animals, often with a shell, and a muscular foot for locomotion. They have a well-developed circulatory, digestive, and nervous system.
Here are some examples of Mollusks:
- Garden snails (Cornu spp.)
- Clams (Veneridae)
- Squids (Loliginidae)
- Octopuses (Octopodidae)
Arthropoda (Arthropods)
Arthropods are Segmented animals with a hard exoskeleton and jointed appendages. They have a well-developed nervous system and an open circulatory system.
Arthropods include:
- Honey bees (Apis spp.)
- Spiders (Araneae)
- Horseshoe crabs (Limulidae)
- Shrimp (Caridea)
Echinodermata (Echinoderms)
Echinoderms are Radially symmetrical marine animals with a unique water vascular system. It is a network of fluid-filled canals that is used for locomotion, feeding, and respiration.
Some examples of echinoderms are:
- Starfish (Asteroidea)
- Sea urchins (Echinoidea)
- Sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea)
- Feather stars (Crinoidea)
Segmented Invertebrates With Six Legs
- Atlantic White Shrimp
- Bees
- Black Carpenter Ant
- Cecropia Moth
- Giant Darner Dragonfly
- Common Eastern Bumble Bee
- Fireflies
- Millipedes
- Monarch Butterfly
- Periodical Cicadas
- Rhinoceros Beetles
- Walking Sticks
- Water Striders
- Yucca Moths
- Wood Ants

Wingless Invertebrates With Eight Leg
- Common House Spider
- Tan Jumping Spider
- Tarantulas
- Yellow Garden Spider
- Legless invertebrates
- Earthworms
- Kahului Tree Snails
- Atlantic White Shrimp
- Blue Crab
- Horseshoe Crab
- Octopuses
- Sea Cucumbers
- Vernal Pool Fairy Shrimp


 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply