Food Preservation – Definition, Importance and Methods
What is food preservation?
Food preservation is the process in which food is prevented from spoilage, extends its shelf life and maintain its nutritional value. Besides making food last longer, it helps to reduce food waste.
For many years, people have used food preservation methods to save food for future use. Food companies also use these methods to keep their products fresh for a longer time. Although there are different ways to preserve food, they all aim to keep it safe and fresh.
Why Food Preservation is important?
Here are some reasons that show why we should use food preservation methods:
- Food Safety: Food storage for a long time leads to spoilage from bacteria like E.coli or Salmonella. So food preservation inhibits microbial growth and keep the food safe.
- Maintains Quality: Food preservation maintains food smell, taste and look and that’s how it maintains its nutritional value.
- Prevents Wastage: Around 2.5 billion tons of food are wasted globally each year, which could provide over 2,500 meals per person for those in need. So these methods minimize food wastage and extends its shelf life.
- Cost Savings: Reducing food waste saves money by avoiding loss of uneaten food.
- Environmental Impact: Wasted food in landfills produces methane gas after decomposition which cause global emissions. So food preservation prevent these affects.
Common Food Preservation Methods
Here are the common food preservation techniques that are used in both homes and businesses.

1. Drying
Drying is one of the oldest methods of food preservation. It’s a food dehydrating method in which water content is removed from food to avoid bacterial growth. It also makes foods light weight and easier to transport.
Traditional techniques include sun and wind drying. But modern methods are advanced that include food dehydrators, bed dryers, spray drying, shelf dryers, freeze drying, and household ovens. Meat and fruits like apples, grapes, apricots and plums are commonly dried using this method.
2. Chilling
Keeping food cold is the easiest way to preserve it. The low temperature in our fridges slows down bacterial growth and reduces spoilage. Most foods can be refrigerated without much preparation before storage.
To chill food at homes, right temperature of refrigerator should be between 1°C and 4°C. But for commercial use, Food must be stored under 8°C. In domestic fridges, fruits and vegetables are usually stored on the lowest shelf to keep them separate from meat and dairy. It helps to prevent cross-contamination.
In commercial kitchens, multiple refrigerators are used to keep food separated. Food should be organized using the FIFO (First In, First Out) system, where items with the closest expiry dates are kept at the front to be used first.
3. Freezing
Freezing is one of the simplest methods for preserving fresh vegetables and fruits. It inhibits bacterial growth and keeps its nutritional value. By freezing food between -18°C and -22°C, the microbial growth is slowed down, which extend the food’s shelf life. This method just requires a freezer and airtight containers or freezer bags.
For best results, freeze food when it is fresh and nutritious. Make sure not to refreeze it, if once it is defrosted as bacteria can grow during the thawing process. Hence, freezing is low-effort and a quick method to keep food safe for long term.
4. Salting
Salt is beneficial for removing water from foods. It binds with water molecules and prevent spoilage. There are two methods of salting; wet curing and dry curing. In wet curing, salt is mixed with water and foods are added in this brine. While dry curing is where salt is applied directly to foods, like meat, to draw out its moisture. After dry salting, the food is stored in a cool, dry place, usually in airtight containers to avoid moisture.
5. Pickling
Pickling is a common food preservation method where foods are soaked in vinegar (acidic solution), to prevent spoilage. This acidic environment controls microbial growth and also changes the food’s flavor and texture. Many fruits and vegetables, like cucumbers, apples, and carrots, are pickled. The process often- involves heating vinegar, salt, and sugar before pouring it over the food.
6. Sugaring
Sugaring is similar to pickling but uses sugar instead of vinegar. It involves drying food and then filling it with sugar (like granulated sugar, syrup or honey) to preserve it.
Sugaring is used to make jams, jellies, and relishes from fruits (apples, peaches, plums) and vegetables (ginger, carrots). Sugar molasses with salt is used in brines for preserving meats and fish.
7. Canning
Canning is the process of cooking food, sealing it in sterile and air tight jars, and boiling them to kill any remaining bacteria.
In canning process, cooked food is stored in clean and air tight jars and then boiling them to kill remaining bacteria. It’s important to use proper canning jars designed to be airtight. It preserves the food by preventing it from oxygen.
High-acid fruits like strawberries only need a quick boil and don’t need preservatives. Tomatoes require a longer boil and some added acids. While low-acid foods, like vegetables and meats, need pressure canning to keep them safe.
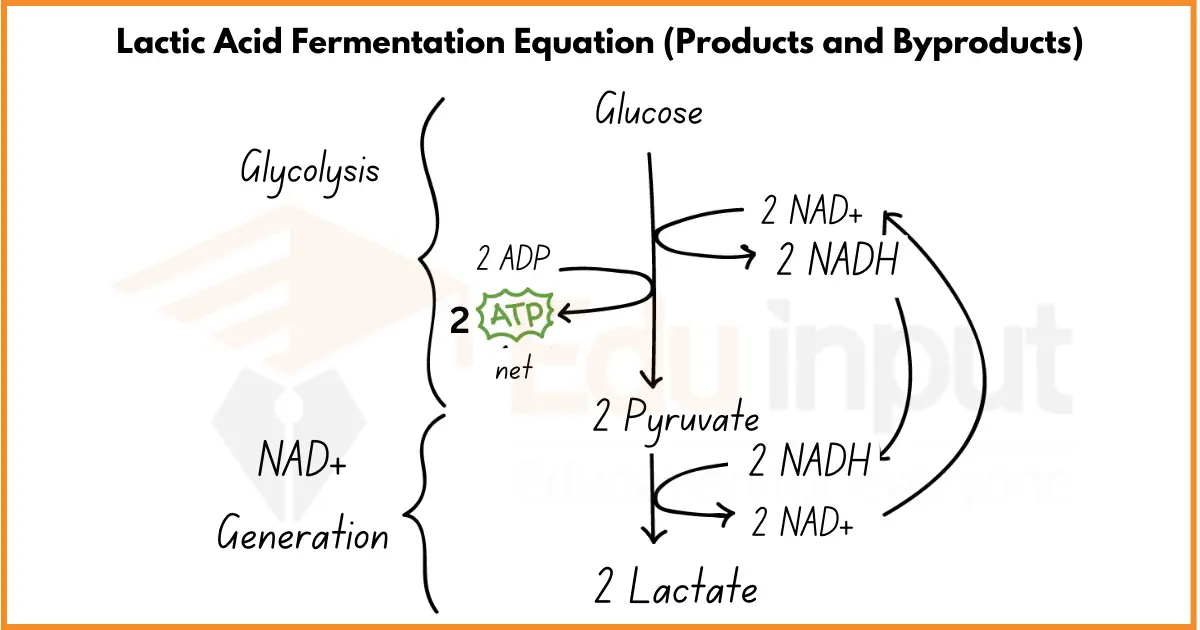
8. Fermentation
Fermentation is a popular food preservation method where microbes like bacteria or yeast break down carbohydrates into acids or alcohol without oxygen. These acids are natural preservatives that prevent bacterial development.
Fermentation helps keep vegetables fresh for 6 months to a year, extending the shelf life. It also creates unique flavors in foods like cheese, yogurt, kefir, kimchi (fermented Korean dish), and sourdough bread.
9. Vacuum packing
Vacuum packing is a method that preserves the food by removing air from the packaging, which prevents multiplication of germs.
Unlike canning, vacuum packing maintains the food qualities like smell, taste, and texture without adding extra ingredients. It also helps retain the food’s moisture. However, care must be taken to avoid the growth of harmful bacteria, like C botulinum, which can grow in low-oxygen environments. Vacuum packing is also useful in food preparation, allowing precise cooking techniques.
10. Smoking
Smoking is an ancient method of food preservation that involves exposing food, like meats and fish, to smoke from burning wood. The smoke contains anti-bacterial properties that prevents the spoilage of fats. This process not only helps in adding flavor but also extends the food’s shelf-life. smoking can also be used for other foods like cheese, vegetables, and spices, it’s important to note that excessive consumption of smoked foods may increase the risk of cancer.





Leave a Reply