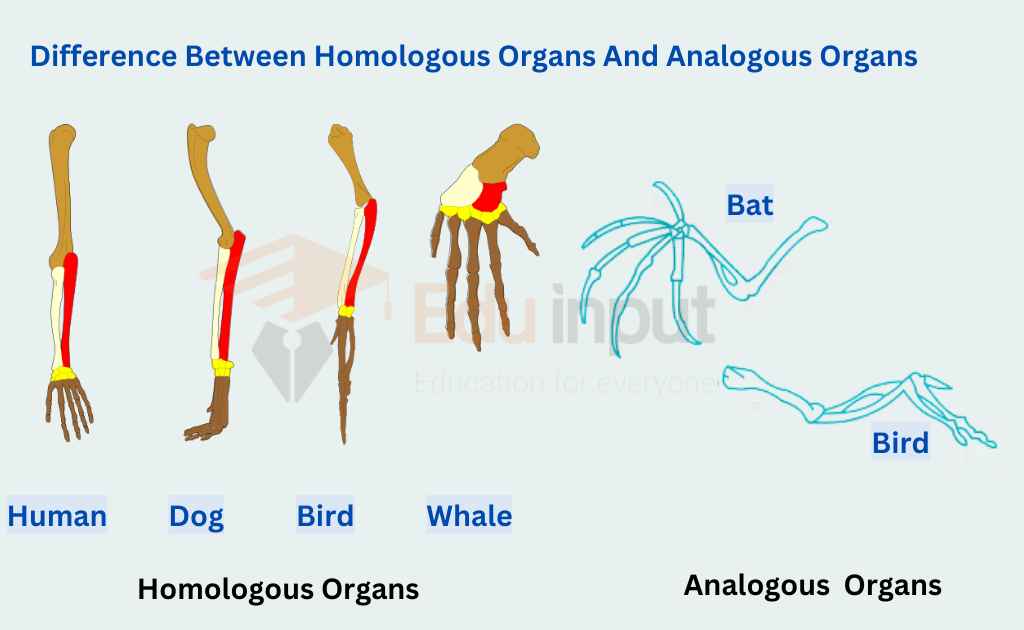
Difference Between Homologous Organs And Analogous Organs
One of the main differences between homologous and analogous organs is that one has a similar embryonic origin. Some of the organisms may be very closely related to each other, even though there is a minor genetic change that makes them look very different. As an example, the bones within the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones within the human arm.
Homologous Organs
The similarity in characteristics due to common ancestry is known as homology. The anatomical structures with common ancestry are called homologous structures.
Homologous organs are functionally different but structurally alike. For example, the forelimbs of humans cats, whales, bats, and all other mammals perform different functions. But these appendages are made up of similar skeletal bones.
This basic similarity is due to the descent of all mammals from a common ancestor. Variations in common basic structures produce forelegs, wings, flippers, and arms of different mammals. These appendages have been modified for different functions.
Comparative anatomy supports that evolution is a remodeling process. The ancestral structures functions in one capacity. They modify and take on new functions.
The flower parts of a flowering plant are homologous. They evolved from leaves. These leaves form sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
Analogous Organs
The organs which show similarity in function but are structurally different and evolve from different ancestors are called analogous organs. They are functionally alike but structurally different. Analogous organs show evolution. For example, wings are Convergent of bats, birds, insects, etc.
Difference Between Homologous Organs And Analogous Organs
Even though there was a small genetic change that made them look different, some of the organisms could be very closely related. Seemingly similar organisms could be very different and distantly related. Here are some Key Difference Between Homologous Organs And Analogous Organs
| Homologous organs | Analogous organs |
| The anatomical structures with common ancestry are called homologous structures. | The organs which show similarity In function but are structurally different and evolve from different ancestors are called analogous organs. |
| Homologous organs are different but structurally alike functionally. | They are functionally alike but structurally different. |
| Homologues organs shows divergent evolution | Analogous organs show convergent evolution. |
| Adaptation to a different environment causes the development of homologous organs. | Adaptation to a similar environment leads to the development of analogous organs. |
| They have similar Anatomy. | They show Dissimilar anatomy. |
| Homologous organs are Inherited from a common ancestor. | They are Not inherited from ancestors. |
| For example, the forelimbs of humans, and cats. whales, bats, and all other mammals perform different functions. | For example wings of bats, birds, and insects, etc. |




Leave a Reply