Introduction to sentence analysis-Eduinput
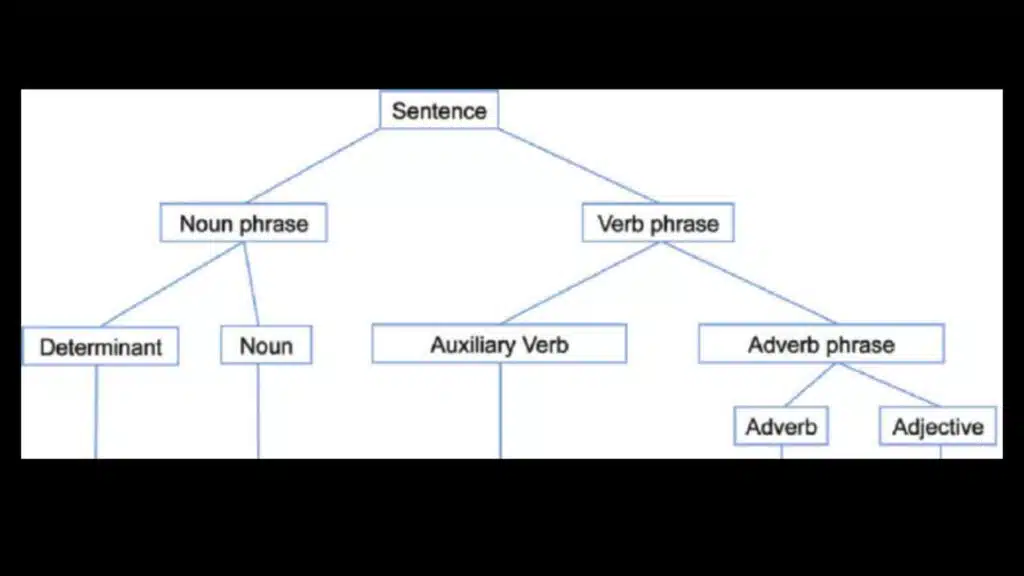
What is Sentence analysis?
Every clause consists of a subject (the thing talked about), a verb or predicate (which makes a statement about the subject), and when the verb is not complete, an object (with a transitive verb) or a predicate noun or adjective (with a linking verb). The remaining words in the clause are modifiers of one of these elements.
Also read: Introduction to sentence structure
The old house which we purchased from Mr. Shahid has been a constant source of expense.
This is a complex sentence. The independent or main clause is the old house has been a constant expense. The dependent clause is which we purchased from Mr. Shahid.
In the independent clause house is the subject. It is modified by the adjectives the old and by the adjectival clause which we purchased from Mr.Shahid. Has been is the verb. The source is the predicate noun and it is modified be the adjectives and constant.
In the adjectival clauses, we is the subject, and purchased is a transitive verb modified be the prepositional phrase (used like an adverb) from Mr. Shahid, which is the direct object.
They promised us that the boat would be ready, and having done business with them before, we accepted their promise.
This is a compound-complex sentence, consisting of two independent clauses connected by and, and one dependent clause, they is the subject, promised is the transitive verb, the noun clause that the boat would be ready is the direct object, us is the indirect object.
In the second independent clause, we is the subject modified by the adjective participial phrase having done business with them before, accepted is the verb, a promise is an object, modify be the possessive adjective, their.
In the dependent noun clause, a boat is a subject, modified, modified be the , would be is the linking verb, ready is the predicate adjective, that is used only to introduce the clause. In the participial phrase, the verbal having done has an object, business, and an adverbial modifier, the phrase with them.



Leave a Reply