Projectile Motion-Height of Projectile, Time of Flight, and Range of Projectile
Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle (projectile) that is projected near the surface of the earth and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity.
Projectile motion is a two-dimensional motion under constant acceleration due to gravity.
What is a Projectile?
A projectile is any object projected in space with a certain initial velocity in an arbitrary direction and then allowed to move under the influence of gravity.
What is Trajectory?
The path followed by the projectile is called the trajectory
Examples
- A football kicked by a player
- A ball was thrown by a cricketer
- Rocket Propulsion.
All bodies projected at some angles with the horizontal are examples of projectiles.
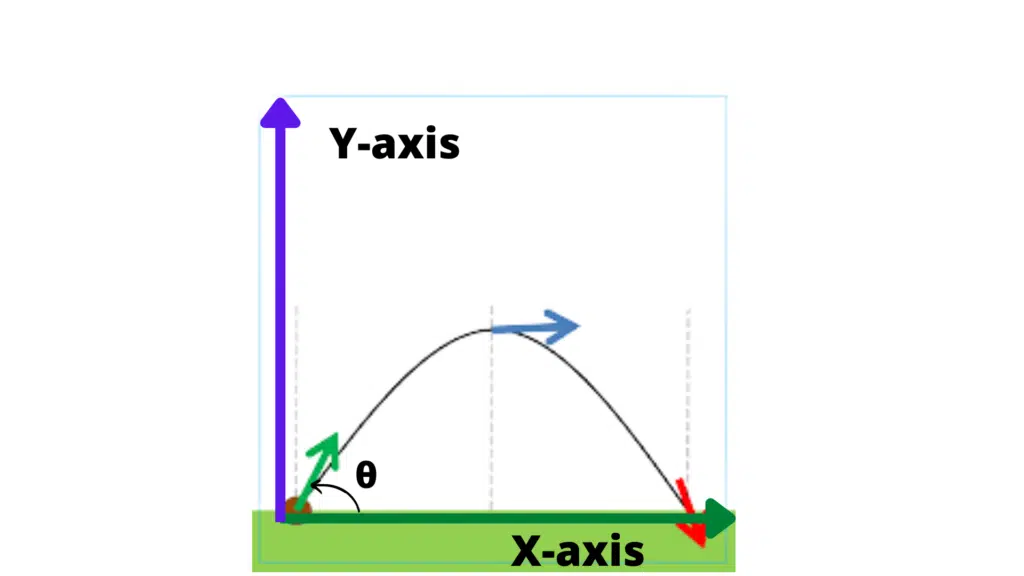
Consider the motion of a ball, when it is thrown horizontally from a certain height observed that the ball travels forward direction as well as falls down until it strikes something.
The motion of a projectile can be studied easily by resolving it into horizontal and vertical components which are independent of each other
Horizontal Projectile Motion
Suppose that the ball leaves the hand of the thrower at point A its velocity at that instant is completely horizontal
Let this velocity be Vx
- According to Newton’s law of motion, there will be no acceleration in the horizontal direction, unless a horizontally directed force acts on the ball.
- A body remains at rest or continues to move with constant velocity provided no external force acts on the body.
Ignoring the air friction, the only force acting on the ball during flight is the force of gravity. There is no horizontal force acting on it.

So its horizontal velocity will remain unchanged and will be Vx until the ball hits something. The horizontal motion of the ball is simple.
The ball moves with a constant horizontal velocity component.
The horizontal distance of Projectile:
Horizontal distance x is given by
X=Vx xt
Vertical Projectile Motion:
The ball will accelerate downward under the force of gravity and hence a=g. This vertical motion is the same as for a freely falling body. Since the initial vertical is zero.
The vertical distance of Projectile:
The vertical distance of the object can be calculated as,
S=Vit+(1/2)at2
y=(0)t+(1/2)gt2
y=(1/2)gt2
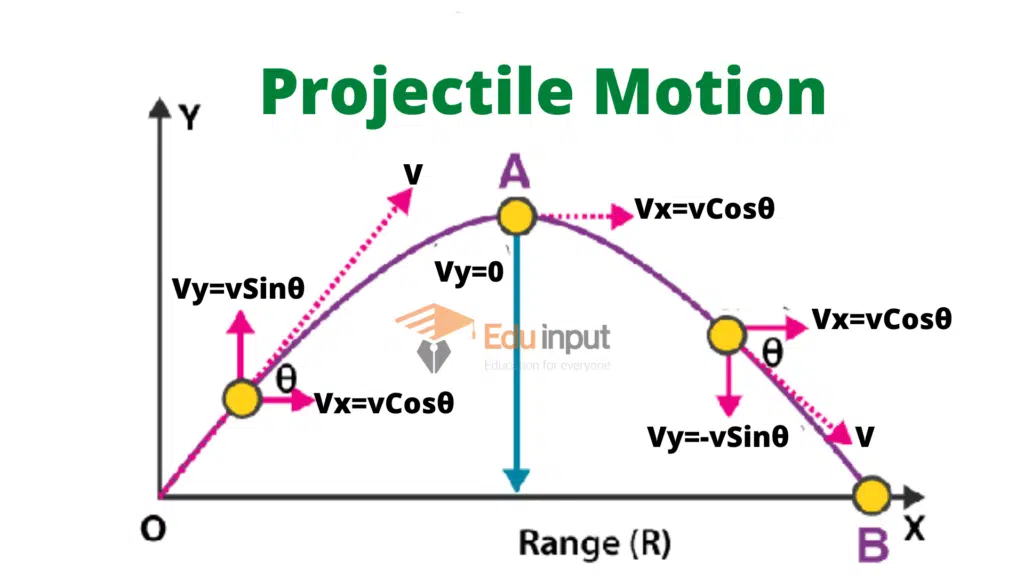
When the projectile is making some angle with the horizontal axis. Suppose that a projectile is fired at an angle θ with the horizontal velocity Vi.
Let components of velocity Vi along the horizontal and vertical direction be Vi cosθ and Vi sinθ respectively.
Horizontal Velocity of Projectile Motion
The horizontal acceleration is ax = 0 because air resistance has been neglected and no other force is acting in this direction. Hence the horizontal component Vix remains constant and at any time t
Vfx = Vi = Vi cosθ
Vertical Velocity of Projectile Motion
In vertical motion, vertical acceleration ay= g. The initial vertical component of the velocity is Vi sin θ in the upward direction
Viy = Vi Sinθ
The vertical component Vfy of the velocity at any instant t is given by
Vf=Vi-at
Vfy= Vi Sinθ -gt
Instantaneous Velocity of the Projectile
The magnitude of velocity at any instant t is

Equation of Direction of projectile motion
Tanθ=Vfy/Vfx
θ is the angel with which body is projectile
Height of Projectile:
“The greatest vertical distance reached as measured from the horizontal projection plane”.
In order to determine the maximum height of the projectile, we use 3rd eq. of motion
2as = vf² – vi²
The body moves upward, so a = -g
initial vertical velocity= Viy = ViSinθ
the body comes to rest after reaching the highest point, so Vfy= 0

Time of Flight
“The time is taken by the body to cover the distance from the place of its projection to the place where it hits the ground is called the time of flight”.
Let’s consider if the body is projected with velocity v making an angle θ with the horizontal, then its vertical component will be Vi Sin θ.
s = h = 0 because the body goes up and comes back to the same level, thus covering no vertical distance

Where t is the time of flight of the projectile when it is projected from the ground
Range of the Projectile
The maximum distance that a projectile covers in the horizontal direction is called the range of the projectile.
The range R of the projectile is equal to the product of the horizontal component of the velocity of projection with the total time taken by the body to hit the ground after leaving the point of projection.

Dependence of range:
Thus the range of the projectile depends upon the velocity of projection and the angle of projection.
What is the maximum range of projectile?
For range R to be maximum, the factor sin2θ should have a maximum value which is 1
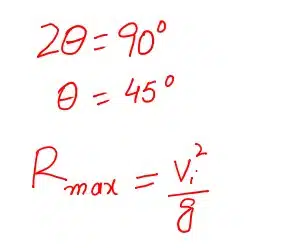

Frequently Asked Question
What does Projectile motion mean?
Projectile motion is a two-dimensional motion under constant acceleration due to gravity.
What are the main factors that affect the projectile motion?
There are three main factors on which projectile motion depends.
- The projection angle
- The magnitude of projection velocity
- Height of the projection
When does the projectile have maximum range?
The projectile has a maximum range at an angle of 45.





Leave a Reply