Comparison of Male and Female Reproductive System of Humans
The reproductive system in males and females play important role in human reproduction, but have some major anatomical and functional differences.
This article will compare and contrast the structure and function of the external and internal reproductive organs in males and females.
External Genitalia
In Males
The male external genitalia include the penis, scrotum, and testicles. The penis is a cylindrical organ used for urination and sexual intercourse. It contains erectile tissue that fills with blood during arousal, causing it to become erect.
The scrotum is a sac of skin that contains the testicles. It helps to regulate their temperature, which is important for sperm production. The testicles are oval-shaped organs that produce sperm and testosterone.
In Females
The female external genitalia are collectively known as the vulva. This includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and vaginal opening. The mons pubis is a fleshy area above the vulva.
The labia majora are the outer folds of skin that surround the vulva. The labia minora are the inner folds of skin. The clitoris is a small, sensitive organ that is homologous to the penis. The vaginal opening is the opening to the vagina.
Internal Genitalia
In Males
The male internal reproductive organs include the epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. The epididymis is a long, coiled tube where sperm mature and are stored. The vas deferens is a tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
The ejaculatory duct is a short tube that carries sperm from the vas deferens and seminal vesicles to the urethra. The seminal vesicles produce a fluid that nourishes and protects the sperm. The prostate gland produces a fluid that is added to the semen. The bulbourethral glands produce a lubricating fluid that is released into the urethra during ejaculation.
In Females
The female internal reproductive organs include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. The fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
The uterus is a pear-shaped organ where a fertilized egg implants and grows into a fetus. The cervix is the neck of the uterus, which opens into the vagina. The vagina is a muscular tube that connects the cervix to the outside of the body.
Function and Similarities
The main function of the male reproductive system is to produce and deliver sperm. The main function of the female reproductive system is to produce and mature eggs, and to provide a suitable environment for a fertilized egg to implant and grow into a fetus.
Both the male and female reproductive systems produce hormones that are essential for sexual development and function. Both systems also have organs that produce fluids that nourish and protect the gametes (sperm and eggs).
Differences
The main difference between the male and female reproductive systems is that the male system is designed to produce and deliver sperm, while the female system is designed to produce and mature eggs, and to implant and develop a fertilized egg into a fetus. This difference is reflected in the different structure and function of the external and internal genitalia.
Related FAQs
What are the male reproductive organs?
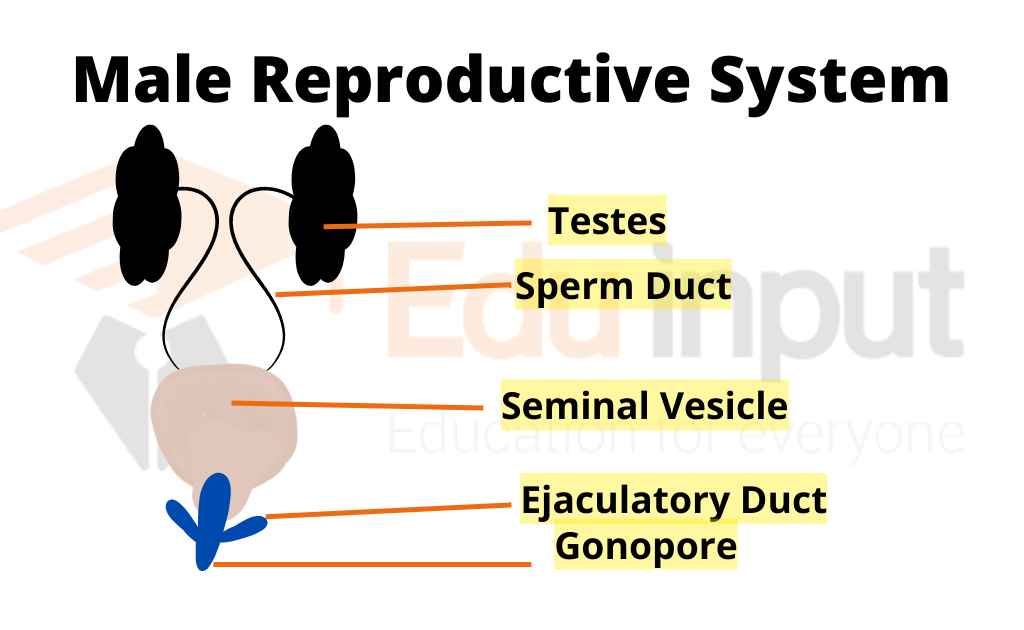
There are the following reproductive organs in males:
Testes
Seminal vesicles
Spermatophores
Copulatory organ
Accessory glands
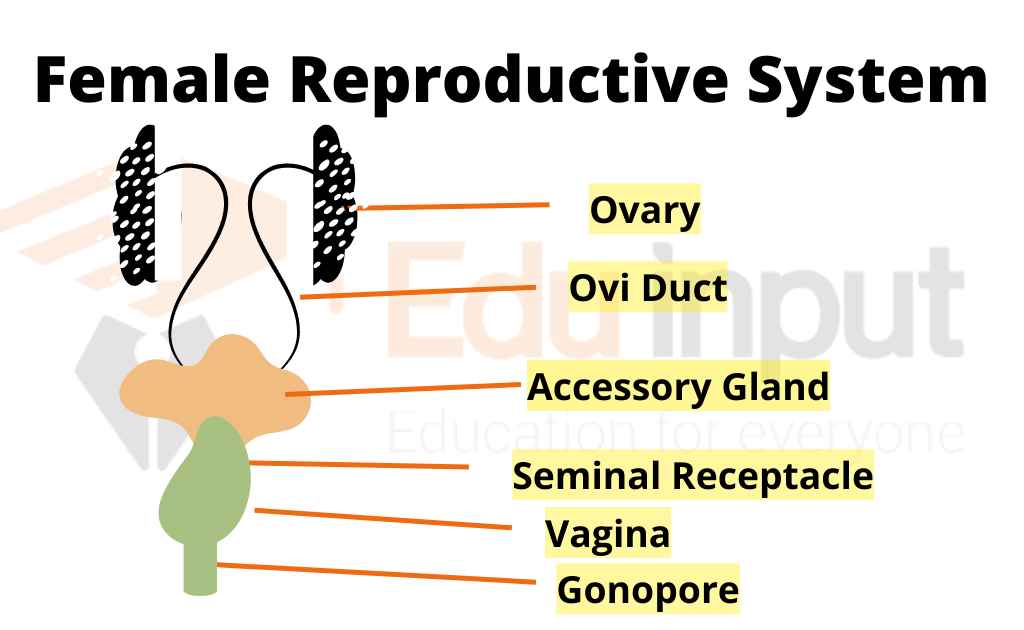
What are the female reproductive organs?
The female reproductive system includes the following organs;
Ovaries
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Vagina
What is Hermaphroditism?
The animals which have both functional male and female reproductive systems are called hermaphrodites. It is also called a monoecious condition. Its mechanism is called Hermaphroditism.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply