Tropic and Nastic Movement in Plants | Paratonic Movement in Plants
Higher plants move in response to a variety of stimuli, including touch, gravity, light, and water. These motions are called tropisms, and they allow plants to orient themselves toward or away from external stimuli. There are also plant movements that occur without any external stimuli; these are called nastic movements. Nastic movements include things like curling up of leaves in response to changes in temperature or light intensity.
Types Of Movements
Plants show two types of movements;
- Autonomic movements
- Paratonic movements
The spontaneous movement due to internal causes is called autonomic movement. The stimulus for autonomic movements may be internal or external. There are three types of autonomic movement;
• Tactic Movements
• Turgor Movement
• Growth Movement
Paratonic Movements
The movements due to external causes are called paratonic movements. There are following types of paratonic movements:
Tropic Movements
The movements in the curvature of the whole organ towards or away from the stim such as light, gravity, and touch are called tropic movements. Following are t common tropic movements:
Phototropism:
The tropic movement of the part of the plant in response to the stimulus of light is called phototropism. It is caused due to differential growth of parts of the plants like root, stem, or root.
Thigmotropism:
The tropic movement in response to the stimulus of touch is called thigmotropism. For example, climbing vines. When they come in contact with some solid object the growth on the opposite side of the contact increases. So tendrils coils around the support.
Chemotropism:
The tropic movement in response to some chemical is called chemotropism. The hyphae of the fungi are chemotropic.
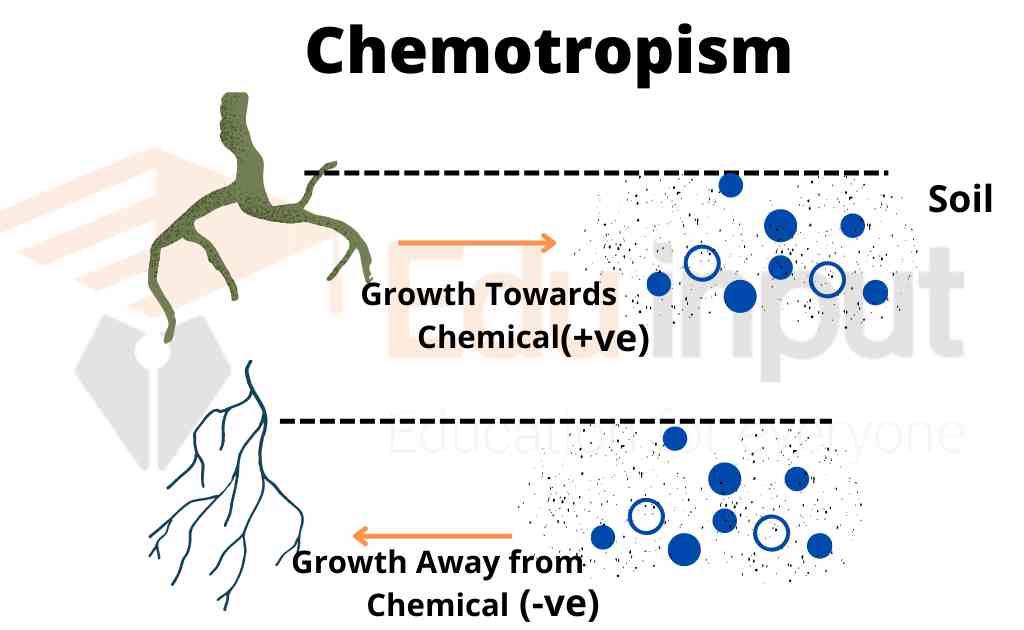
Hydrotropism:
The tropic movement of the plants in response to the stimulus of water is called hydrotropism. The growth of roots toward water is due to positive hydrotropism. The shoot grows away from water. It is negative hydrotropic.
Geotropism:
The tropic movements in response to gravity are called geotropism. Roots show positive geotropism. But shoot shows negative geotropism.
Nastic Movement
the non-directional movement of the plant in response to external stimuli is called nastic movement. There are two types of nastic movement.
Nyctinasty:
The sleep nastic movements are called nyctinasty. The nyctinastic movements are shown by the organs in response to external stimuli. These movements take place due to turgor and growth changes.
It may be of three types.
Photonasty:
The principal stimulus is the photoperiod for photo nasty. The flower opens and closes due to light intensity.
Thermonasty:
The stimulus for the term nasty is temperature. There is rapid growth in the lower side of the petals of the tulip flower at night. It causes upward and inward bending of petals. This flower tulip close at night.
Haptonastic:
These movements occur in response to contact with any object. For example, the action of Venus flies trap.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply