20 Types of Figures of Speech
Types of Figures of Speech enhance language by adding depth, emotion, and creativity. From simile, metaphor, and irony to alliteration, onomatopoeia, and paradox, each type of figurative language conveys meaning beyond the literal.
In this article, we will discuss different types of figurative language that will help you master figurative devices for impactful communication.
Types of Figures of Speech
Figures of speech are a form of figurative language used to express ideas creatively. Below is a list of figurative language types, their definitions, and examples.
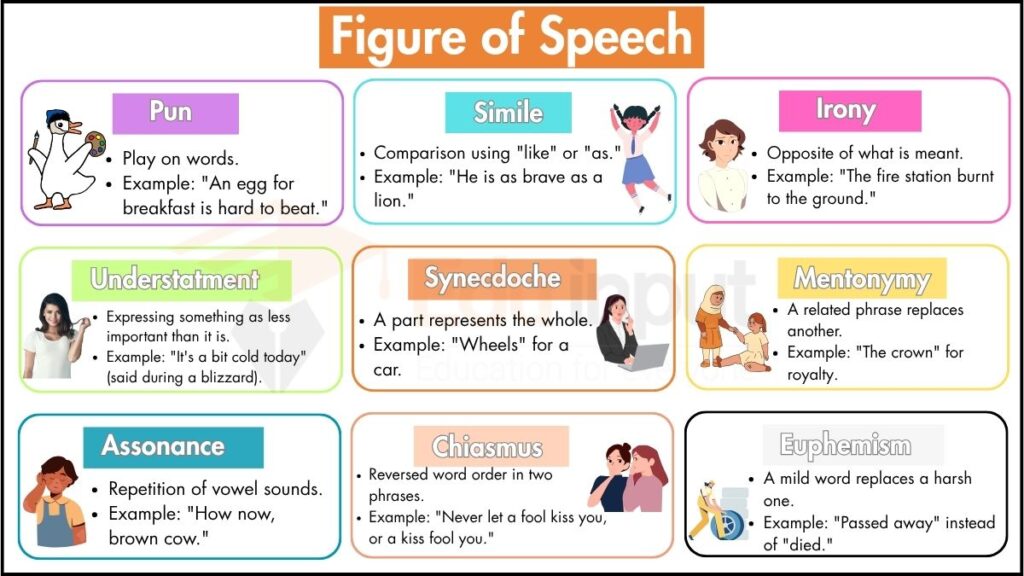
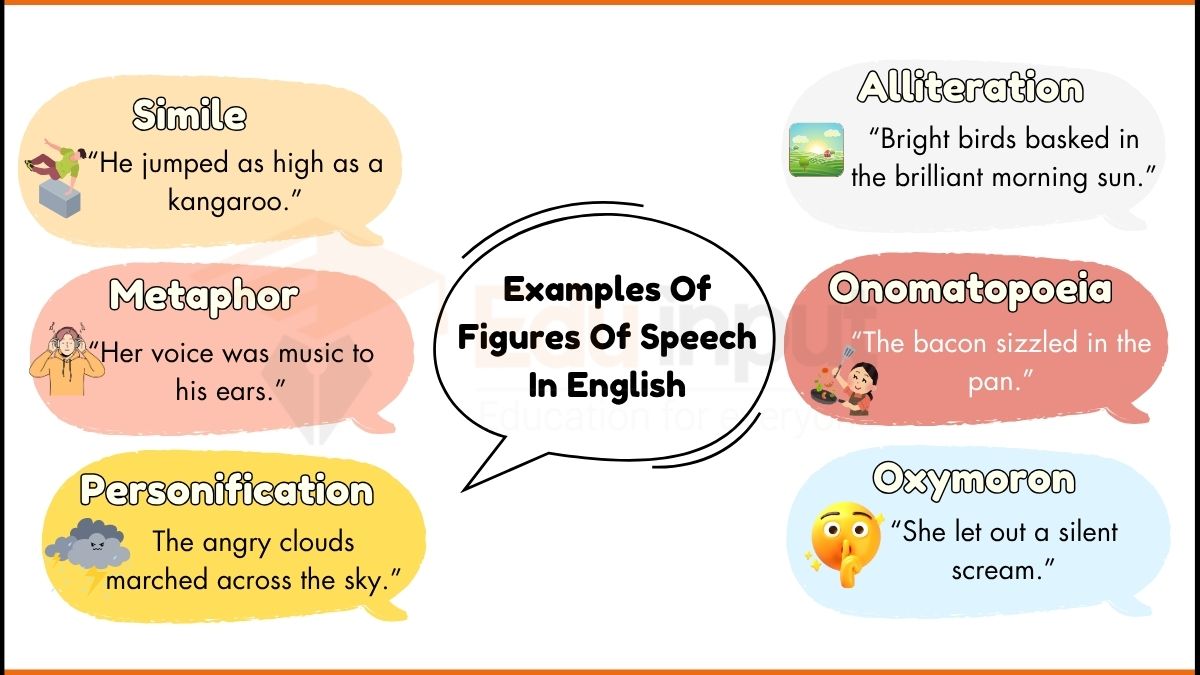
1. Simile
A simile is a type of figurative language that compares two different things using “like” or “as.”
Usage Examples of Simile
- Her smile was as bright as the sun. (Compares a smile to sunlight)
- He ran like the wind. (Compares running speed to wind)
- She was as cold as ice. (Compares coldness to ice)
- The car was as fast as a cheetah. (Compares speed to a cheetah)
- His words cut like a knife. (Compares words to a knife’s sharpness)
2. Metaphor
A metaphor is a figurative device that directly compares two unrelated things without using “like” or “as.”
Usage Examples of Metaphor
- Time is a thief. (Time takes moments like a thief steals)
- She has a heart of stone. (Her heart is unfeeling)
- The classroom was a zoo. (Compares a noisy classroom to a zoo)
- His words were a dagger. (Compares painful words to a dagger)
- The sky was a blanket of stars. (Compares stars to a blanket)
3. Personification
Personification gives human qualities to non-human things.
Usage Examples of Personification
- The wind whispered through the trees. (Wind is given the ability to whisper)
- The stars danced in the sky. (Stars are given the ability to dance)
- The alarm clock screamed at me. (Clock is given the ability to scream)
- The sun smiled down at us. (Sun is given the ability to smile)
- The leaves waved in the wind. (Leaves are given the ability to wave)
4. Hyperbole
A hyperbole is an exaggeration used for emphasis.
Usage Examples of Hyperbole
- I’ve told you a million times! (Extreme exaggeration)
- He was as tall as a skyscraper. (Exaggeration of height)
- I am so hungry I could eat a horse. (Exaggeration of hunger)
- She cried an ocean of tears. (Exaggeration of crying)
- This bag weighs a ton! (Exaggeration of weight)
5. Understatement
An understatement makes something seem less important than it is.
Usage Examples of Understatement
- It’s just a scratch. (Minimizing a serious wound)
- The storm was a little windy. (Minimizing a severe storm)
- He’s not bad at basketball. (Downplaying great skill)
- Losing my job was a bit unfortunate. (Minimizing a big loss)
- The earthquake caused some movement. (Downplaying a disaster)
6. Metonymy
Metonymy replaces the name of a thing with something closely associated with it.
Usage Examples of Metonymy
- The White House issued a statement. (White House = U.S. government)
- Hollywood is obsessed with superhero movies. (Hollywood = film industry)
- The crown will pass to the prince. (Crown = monarchy)
- The pen is mightier than the sword. (Pen = words, Sword = force)
- Wall Street reacted negatively. (Wall Street = financial sector)
7. Synecdoche
Synecdoche uses a part of something to represent the whole or vice versa.
Usage Examples of Synecdoche
- All hands on deck. (Hands = workers)
- He bought a new set of wheels. (Wheels = car)
- The world watched in shock. (World = people)
- She won gold at the Olympics. (Gold = gold medal)
- We need more boots on the ground. (Boots = soldiers)
8. Irony
Irony is a contrast between expectation and reality.
Usage Examples of Irony
- A fire station burned down. (Unexpected situation)
- A traffic cop gets a speeding ticket. (Contradiction of roles)
- A pilot is afraid of heights. (Contradiction of expectations)
- Posting online about hating social media. (Contradiction in action)
- A marriage counselor gets divorced. (Contradiction of profession)
9. Sarcasm
Sarcasm is a form of verbal irony used to mock or insult.
Usage Examples of Sarcasm
- Oh great, another meeting! (Unenthusiastic about a meeting)
- Nice job breaking that! (Mocking someone for breaking something)
- Wow, you’re so helpful! (Sarcastic when someone is not helping)
- I love waiting in long lines. (Said when frustrated)
- Oh sure, because that was totally my fault! (Mocking blame)
10. Alliteration
Alliteration is the repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words.
Usage Examples of Alliteration
- Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers. (Repeating ‘p’ sound)
- She sells seashells by the seashore. (Repeating ‘s’ sound)
- Big brown bears bounce boldly. (Repeating ‘b’ sound)
- Lazy lizards lying low. (Repeating ‘l’ sound)
- Daring dogs dive deep. (Repeating ‘d’ sound)
11. Assonance
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds in words close together.
Usage Examples of Assonance
- The rain in Spain stays mainly on the plain. (Repeating ‘ai’ sound)
- Fleet feet sweep by sleeping geese. (Repeating ‘ee’ sound)
- The moon rose over the open road. (Repeating ‘o’ sound)
- Go slow over the road. (Repeating ‘o’ sound)
- Try to light the fire. (Repeating ‘i’ sound)
12. Consonance
Consonance is the repetition of consonant sounds within or at the end of words in close proximity.
Usage Examples of Consonance
- Mike likes his new bike. (Repeating ‘k’ sound)
- The black duck quacked back. (Repeating ‘ck’ sound)
- Pitter-patter, pitter-patter. (Repeating ‘t’ and ‘r’ sounds)
- Strong strings stretch silently. (Repeating ‘str’ sound)
- All mammals named Sam are clammy. (Repeating ‘m’ sound)
13. Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a type of figurative language where a word imitates a sound.
Usage Examples of Onomatopoeia
- The bees buzzed in the garden. (“Buzzed” mimics bee sounds)
- The door creaked open. (“Creaked” imitates the sound of a door opening)
- The car honked loudly. (“Honked” imitates a car horn)
- The bacon sizzled in the pan. (“Sizzled” mimics frying sounds)
- The clock went tick-tock. (“Tick-tock” mimics clock sounds)
14. Anaphora
Anaphora is the repetition of the same word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses or sentences.
Usage Examples of Anaphora
- “I have a dream” speech by Martin Luther King Jr. (Repeated phrase “I have a dream”)
- Every day, every night, in every way, I am getting better. (Repeats “every”)
- We will fight for justice. We will fight for freedom. We will fight for peace. (Repeats “We will fight”)
- It was the best of times, it was the worst of times. (Repeats “It was the”)
- I will not stop. I will not quit. I will not fail. (Repeats “I will not”)
15. Epistrophe
Epistrophe is the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences.
Usage Examples of Epistrophe
- See no evil, hear no evil, speak no evil. (Repeats “no evil”)
- Government of the people, by the people, for the people. (Repeats “the people”)
- When I was a child, I spoke as a child, I understood as a child. (Repeats “as a child”)
- Keep moving forward. Just keep moving forward. Always keep moving forward. (Repeats “keep moving forward”)
- I want pizza, she wants pizza, we all want pizza! (Repeats “want pizza”)
16. Euphemism
A euphemism is a polite or mild word/phrase used to replace a harsh or direct one.
Usage Examples of Euphemism
- Passed away (Instead of “died”)
- Let go (Instead of “fired”)
- Senior citizen (Instead of “old person”)
- Economically disadvantaged (Instead of “poor”)
- Correctional facility (Instead of “prison”)
17. Oxymoron
An oxymoron is a figure of speech that combines two contradictory terms.
Usage Examples of Oxymoron
- Deafening silence (Silence that is overwhelmingly loud)
- Bittersweet (Something that is both bitter and sweet)
- Jumbo shrimp (A shrimp that is “jumbo” or large)
- Act naturally (Telling someone to “act” while being “natural”)
- Living dead (Refers to zombies or something between life and death)
18. Paradox
A paradox is a statement that seems contradictory but actually reveals a truth.
Usage Examples of Paradox
- Less is more. (Sometimes simplicity is better)
- The only constant is change. (Change is always happening)
- I am nobody. (A contradiction, but suggests humility)
- The more you learn, the less you know. (Learning reveals how much more there is to know)
- To win peace, we must prepare for war. (Contradictory, but historically true)
19. Pun
A pun is a play on words that exploits multiple meanings or similar sounds.
Usage Examples of Pun
- I used to be a baker, but I couldn’t make enough dough. (“Dough” = money and bread dough)
- Time flies like an arrow; fruit flies like a banana. (Play on “flies” as an insect and movement)
- I wanted to be a doctor, but I didn’t have the patience (patients). (Play on “patience” vs. “patients”)
- I’m reading a book about anti-gravity. It’s impossible to put down! (“Put down” refers to both the book and gravity)
- The math book was sad because it had too many problems. (“Problems” = math exercises and real-life issues)
20. Allusion
An allusion is a reference to a well-known person, event, story, or work of art.
Usage Examples of Allusion
- He’s a real Romeo with the ladies. (Alludes to Shakespeare’s Romeo)
- She opened Pandora’s box. (Alludes to Greek mythology)
- His Achilles’ heel is chocolate. (Alludes to Achilles from Greek mythology)
- I felt like I had a golden ticket. (Alludes to Charlie and the Chocolate Factory by Roald Dahl)
- She’s the Einstein of our class. (Alludes to Albert Einstein as a symbol of intelligence)





Leave a Reply