What are Grasslands Ecosystem?-Definition, Types, And Human Impact
The ecosystem with grassy lands and with annual rainfall from 250 to 750 mm (10-30 inches) is called the grassland ecosystem. Location in Pakistan: The grasslands ecosystem are found in Gilgit, Kashmir, Waziristan, and lower.
What are Grasslands Ecosystem?
Large grasslands are present in the center of the Eurasian continents. Grasslands cover over 40% of Earth’s land surface. They provide vital ecosystem services such as carbon storage, water filtration, soil formation, and erosion control. Grasslands also support wildlife habitat, food production, and cultural heritage.
Types Of Grasslands
There are two types of grasslands:
(a) Prairies (Pampas): The grassland without woody trees is called prairies. These grasslands are preset in temperate climates. For example Pralines of North America, the Pampas of Argentina.
(b) Savanna: The grassland with scattered woody trees is called the savanna. These are the grassland of tropic climates They have woody trees. So these grasslands are called Savanna.
Rainfall in Grassland Ecosystem:
Annual rainfall is 250 to 750 mm (10-30 inches) This rainfall is midway between a forest and a desert Grassland faces severe droughts Grasslands have a continuous cover of grass. Trees are present only along the rivers Water and fire play important role in the competition between grasses and trees
Layering:
Layering is the characteristic feature of the grassland.
(a) First layer: It has tall grasses (Andropogon, Panicum)
(b) Med layer: It is composed of mid-high grasses (Stipa, Sporobolus, and Oryzopsis).
(c) Third layer: The third layer is formed by short grasses, forbs, and warfare species (Poa Bromus). This layer also has some mosses and lichens.
Plant Life In Grasslands:
Dominant species are graminoids i.e grasses, and grasses-like plants. Certain forbs like composites, legumes, and many other herbaceous plant species are also associated with grasses.
Soil Conditions In Grasslands:
Grasslands have low precipitation (raining) Soil has a high evaporation rate so the soil moisture is limited. The upper soil layer is kept moist. But deeper layers are dry. The soil of grassland is impermeable. It has excessive salinity.
Animal life in Grassland:
Dominant species in grassland are herbivores. Invertebrates like insects are very numerous Grasshoppers are also numerous. So grasshoppers compete with other herbivores for plant foliage. Predators are reptiles, amphibians, and mammals like lizards, toads, and turtles. They prey on insects. Foxes and wolves are very common.
Decomposers: The most common decomposers are actinomycetes bacteria, and fungi like molds, yeasts, mushrooms, and bracket fungi. Large animals like zebras, wild horses, and bison are important.
Productivity of Grassland:
Different grasslands have different productivity rates:
(a) Temperate grassland: Their rate of primary production is about 700-1500 g/m annually.
(b) Sub-humid tropical grassland: Their productivity rate is more than 4000 g/m.
(c) Annual grassland: Large grazing animals consume a small amount of (5-10%) of the total herbage. Invertebrates, rodents, and birds consume equal amounts or a little more
Human Impact on Grassland Ecosystem:
The natural grasslands in the world are used for crop production and livestock management. There is an acidic condition, soil erosion, and salinity in these grasslands. So only a small fraction of the world’s grassland is under cultivation. Grazing has great effects on grassland, Over-grazing causes a reduction in herbage cover. It results in soil erosion. There is overgrazing in many grasslands. Therefore, many grasslands are converted into deserts by a process called desertification.

 written by
written by 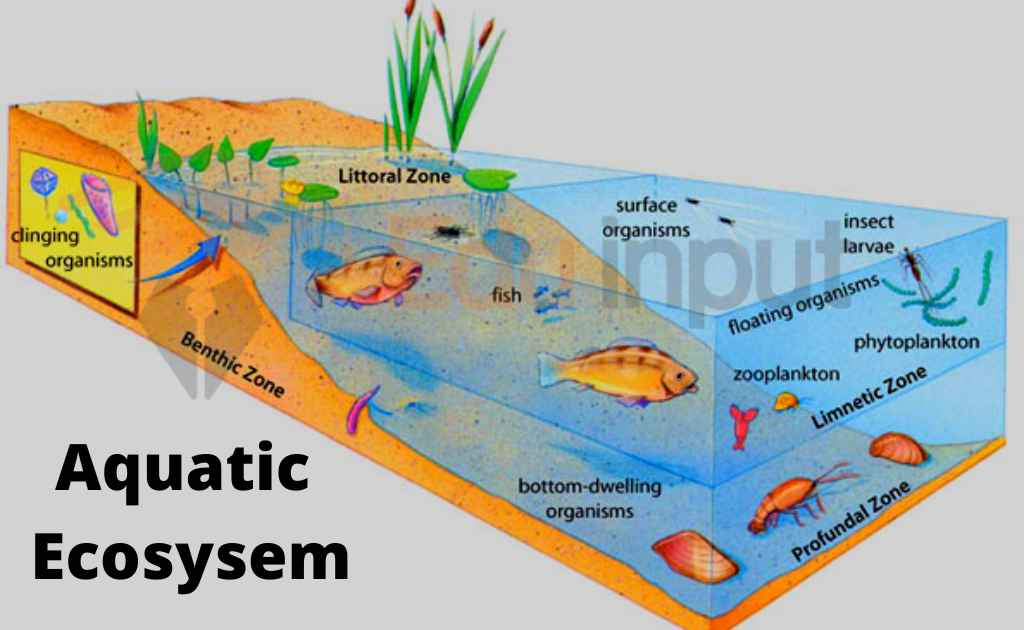




Leave a Reply