Mammalia-Characteristics and Classification of Mammals
Mammals are a unique class of animals characterized by several distinct features. First and foremost, all mammals have mammary glands which they use to feed their young.
In addition, all mammals are warm-blooded and have fur or hair covering their bodies. Finally, most mammals have teeth (except the toothless anteater). Humans, dogs, whales, elephants, and horses are all examples of mammals.
Mammals belong to:
• Kingdom: Animalia
• Phylum: Chordata
• Subphylum: Vertebrata
• Class: Mammalia
Characteristics of Mammals:
Mammals have the following characteristics that distinguish them from other animals.
- They have a more complex brain than other animals.
- The mammals have hair or fur on their body.
- They possess Sweat glands.
- Glands specialized to produce milk, known as mammary glands are present in mammals (female).
- There are three middle ear bones in mammals.
- They have a more complex brain than other animals.
- They have Specialized teeth.
- Their heart comprises four chambers.
- They have a more complex brain than other animals.
Also read about Gustation in Mammals
Species Of Mammals
It is estimated that there are more than 5,500 living mammal species. Mammals are incredibly diverse and can be found in every major habitat.
There are many different types of body shapes in the animal kingdom, but the quadruped is the most common. Most mammals use all four of their limbs to move around on land, but some animals have extremities that are better suited for living in water, flying, or tree-dwelling. Some creatures even spend their lives underground or on two legs instead of four.
Habitat of Mammals
Mammals live in all sorts of environments including the ocean, underground, and on land. Some mammals, bats, for example, can even fly.
Terrestrial Mammals:
Terrestrial animals are animals that inhabit the land. Mammals are warm-blooded, breathe air, have hair at some point in their lives, give birth to live young (as opposed to laying eggs), and nourish their young by secreting milk.
Marine Mammals
There are 128 known species of marine mammals, including whales, sirenians, pinnipeds, marine otters, sea otters, and polar bears. These animals live in or near the ocean, and play an important role in the ecosystem.
Divisions Of Mammals
Mammals are sometimes divided into three divisions based on how they give birth and take care of their young.
• Monotremes Mammals
• Marsupial Mammals
• Placental Mammals
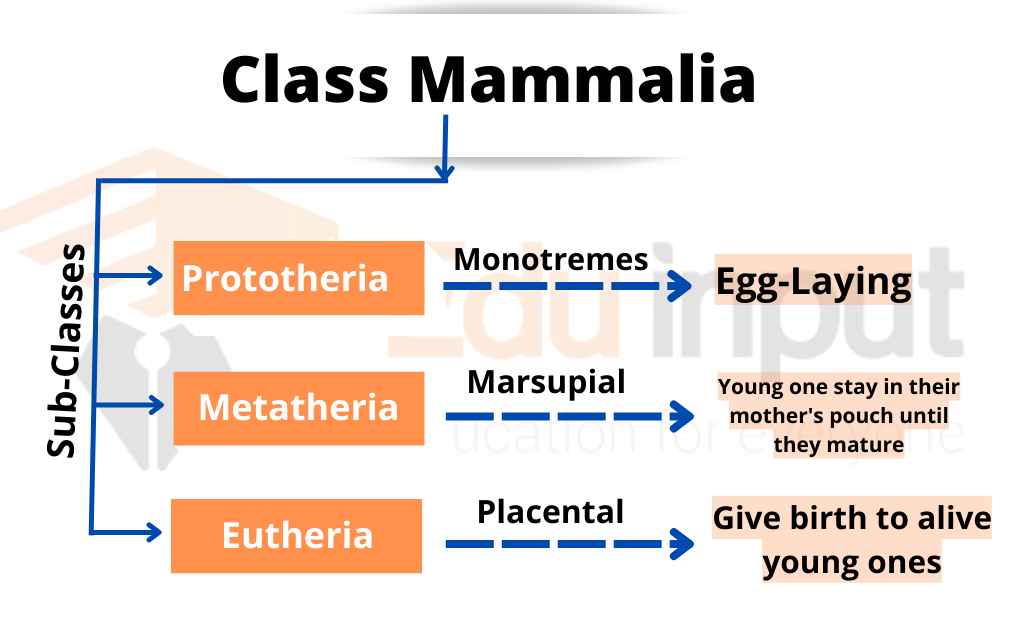
Subclasses Of Mammalia
Class Mammalia is divided into three subclasses:
Prototheria
They are Also known as Monotremes, the sub-class Prototheria consists of egg-laying mammals.
Metatheria
They are also known as Marsupial Mammals. The young mammals in this subclass are born immature. They stay in their mother’s pouch until they mature.
Eutheria
Mammals under this subclass give birth to live young ones. The young ones are developed inside the mother and derive nutrition through the placenta from the mother they are also known as Placental Mammals.
Sources of Nutrition in Mammals
Meat-eating mammals are called carnivores, which can include animals like lions, tigers, and seals. The largest mammal carnivore is the polar bear.
Herbivores are mammals that only eat plants, and some examples are cows, elephants, and giraffes. Lastly, there are omnivores which are mammals that eat both meat and plants. Humans fall into this category.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply