What are Lymphocytes? – T cells, B cells, and Natural Killing Cells
Lymphocytes are white blood cells that play a vital role in our immune system. They are also involved in fighting infections and repairing damaged tissue. Lymphocytes are part of the body’s defense against infection and disease.
They are found throughout the lymphatic system, which consists of two main parts, the lymph nodes, and the bloodstream. The lymph nodes filter out bacteria and other foreign material from the bloodstream.
Production of Lymphocytes
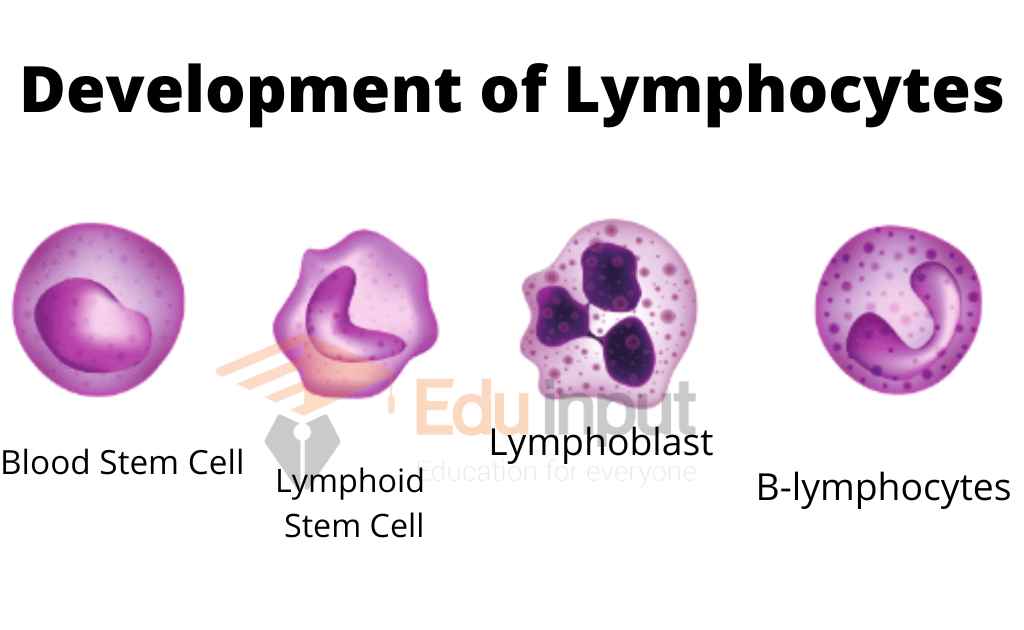
Lymphocytes protect the body against foreign substances. They are made in the bone marrow but can be found in the blood and lymph tissue. The immune system is a complex network of cells, which includes lymphocytes. These cells work together to defend the body against foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells.
Firstly they are made in bone marrow, and then they are migrated to the parts of the lymphatic system.
Role Of Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system plays an important role in the transportation and storage of lymphocyte cells within the body. Lymph vessels help to transport lymphocytes throughout the body and also help to filter out any dead cells or invading organisms, such as bacteria.
Lymphatic cells have surface receptors that help them to identify foreign substances. These receptors are very particular – each one can only match one very specific antigen.
The lymphocyte cells travel through your body until they find an antigen of the right size and shape to match their specific receptors. It might seem limited that the receptors of each lymphocyte cell can only be my specific type of antigen, but the body makes up for this by many different lymphocyte cells that the immune system can nearly all invaders.
Types Of Lymphocytes
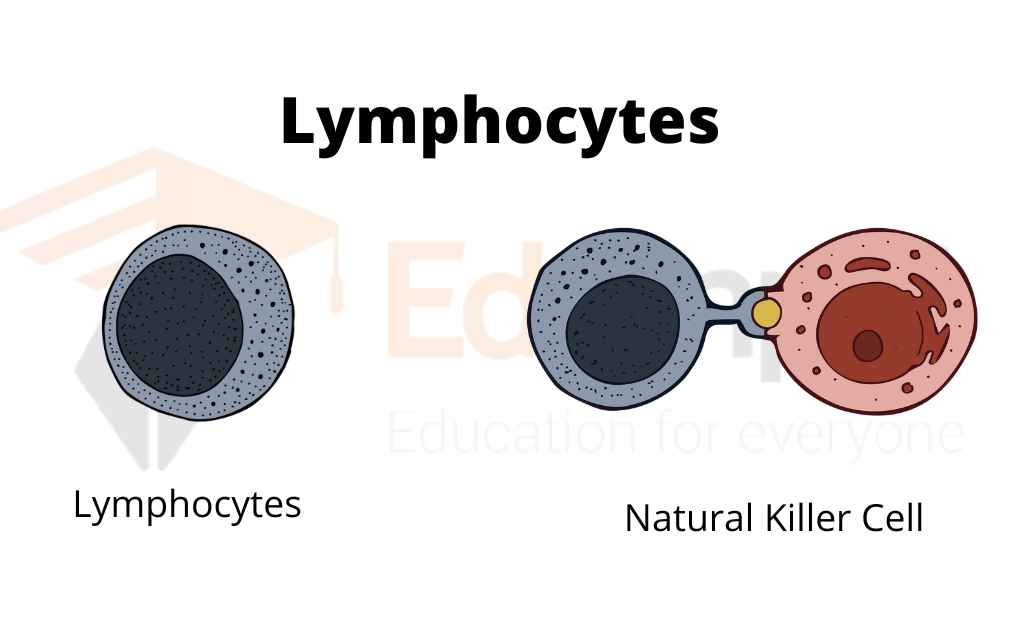
Lymphocytes come in three different kinds;
- B Lymphocytes (B Cells)
- T Lymphocytes (T Cells)
- Natural Killer Or NK
Both the B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes originate from stem cells in the bone marrow. T cells travel to the thymus, where they mature, while B cells remain in the bone marrow and mature there.
Function of B Cells:
B lymphocytes (B cells) function to make immunoglobins (antibodies). They are proteins in nature and are being produced by the immune system to fight foreign substances known as antigens.
Each B cell makes one specific antibody. Each antibody matches an antigen for destruction. The process of matching is similar to how a key fits into a lock.
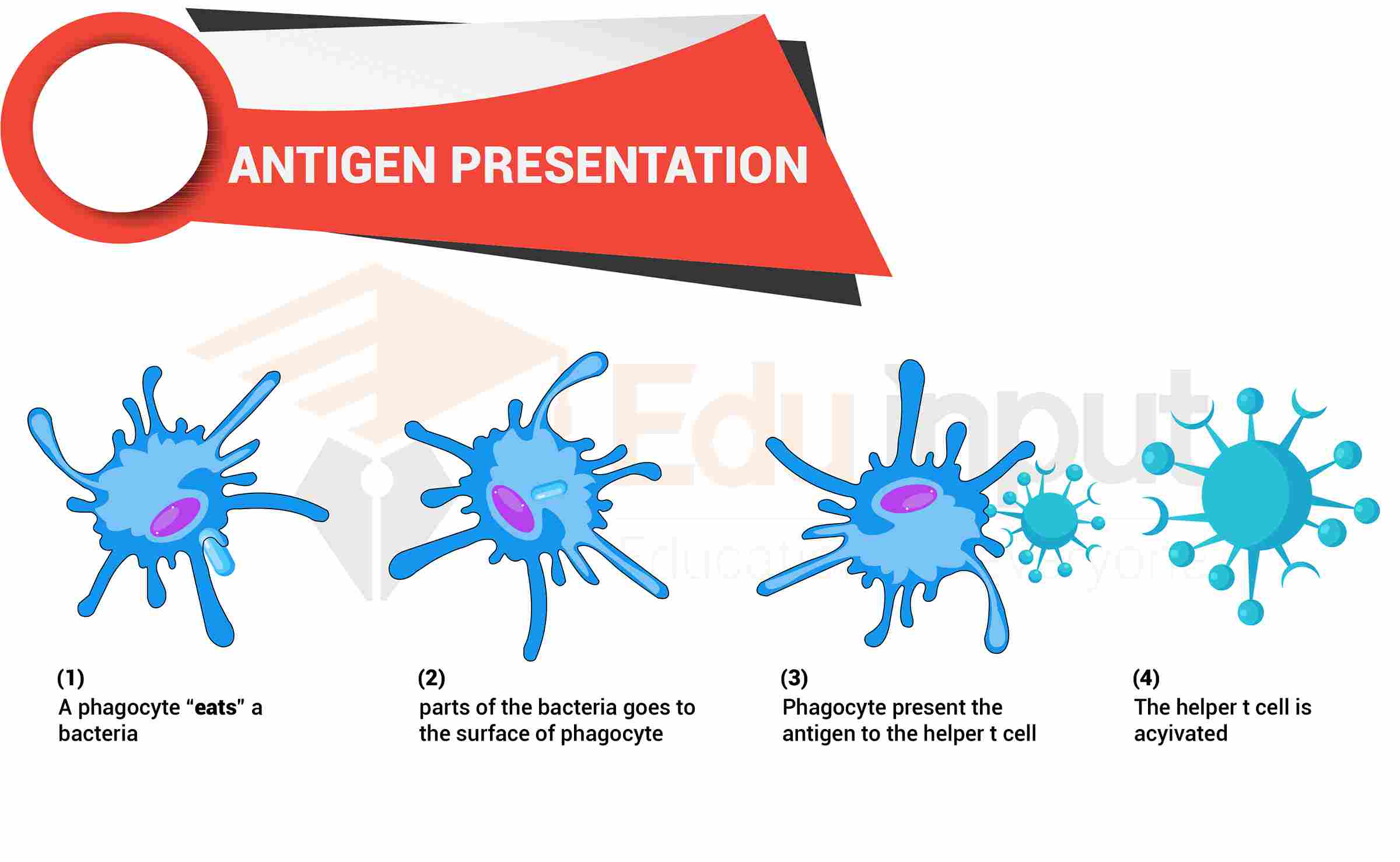
Function of T Cells:
The job of T cells is to help the body fight off infection and disease. They do this by attacking and destroying cells in the body that have been taken over by viruses or become cancerous.
Function of NK Cells:
The third type of lymphocyte, known as a natural killer or NK cell, comes from the same place as B and T cells. NK cells respond quickly to several foreign substances and are specialized in killing cancer cells and virus-infected cells.

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply