What is Binary Fission?-Definition, Types and Mechanism
The term binary fission refers to the division of cells, which occurs when a single-celled organism divides into two identical daughter cells. In order to divide, the cell must first undergo a process known as cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis is the separation of the cytoplasm between the mother cell and the newly formed daughter cell. Once the cell membrane has been broken down, the contents of the cell (cytoplasm) are divided equally between the two daughter cells.
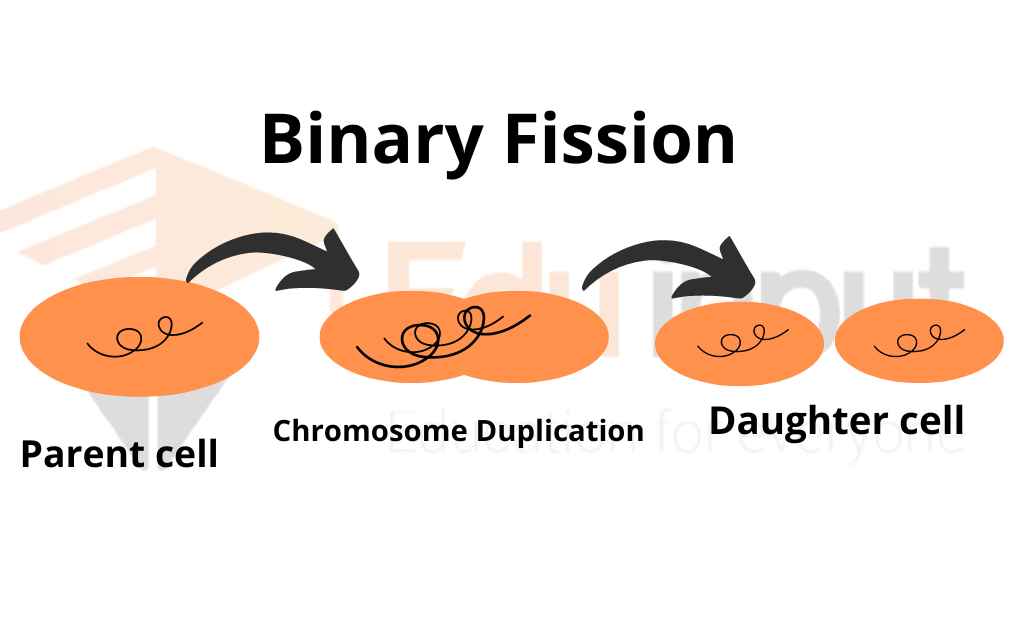
Binary fission is a way for an organism to reproduce asexually by dividing into two new bodies. In binary fission, the organism first duplicates its genetic material, or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Then, the organism divides into two parts (cytokinesis), with each new organism receiving one copy of DNA.
Why is it called binary fission?
It Is called Binary fission because the organism splits into two during reproduction. This process is the simplest and most common method of asexual reproduction.
Amoeba is a single-celled organism that, similar to bacteria, creates new cells through binary fission.
Difference Between Binary Fission And Mitosis
During binary fission and mitosis, chromosomes are copied in order to create two new daughter cells. The main difference between the two processes is that binary fission occurs in prokaryotic cells while mitosis occurs in eukaryotic cells.
Types Of Binary Fission
There are four main types of binary fission:
- Simple
- longitudinal
- Oblique
- Transverse
Each type involves a different orientation of the cell during division, and results in different shapes and sizes of the resulting cells.
It’s similar to mitosis in eukaryotic cells, but there is no spindle apparatus formation. The single DNA molecule replicates and each copy attaches to the cell membrane. The cell divides and the original and replicated chromosomes go to opposite sides.
Process Of Binary Fission
- The bacterium uncoils, and then replicates its chromosome. This process essentially doubles the bacterium’s genetic content.
- After the chromosome is copied, the bacterium begins to grow in preparation for binary fissions. Cytoplasmic content also starts to increase. Another sign that binary fission is about to occur is that the two strands of DNA start to migrate to opposite poles of the cell.
- Elongation is a phase of the cell cycle in which the cell grows in length. A septum, or division wall, begins to form in the middle of the cell during elongation. The two chromosomes are also separated during elongation.
- The parent cell divides into two new daughter cells during this phase. A new cell wall is formed, and the cell splits at the center. The nuclear materials and necessary organelles are copied into each of the daughter cells.


 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply