What Is Biological Classification?-Basis And Units
Classification is the process of identifying organisms and classifying them into relevant groups. Its main goal is to establish a hierarchy of classifications based on the relationships between species and the similarity of their forms and structures.
Why Do We Need Classification?
There are several reasons why classification is important:
- There are more than half a million (5 lacks) known species of plants and over 1.5 million (15 lakh) known species of animals. Accordingly, there is a wide range of diverse morphologies. As a result, we require an organism classification system.
- There are other classification methods too, that is based on appearance. Consider the classification of flowering plants, for instance. It depends on the person’s color, height, or any other characteristic. Such a classification is useless. It doesn’t provide information on the traits that make up different people’s similarities and variations.
Basis of Classification
There are the following basis of classification:
1. Each organism has an evolutionary history that is linked to the other. Some organisms are more closely related than others. For instance, sparrows have more characters in common with pigeons than with insects. As a result, pigeons and sparrows are gathered in the same group.
2. The foundation of classification is the similarity of the form and structure of organisms. Classification is based on how people are related to one another. shape and structural resemblance are the bedrock of classification. The organisms have been divided into two categories by biologists based on their similarities.
3. The classification of organisms is also based on homology, comparative biochemistry, cytology (cell biology), and genetics.
4. Smaller groups, down to species, are formed from the big group. A species is a collection of reproductive natural populations that can freely breed with one another and produce fertile children.
Isolated several of these groupings in nature consist primarily of asexually reproducing creatures. Inbreeding species cannot, therefore, be used as a criterion for recognition. Each species has unique structural, ecological, and behavioral characteristics.
Therefore, a specie is a separate entity from an evolutionary unit. Genes across different species are not exchanged.
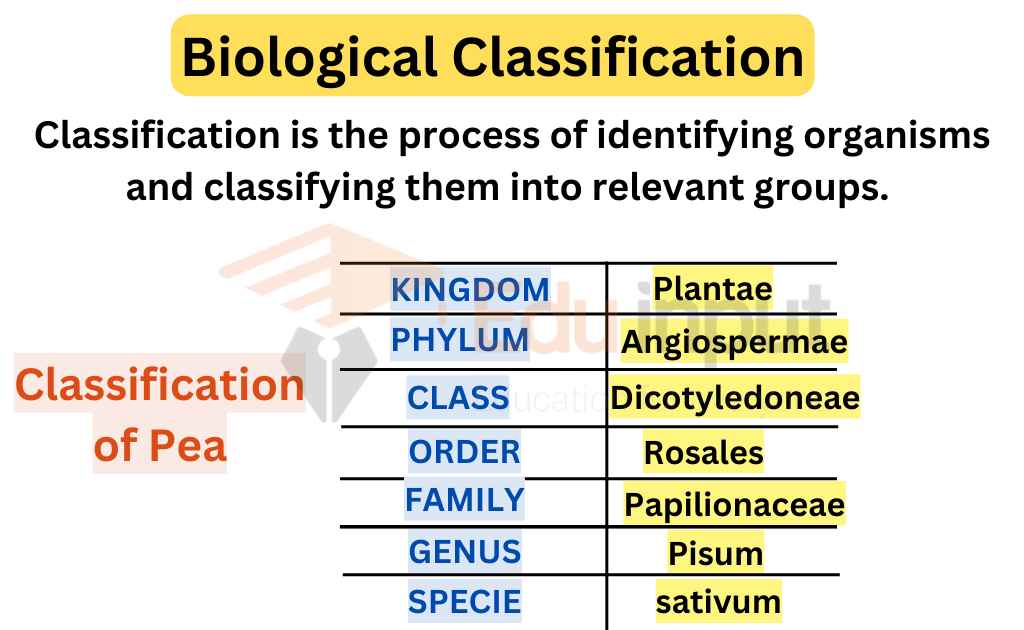
Units of Classification
There are the following units of classification:
- Kingdom: For long, living things are divided into kingdoms: plants and animals.
- Phylum (Division): Each kingdom is divided into smaller groups called phylum. Phylum is also called division in plants, algae, and fungi.
- Class: A phylum is divided into classes.
- Order: Class is divided into orders.
- Families: Order is divided into Families.
- Genera: Family contains related genera.
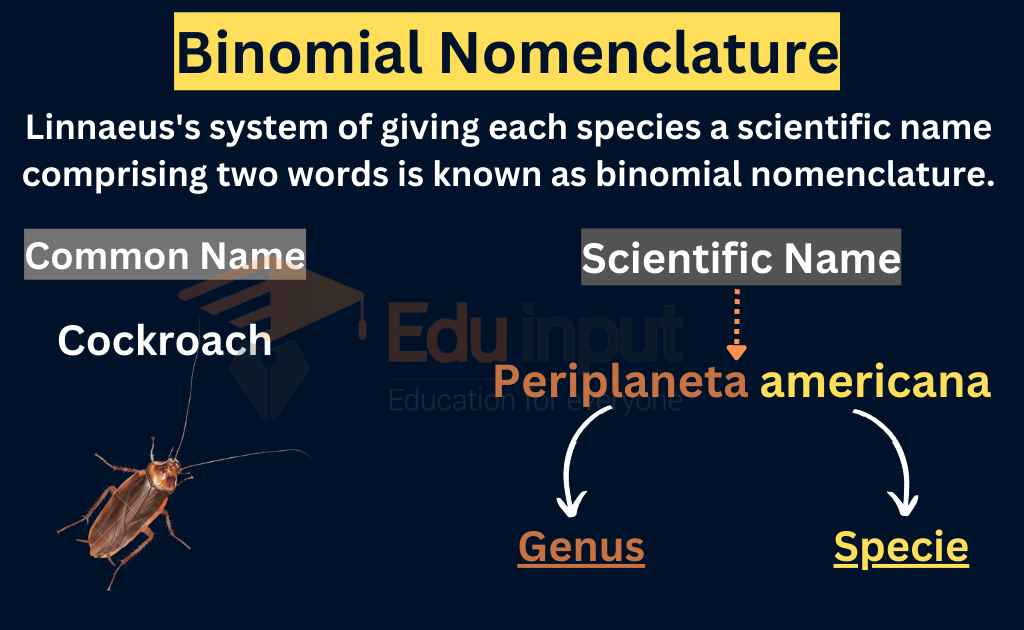
- Specie: A genus is composed of one or more species. Specie is the basic unit of classification.
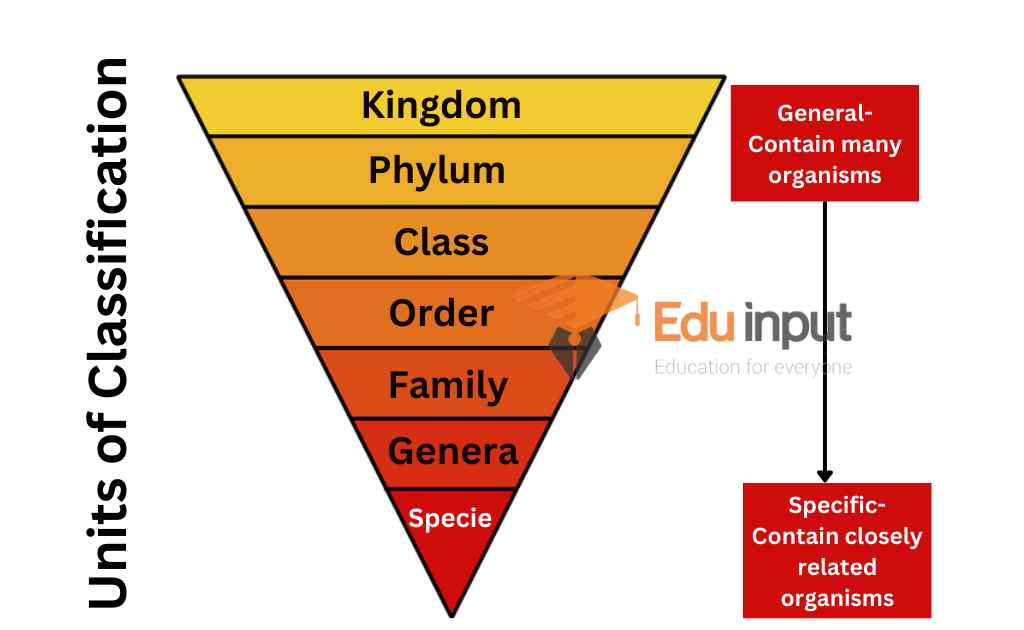
How Hierarchy Is Formed?
On the other hand, organisms are categorized into vast, different groups (taxa). In comparison to the taxonomy or category below it, every category is more general. It exhibits innovative qualities. A hierarchy is formed by taxonomic categories, from species to kingdoms. Compared to higher taxa, members of lower categories resemble one another more.
Latest Research In Field Of Biological Classification
- Scientists have made progress in understanding the diverse spectrum of breast cancer (BC) with the identification of specific molecular subclasses. The traditional pathological classification remains important, but single gene and multigene assays can guide systemic therapy decisions. Accurate diagnosis and morphological characterization are essential for all approaches to BC classification. [1]
- Scientists have classified extracellular vesicles (EVs), which carry various molecules and are used as biomarkers. They mediate intercellular communication between cancer cells and associated cells, leading to cellular transformation, immunosuppression, and resistance to therapy. This review covers the classification of EVs and their effects on hot tumors, immune cells, and nonimmune cells. [2]
- Scientists establish an approach for validating 16S rRNA metagenomic data. New metrics and a synthetic negative control method are proposed, and the importance of curated taxonomic annotations and read length is highlighted. [3]
What is meant by biological classification?
The process of biological classification involves organizing living organisms into a hierarchical system based on their similar and different characteristics. It helps to understand the relationships between different species and to study them more conveniently.
Who gave biological classification?
Carolus Linnaeus, the Swedish naturalist is known as the pioneer of biological classification. He published the 10th edition of his book Systema Naturae in 1758, which contains a list of scientific names for various organisms. That is considered the starting point for modern classification systems.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply