Genetic Code-Definition, Composition, and Characteristics
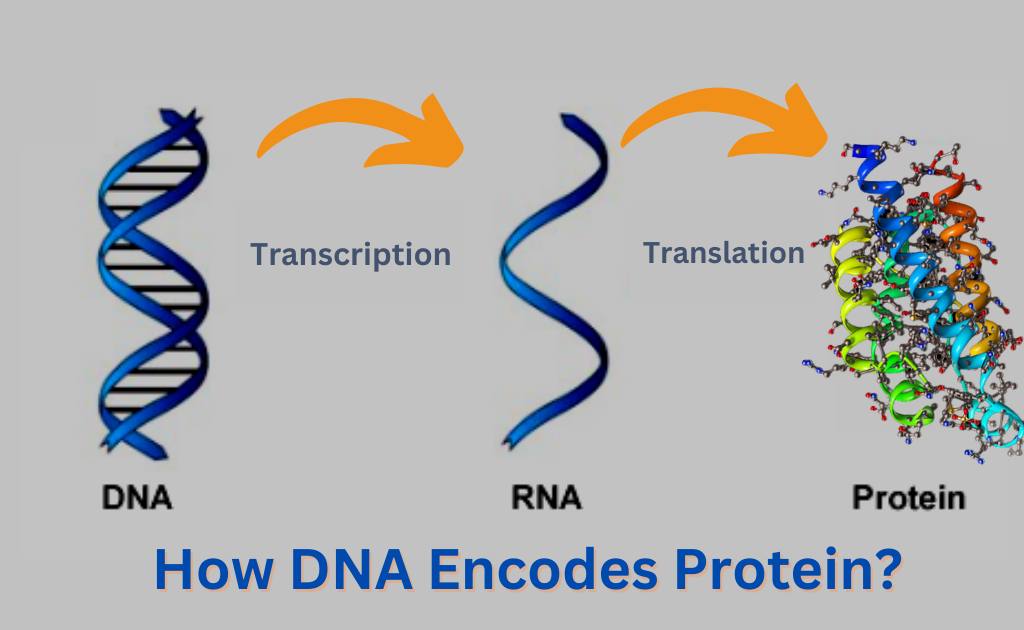
The sequence of nucleotides in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) is referred to as the genetic code. This code determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which play a vital role in the function of cells.
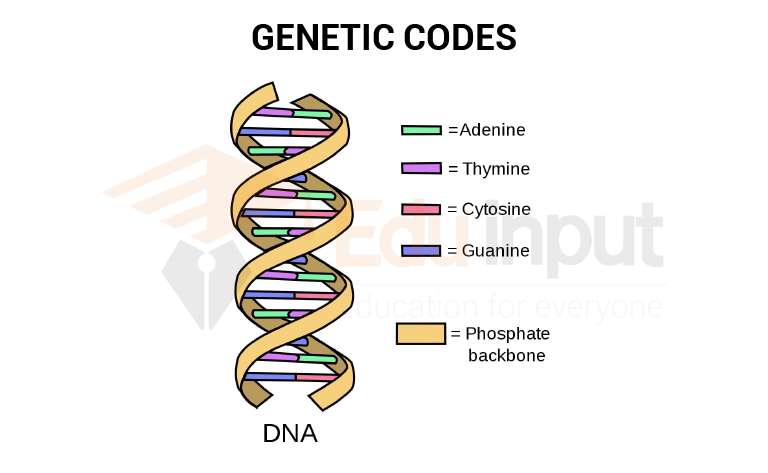
The genetic code or simply codons is defined as the three nucleotides in the triplet base sequence that act as code words for the amino acids in the molecule. The sequence of the amino acids is determined by the sequence of the A, G, C, and U nucleotide bases in the genetic code. There are four bases in the codons.
Purines
- Adenin
- Guanin
- Cytocin
Pyrimidines
- Thiamin
- Uracil (In RNA)
Composition and Function of Codon
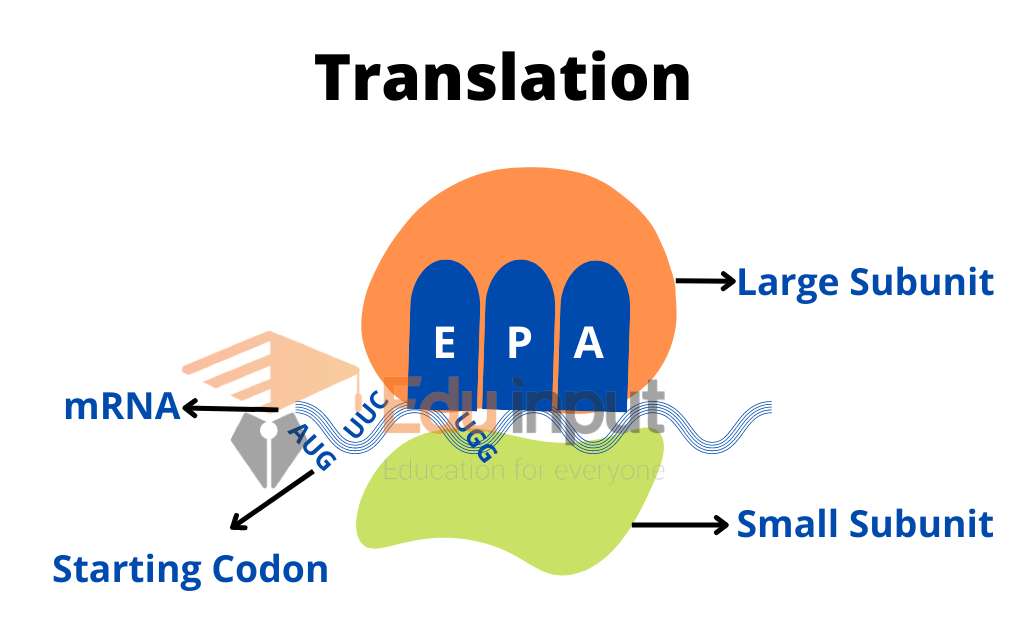
There are 64 different combinations of three base codons. The sequence of the codon is written from the beginning to the end. There are 61 codons that code for the 20 amino acids found in the human body. Three codons do not code for amino acids, which are UAA, UAG, and UGA do not code for amino acids.
They act as stop signals in the synthesis of the protein. Three codons are collectively known as nonsense codons. The codons UGA, UAG, and UAA are sometimes referred to as amber, ochre, and opal codons. Sometimes the chain starts with the codons AUG and sometimes.
Characteristics Of The Genetic Code
Universal, specific, nonoverlapping, and degenerate are some of the characteristics of the genetic code.
The universality of Genetic Code:
All living organisms use the same codons to code for their amino acids. During evolution, the genetic code has been maintained. Genetic code is considered universal because of that. There are, of course, a few exceptions.
The codon for methionine in the mitochondria is known as the start codon. The isoleucine codes are the same as the codon codes. The genetic code is universal, however, there are some exceptions.
Specificity OF Genetic Code:
The genetic code is highly specific because a particular codon always codes for the same acid. UGG is the codon for sleep (tryptophan).
Non-Overlapping Characteristics:
The genetic code can be read from a fixed point or a continuous base sequence. It’s non-overlapping, non-complimentary, and without any punctuations. For instance, UUUCUUAGAGGG will be read UUU/CUU/AGA/GGG.
It is possible to change the message sequence with the addition or deletion of one or two bases. There will be a different protein synthesis from such mRNA will be different. This is encountered when there is a change in the reading frame of the messenger RNA.
Degenerative Ability:
The majority of the amino acids have more than one codon. The codon is redundant since 61 codons can be used for only 20 acids. The four codons are for glycine. A synonym is the codons that designate the same amino acid.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply