How DNA Encodes Protein?
Some genes are involved in the synthesis of proteins and some are involved in the assembly of regulatory molecules. The journey from genes to proteins takes place inside the cells and is very intricate and tightly controlled.
How DNA Encodes Protein?
The two most important steps are transcription and translation. Gene expression is the combination of transcription and translation.
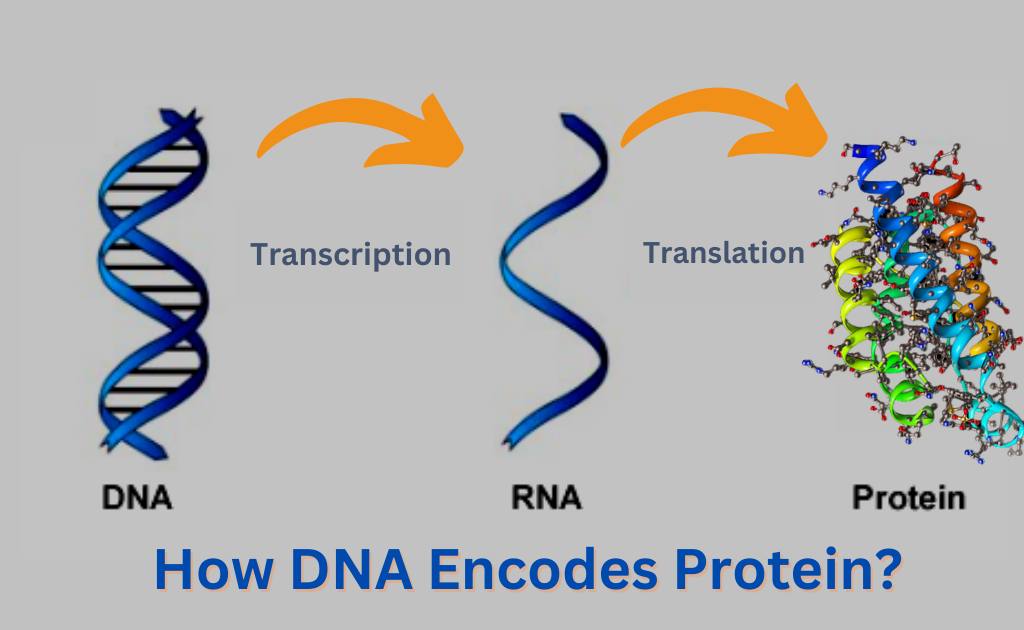
During the process of transcription, the information stored in a gene’s DNA is passed to RNA in the cell nucleus. RNA and DNA have the same components, but there’s one tiny difference between them, that is DNA has the base pair Thiamin, while RNA contains Uracil instead of Thiamine.
The type of RNA that carries the information for making proteins is called messenger RNA (mRNA). This information gets transported from the nucleus out into the cytoplasm.
This step involves the translation of the genetic information into the amino acids that constitute the protein. This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
The mRNA and its partner, the ribosome, interact to read the sequence of mRNA nucleotides. In the process of translation, the information in each codon is translated into an amino acid. It’s possible to translate information by reading from the codons. Protein synthesis continues until the ribosome encounters a stop codon.
Work of Frederick Sanger
A British biochemist, Frederick Sanger, described the complete sequence of amino acids that makes up insulin. It was an important achievement of Sanger. He showed for the first time that proteins are made of sequences of amino acids.
Enzymes and other proteins are made up of amino acids, which are strings of elements called atoms. They are arranged in a definite order.
Work of Vernon Ingram
Vernon Ingram 1956 discovered the molecular basis of sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia is a protein defect. It is inherited as a Mendelian disorder. Vernon analyzed the structure of normal and sickle cell hemoglobin.
He showed that sickle cell anemia is caused due to change of one amino acid at a single position in the protein. Glutamic acid is replaced by valine. There is a change in the alleles of the gene of hemoglobin at one point. It caused this change of amino acid.
Role Of The Gene In Amino Acid Sequences
The changes in protein structure caused sickle cell anemia and most other hereditary traits. Alteration in the sequence of amino acids of the proteins occurs. The order of nucleotides in a particular region of chromosomes controls this sequence of amino acids.
For example, sickle cell anemia is caused due to a mutation. This mutation replaces a single thymine with an adenine. It occurs at the position that codes for glutamic acid. Thus it changed the position to valine. The sequence of nucleotides that determines the amino acid sequence of a protein is called a gene.
Related FAQs
How does DNA encode information?
DNA encodes information by reading the base sequence, order, or position of the nucleotide along both strands.
What part of DNA encodes proteins?
Exon is the part of DNA (or RNA), that specifically codes for the protein.
Does all DNA encode proteins?
99% of the DNA is noncoding. Only 1% of the DNA contains the genes that codes for Proteins.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply