Gibberellin (GA) – Discovery, Structures, and Applications
Gibberellin are plant hormones that help control different growth processes, like how tall a plant’s stem is, when a plant germinates, goes into dormancy, flowers, and so on.
They’re also known to play a role in leaf and fruit aging. Gibberellins are some of the oldest known plant hormones around. People believe that part of the reason why crops got so much better yield during the “Green Revolution” of the 1960s was that farmers were unknowingly choosing crop strains that were lacking in Gibberellin synthesis.
Discovery of Gibberellin
Eiichi Kurosawa was a Japanese scientist who, in 1926, discovered that foolish seedling disease was caused by the Gibberella fungus. Later work at the University of Tokyo showed that this fungus produced a substance that triggered the symptoms of foolish seedling disease, which they named “Gibberellin.”
Distribution of Gibberellins in Plant:
Gibberellins are found in all parts of the higher plants including shoots, roots, leaves, flowers, petals anthers, and seeds. Gibberellin’s activity has also been observed in plastids. In general, reproductive parts contain much higher concentrations of Gibberellin than vegetative parts.
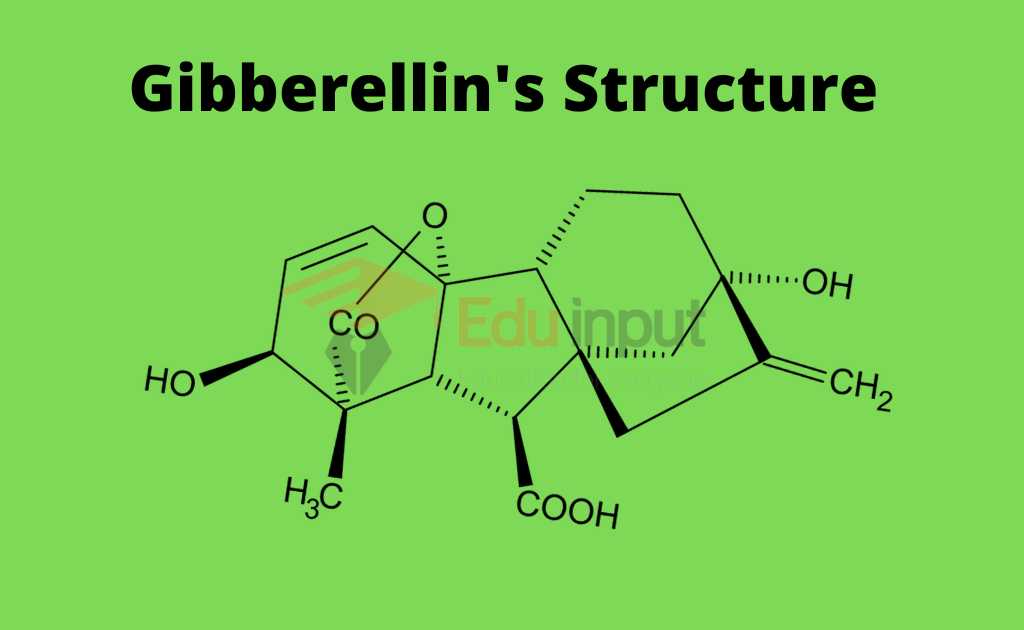
Structure of Gibberellins
Gibberellin is a type of molecule known as a diterpenoid. This class of molecules also includes vitamins A and vitamins E.
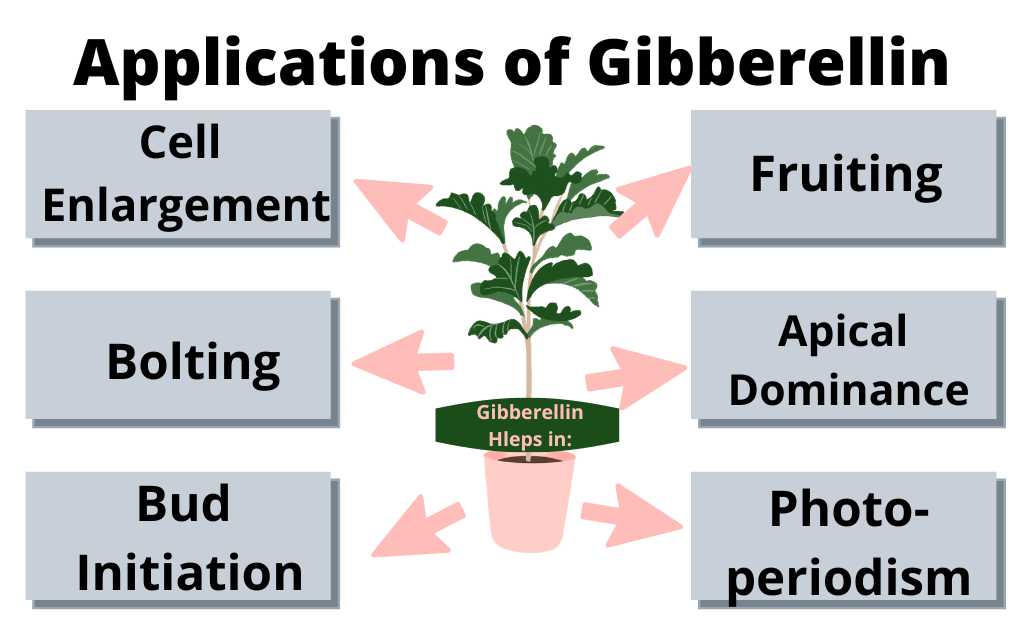
Applications of Gibberellins
Gibberellins are produced commercially from fungal culture. It performs the following functions in plants;
1. Cell Enlargement:
It enhances cell enlargement in the presence of Auxins. It also promotes Cell Division in apical Meristem and Cambium.
2. Bolting:
It promotes the bolting of some rosettes.
3. Bud Initiation:
It promotes bud initiation in shoots of chrysanthemum callus.
4. Fruiting:
It promotes leaf growth and fruit growth. It induces Parthenocarpy.
5. Apical Dominance:
It enhances the action of Auxins in apical dominance.
6. Dormancy:
It breaks bud and seed dormancy.
6. Photoperiodism:
Long-day plants need red light for flowering. Gibberellins can inhibit flowering in short-day plants.
8. Leaf Senescence:
It causes a delay in leaf senescence in a few species.
Commercial Applications Of Gibberellins
Some of their commercial applications are as under.
1. Fruiting: GA promotes fruit setting in tangerines and pears. It is used for growing seedless grapes, (Parthenocarpy). It also increases the berry size.
2. Brewing industry: GA, is used in the brewing industry It stimulates α -amylase enzyme production in barley. The α-amylase promotes malting.
3. Storage of bananas: It delays the ripening of bananas. So it improves the storage life of bananas and grapefruits.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply