Plant Hormones (Phytohormones) – Types and Functions
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel throughout the body and regulate many different processes. In the case of cannabis, hormones play a role in regulating the flowering time, bud formation, and even the size of the flower.
Plant hormones are also known as phytohormones or plant steroids. They control various processes such as cell division, differentiation, elongation, senescence, and death.
Types Of Hormones
There are three types of hormones.
- Steroidal Hormones
- Peptide Hormones
- Amine Hormones
Plant Hormones
Plants have the following hormones;
1. Cytokinins
Cytokinins are a class of naturally occurring compounds that act as plant hormones. These hormones are involved in stimulating cell division and differentiation. They are also responsible for promoting stem elongation and leaf expansion. Cytokinins are present in high concentrations in young seedlings and decrease over time.
Cytokinins are produced naturally by the plant and are present in small amounts. However, they can be supplemented externally using Cytokinin-rich extracts.
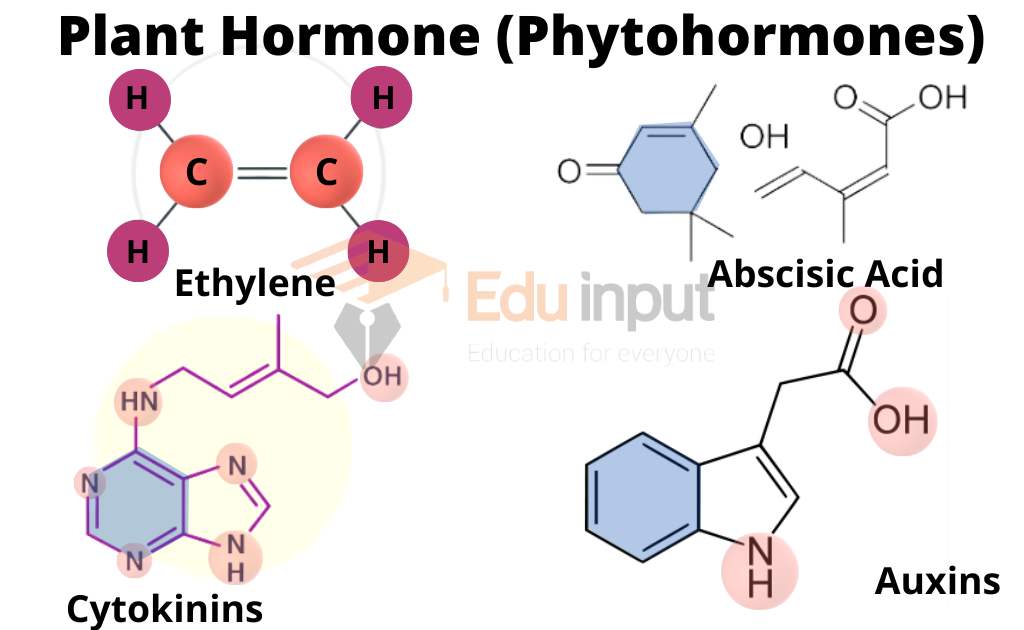
2. Ethylene
Ethylene is a multifunctional phytohormone that promotes fruit ripening, senescence, and abscission. It is also known to promote the production of cannabinoids. Ethylene is produced by plants in response to environmental stimuli.
3. Auxin
Auxin is a type of phytohormone that regulates plant growth and development. Auxin is necessary for root initiation and lateral branching. Auxin is also critical in the regulation of vascular tissue and the formation of flowers. Auxin Stimulates the formation of chloroplast in leaves.
Auxins are synthesized by the plant and are stored in the roots.
4. Abscisic Acid (ABA)
Abscisic acid is a hormone that helps control stomatal closure and prevents water loss. ABA increases during cold temperatures and decreases during warm temperatures.
It also controls the timing of germination and dormancy. Inhibit shoot growth, stimulate the storage of proteins in seeds, and so on.
ABA is also involved in responses to environmental stresses such as salt, cold, drought, and high temperature.
5. Gibberellins
Gibberellins are a group of hormones that stimulate the growth of stems and roots.
They are involved in pollen maturation, and the development of flowers, fruits, and seeds. They also increase the rate of flowering and fruiting.
Gibberellin levels peak at night and decline during the day. They facilitate cell elongation, and help the plants to grow taller.
6. Jasmonates
Jasmonates are a group of hormones associated with defense responses. They protect plant, gainst herbivore attack and pathogen infection; confer tolerance to abiotic stresses, including ozone, ultraviolet radiation, high temperatures, and freezing; and regulate various aspects of development.
They are also involved in the biosynthesis of terpenoids and flavonoids. Jasmonates are released by damaged cells and are thought to help prevent further damage.
7. Brassinosteroids
Brassinosteroids are steroidal hormones that promote cell elongation and stimulate the synthesis of storage compounds. They are also involved with the regulation of cell division and cell death.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply