Savanna Biome-Characteristics, Types, Location, Climate, and Examples
Definition of Savanna Biome
A savanna is a type of grassland biome characterized by scattered trees. Savannas are found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including Africa, South America, Australia, and India.
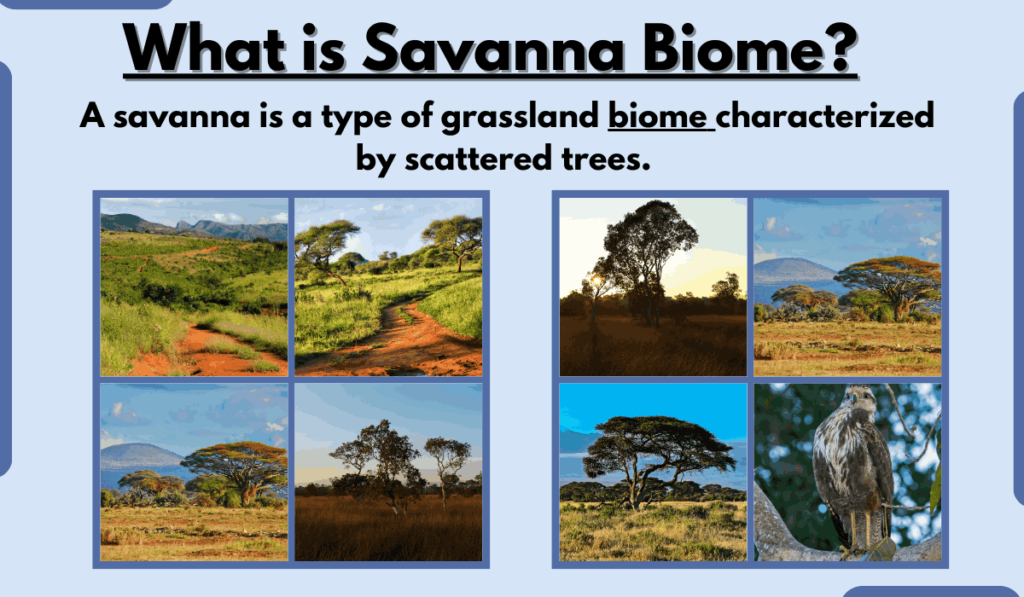
Characteristics of Savanna Biome
Here are Characteristics of Savanna:
- Savannas have a warm climate with a distinct wet and dry season. The wet season typically lasts from 6 to 8 months, while the dry season can last for 4 to 6 months. [source]
- The average annual rainfall in a savanna biome is between 50 and 150 centimeters.
- The temperature in a savanna biome can range from 20 to 30 degrees Celsius.
- The soil in a savanna biome is typically poor in nutrients and is prone to erosion.
- Savannas are home to a variety of plant and animal life.
Types of Savanna Biome
There are three main types of savanna:
1. Tropical savanna
This type of savanna is found in the tropics and is characterized by tall grasses and scattered trees. The trees in a tropical savanna are often deciduous, meaning they lose their leaves during the dry season.
2. Temperate savanna
This type of savanna is found in the temperate regions and is characterized by shorter grasses and more trees. The trees in a temperate savanna are often evergreen, meaning they keep their leaves year-round.
3. Woodland savanna
This type of savanna is a transition between a savanna and a forest. It has more trees than a typical savanna, but the trees are not as tall as the trees in a forest.
Savanna Biome Location
Savannas are found on all continents except Antarctica. The largest savannas are found in Africa, where they cover about 40% of the continent. Other major savanna regions include South America, Australia, and India.
Savanna Biome Climate
The climate of a savanna biome is characterized by a distinct wet and dry season. The wet season typically lasts from 6 to 8 months, while the dry season can last for 4 to 6 months. The average annual rainfall in savannas is between 50 and 150 centimeters.
Savanna Biome Temperature
The temperature in a savanna biome can range from 20 to 30 degrees Celsius. The hottest temperatures are typically found during the wet season, while the coolest temperatures are typically found during the dry season.
Savanna Biome Plants
The plant life in savannas is adapted to the warm climate and the alternating wet and dry seasons. The dominant plants in a savanna are grasses, but there are also a variety of trees, shrubs, and herbs.
- Grasses are the most common plants in a savanna biome. They are adapted to the dry conditions by having deep roots that can reach water far below the surface.
- Trees in a savanna are often scattered and have adapted to the dry conditions by having thick bark that can store water. Some trees in a savanna, such as the baobab tree, have a large, bulbous base that stores water.
- Shrubs are also common in a savanna biome. They are often thorny, which helps to protect them from animals.
- Herbs are small, non-woody plants that are found in all parts of a savanna biome.
Savanna Biome Animals
The animal life in a savanna biome is also adapted to the warm climate and the alternating wet and dry seasons. The savanna is home to a variety of large mammals, including elephants, lions, giraffes, zebras, and rhinoceroses.
- The savanna is home to a variety of large mammals, including elephants, lions, giraffes, zebras, and rhinoceroses. These animals are adapted to the open grasslands by being fast runners or having strong horns or tusks for defense.
- The savanna is also home to a variety of small mammals, including rodents, rabbits, and antelopes. These animals are adapted to the dry conditions by being nocturnal or by burrowing underground.
- The savanna is home to a variety of birds, including eagles, hawks, vultures, and ostriches. These birds are adapted to the open grasslands by being good at flying or by having long legs for running.
- The savanna is also home to a variety of reptiles, including snakes, lizards, and crocodiles. These reptiles are adapted to the dry conditions by being able to go without water for long periods of time.
Facts about Savanna Biome
Here are some facts about the savanna biome:
- The word “savanna” comes from the Portuguese word “savana”, which means “treeless plain”.
- The savanna biome is the second largest biome on Earth, after the tropical rainforest.
- The savanna is home to about 10% of the world’s plant and animal species.
- The savanna is a major source of food and water for humans.
- The savanna is also a major source of timber and other natural resources.
- The savanna is facing a number of threats, including deforestation, climate change, and overgrazing.
Also learn about:

 written by
written by 
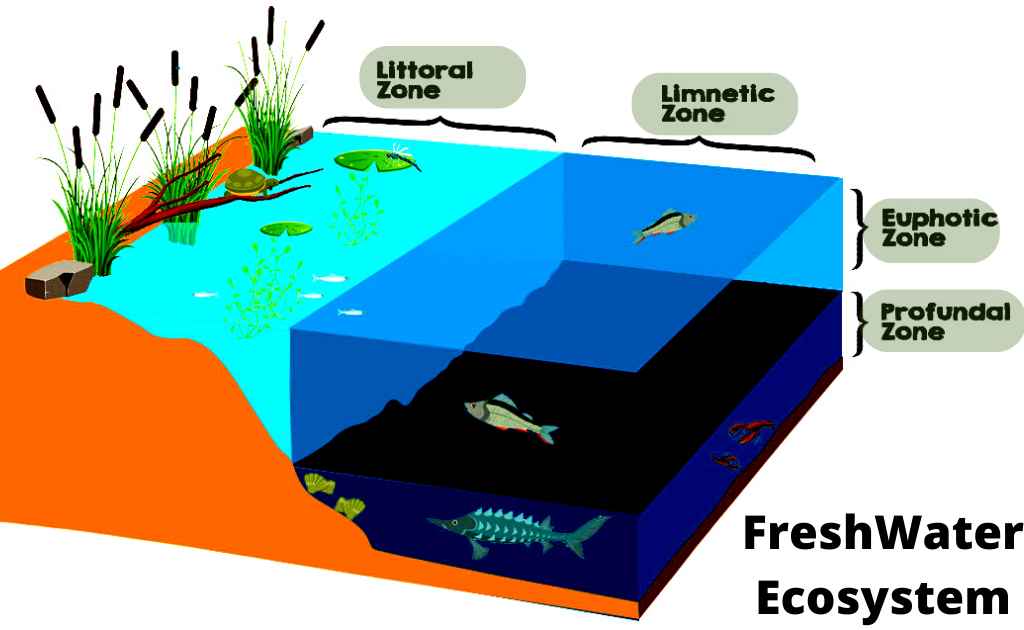



Leave a Reply