Taiga Biome-Characteristics, Location, Climate, Temperature, and Examples
The taiga is a biome characterized by coniferous forests that are found in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the largest terrestrial biome in the world, covering about 17% of the Earth’s land surface. The taiga is also known as the boreal forest or the northern coniferous forest.
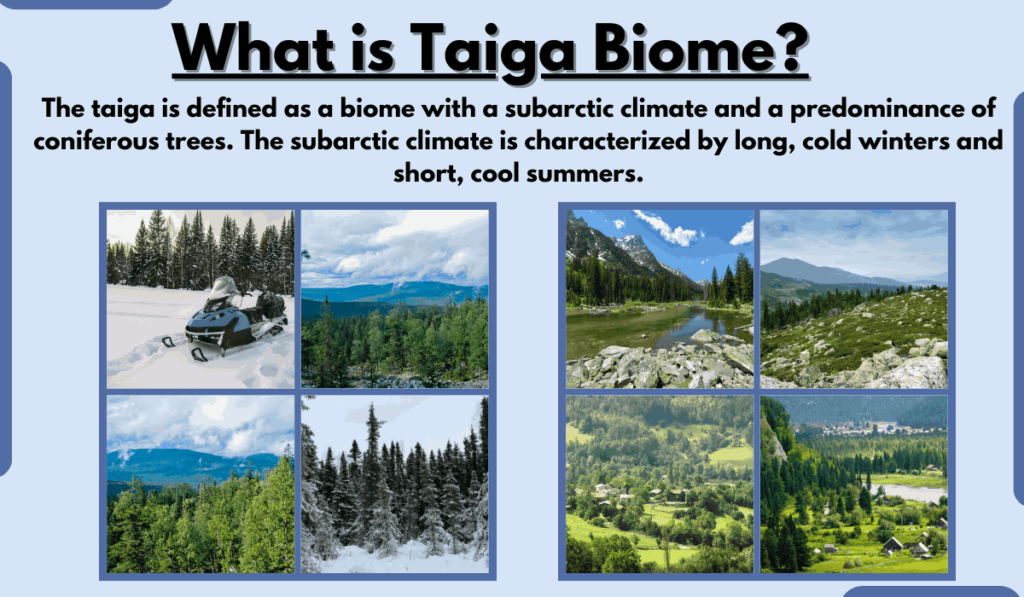
Taiga Biome Definition
The taiga is defined as a biome with a subarctic climate and a predominance of coniferous trees. The subarctic climate is characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers.
The average temperature in the taiga ranges from -50 degrees Celsius (-58 degrees Fahrenheit) in winter to 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit) in summer. [source]
Taiga Biome Characteristics
The taiga is characterized by the following:
1. Coniferous trees
The taiga is dominated by coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, fir, and larch. These trees have needles instead of leaves, which helps them to conserve water during the long, dry winters.
2. Cold climate
The taiga has a cold climate with long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The average temperature in the taiga ranges from -50 degrees Celsius (-58 degrees Fahrenheit) in winter to 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit) in summer.
3. Low precipitation
The taiga receives low precipitation, typically less than 500 millimeters (20 inches) per year. The precipitation is evenly distributed throughout the year, with no distinct wet or dry seasons.
4. Thin soil
The soil in the taiga is thin and acidic. This is due to the slow decomposition of coniferous needles, which are high in acids.
5. Wildlife
The taiga is home to a variety of wildlife, including moose, bears, wolves, foxes, and many species of birds.
Taiga Biome Location
The taiga is located in the Northern Hemisphere, between the tundra to the north and the temperate forests to the south. The taiga can be found in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Taiga Biome Climate
The climate of the taiga is subarctic. This means that the winters are long and cold, and the summers are short and cool. The average temperature in the taiga ranges from -50 degrees Celsius (-58 degrees Fahrenheit) in winter to 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit) in summer.
Taiga Biome Temperature
The temperature in the taiga varies greatly depending on the season. The winters are long and cold, with average temperatures below freezing. The summers are short and cool, with average temperatures around 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit).
Taiga Biome Animals
- Boreal wolves are found throughout the taiga. They hunt in packs and prey on moose, caribou, and other large animals.
- American black bears are found in North America. They are omnivorous and eat a variety of foods, including berries, fish, and small mammals.
- Lynx cats are found in North America and Eurasia. They are solitary hunters and prey on snowshoe hares and other small animals.
- There are many different species of squirrels found in the taiga, including red squirrels, flying squirrels, and chipmunks. They are important seed dispersers and help to keep the forest healthy.
- There are several species of deer found in the taiga, including moose, elk, and reindeer. They are important prey animals for many predators.
Taiga Biome Plants
The taiga is also home to a variety of plants, including:
- Spruce trees are the most common trees in the taiga. They have needle-like leaves that help them to conserve water during the long, cold winters.
- Fir trees are also common in the taiga. They have flat needles that help them to reflect sunlight and stay cool during the hot summer months.
- Larch trees are deciduous, meaning they lose their leaves in the fall. This allows them to conserve water during the winter.
- Mosses are common on the forest floor of the taiga. They help to hold the soil in place and provide food and shelter for small animals.
- There are many wildflowers that bloom in the taiga during the short summer months. These flowers attract pollinators, such as bees and butterflies.
Facts about Taiga Biome
Here are some facts about the taiga biome:
- The taiga is the largest terrestrial biome in the world, covering about 17% of the Earth’s land surface.
- The taiga is located in the Northern Hemisphere, between the tundra to the north and the temperate forests to the south.
- The taiga has a subarctic climate, with long, cold winters and short, cool summers.
- The taiga is dominated by coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, fir, and larch.
- The taiga is home to a variety of wildlife, including moose, bears, wolves, foxes, and many species of birds.
- The taiga is a major source of timber.
- The taiga is also a major source of water, as the trees help to retain moisture in the soil.
- The taiga is a carbon sink, meaning that it absorbs more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it releases.
- The taiga is a fragile ecosystem that is threatened by climate change, deforestation, and pollution.
Also learn about:

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply