What is Sex Determination?-Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determining Genes
Work on the inheritance of Sex began after the discovery of Mendel’s work in 1900. The discovery of Sex chromosomes revealed the genetic basis of Sex determination.
Sex Determination
A sex-determination system is a biological process that decides an organism’s sexual characteristics. Most creatures that have sexual reproduction have two sexes. Some species are hermaphrodites while others reproduce without fertilization, making them only one sex.
In many species, sex determination is genetic, males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals, this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy.
Sexual differentiation is usually triggered by the main gene (a sex locus), with several other genes following a domino effect.
Sex Chromosomes
Sex chromosomes are the chromosomes that determine Sex in different organisms. In humans, there are two types of Sex chromosomes, X and Y. Males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes.
Discovery Of Sex Chromosomes In Drosophila
The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster has eight chromosomes, which are present in the form of four homologous pairs. T.H. Morgan found a difference in chromosomes of male and female Drosophila in 1911.
The chromosomes of the three homologous pairs were similar in both sexes; however, the fourth was heteromorphic and had different structures. The female has two similar, rod-shaped X chromosomes in the fourth pair. The male has one rod-shaped X chromosome but produces a morphologically different one–a J-shaped Y chromosome in the fourth pair.

Sex Chromosomes and Autosomes
Sex chromosomes: The X and Y chromosomes are sex chromosomes that contain genes that determine an individual’s sex.
Autosomes: The chromosomes of the other three pairs are autosomes. All chromosomes besides sex chromosomes are autosomes. Autosomes don’t carry any genes that determine sex.
Sex Chromosomes In Humans
Humans have 46 chromosomes. These are present in 23 pairs, 22 pairs being autosomes and one pair being the sex chromosome. Autosome pairs are common in both sexes, but the 23rd sex chromosome pair is different in males and females.
A woman has two similar X chromosomes in her 23rd pair, while a man has an X chromosome and a Y chromosome. The 23rd pair in man is heteromorphic.
• The female in humans is XX.
• The male is XY.

Male Sex Determining Gene
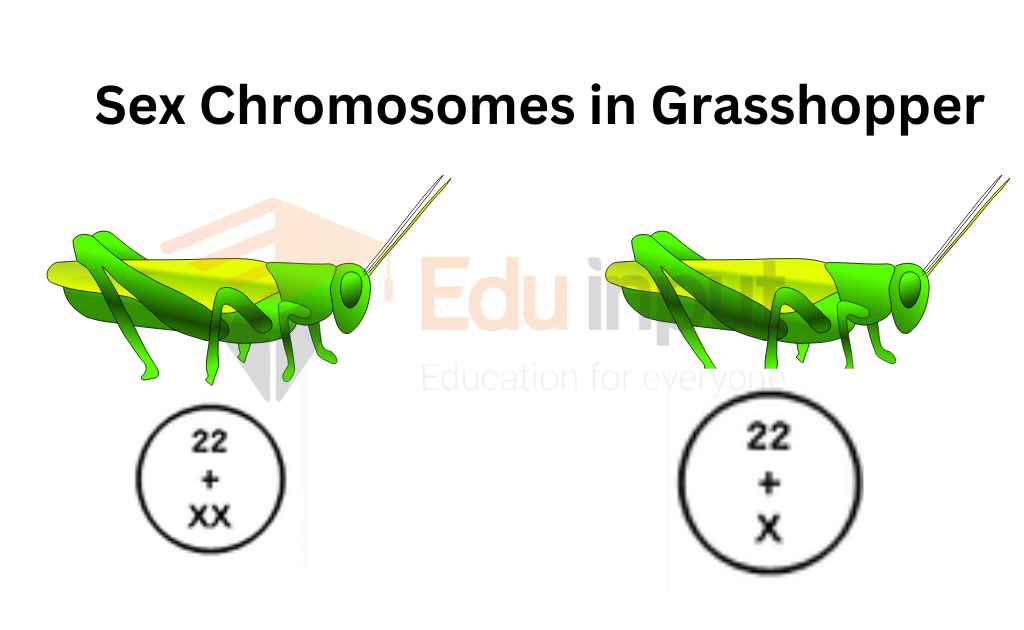
The SRY gene is the male-determining gene. It’s located on the short arm of the Y-chromosome and is responsible for the development of male sex characteristics. In some grasshoppers, males and females have different numbers of chromosomes.
(a) The female has 24 chromosomes, which are present in the form of 11 pairs of autosomes and a pair of X chromosomes. The Female is XX.
(b) The male grasshopper has 23 chromosomes, 11 pairs of autosomes, and one X chromosome. The other sex chromosome is entirely missing in males, making them XO.
Related FAQs
What is Sex Determination?
A sex-determination system is a biological process that decides an organism’s sexual characteristics.
What are Sex Chromosomes?
Chromosomes contain genes that determine an individual’s sex are called sex chromosomes. X and Y chromosomes are sex chromosomes.
What are Autosomes?
Chromosome pairs other than sex chromosomes are called autosomes.



Leave a Reply