Why Are Gonads Mixed Glands?
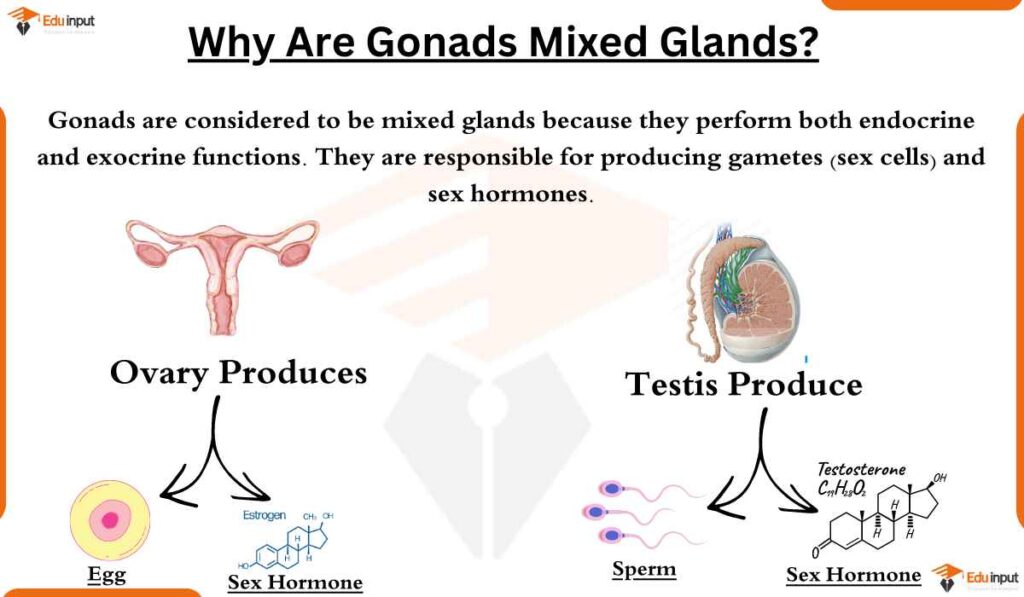
Gonads are considered to be mixed glands because they perform both endocrine and exocrine functions. They are responsible for producing gametes (sex cells) and sex hormones.
The exocrine function of gonads is to produce gametes, which are released from the gonads and travel through the reproductive tract to the site of fertilization.
Endocrine Function of Gonads
The endocrine function of gonads is to produce sex hormones. Sex hormones are responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics, such as breasts in females and facial hair in males.
The main sex hormones produced by gonads are:
- Testosterone is produced by the testes in males. It is responsible for the development of male secondary sex characteristics, such as facial hair and a deep voice.
They are also involved in sperm production and sexual behavior.
- Estrogen and progesterone are produced by the ovaries in females. Estrogen is responsible for the development of female secondary sex characteristics, such as breasts and wider hips.
Gametogenic Function of Gonads
The gametogenic function of gonads is to produce gametes. Gametes are the reproductive cells that unite to form a new organism. The male gamete is called a sperm, and the female gamete is called an egg.
Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. Eggs are produced in the ovaries. The process of producing gametes is called gametogenesis.
Reference: [1]
Are Testes and Ovaries Mixed Glands?
Yes, testes and ovaries are considered mixed glands in the human body because they perform both endocrine and exocrine functions.
Why Ovary Is A Mixed Gland?
The ovary is classified as a mixed gland because it performs both endocrine functions, such as the secretion of hormones like estrogens, and exocrine functions, like producing eggs.
Why Testis Is A Mixed Gland?
The testis is considered a mixed gland because it performs endocrine function like producing and secreting hormones, such as testosterone, into the bloodstream. Additionally, it has an exocrine function like sperm production and release.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply