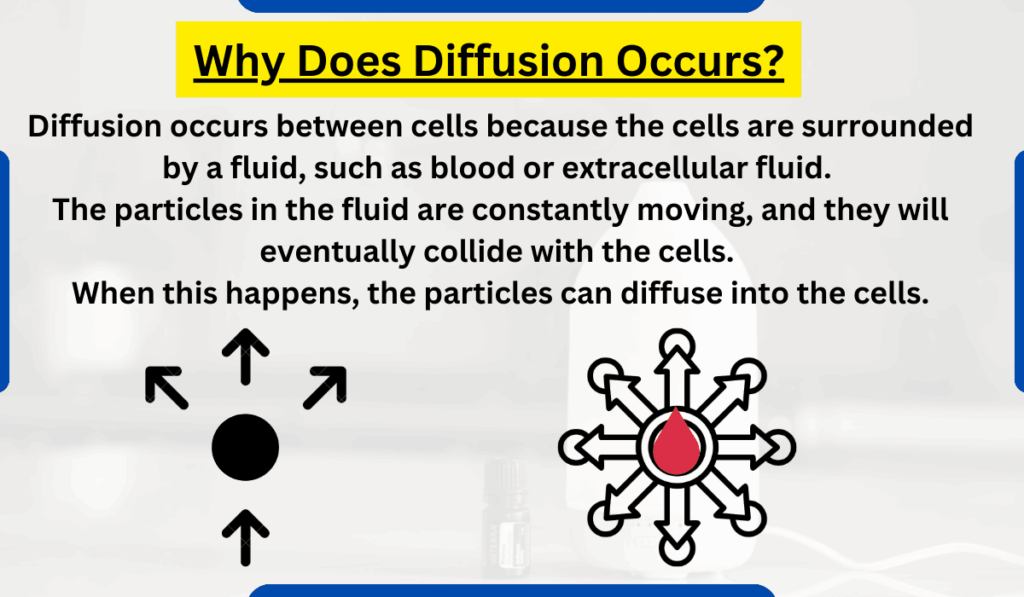
Why Does Diffusion Occurs?
Diffusion occurs between cells because the cells are surrounded by a fluid, such as blood or extracellular fluid. The particles in the fluid are constantly moving, and they will eventually collide with the cells. When this happens, the particles can diffuse into the cells.
Why Diffusion occur in Body, Plants, and Other Systems?
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It occurs naturally and does not require any energy input.
Diffusion is a very important process in the body, plants, physics, chemistry, and biology.
Diffusion in Body
In the body, diffusion is responsible for the movement of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products into and out of cells.
For example, oxygen diffuses from the lungs into the bloodstream, and then from the bloodstream into the cells.
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the bloodstream, and then from the bloodstream into the lungs.
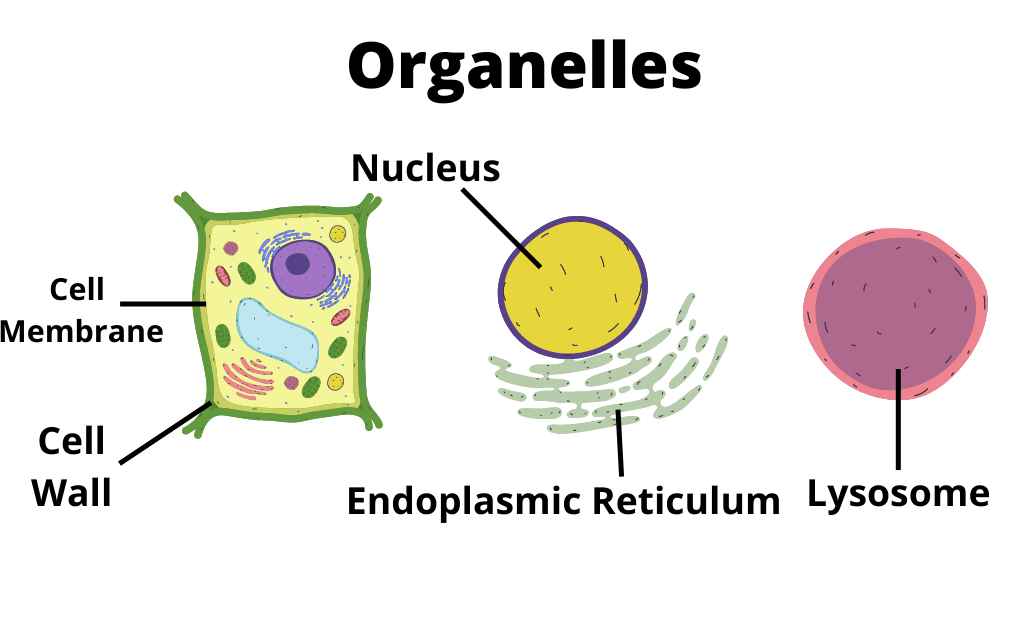
Diffusion in Cells
Diffusion also occurs within cells. The organelles in cells are surrounded by a fluid, and the particles in the fluid can diffuse into the organelles.
This is how nutrients and oxygen get into the organelles, and how waste products get out of the organelles.
Diffusion in Plants
In plants, diffusion is responsible for the movement of water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. It is also responsible for the movement of carbon dioxide from the leaves to the roots.
Diffusion in Physics
In physics, diffusion is a type of Brownian motion, which is the random movement of particles suspended in a liquid or gas. Brownian motion is caused by the collisions of the particles with the molecules of the liquid or gas.
Diffusion in Chemistry
In chemistry, diffusion is a type of mass transfer, which is the movement of matter from one region to another. Mass transfer can occur by diffusion, convection, or advection.
Diffusion in Biology
In biology, diffusion is a type of passive transport, which is the movement of substances across a membrane without the use of energy. Passive transport can occur by diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or osmosis.
Effect of Concentration Gradient on Diffusion
The rate of diffusion is affected by the concentration gradient, the temperature, and the size of the particles. The concentration gradient is the difference in concentration of the particles between two areas.
The higher the concentration gradient, the faster the diffusion. The temperature also affects the rate of diffusion. The higher the temperature, the faster the diffusion.
The size of the particles also affects the rate of diffusion. The smaller the particles, the faster the diffusion.

 written by
written by 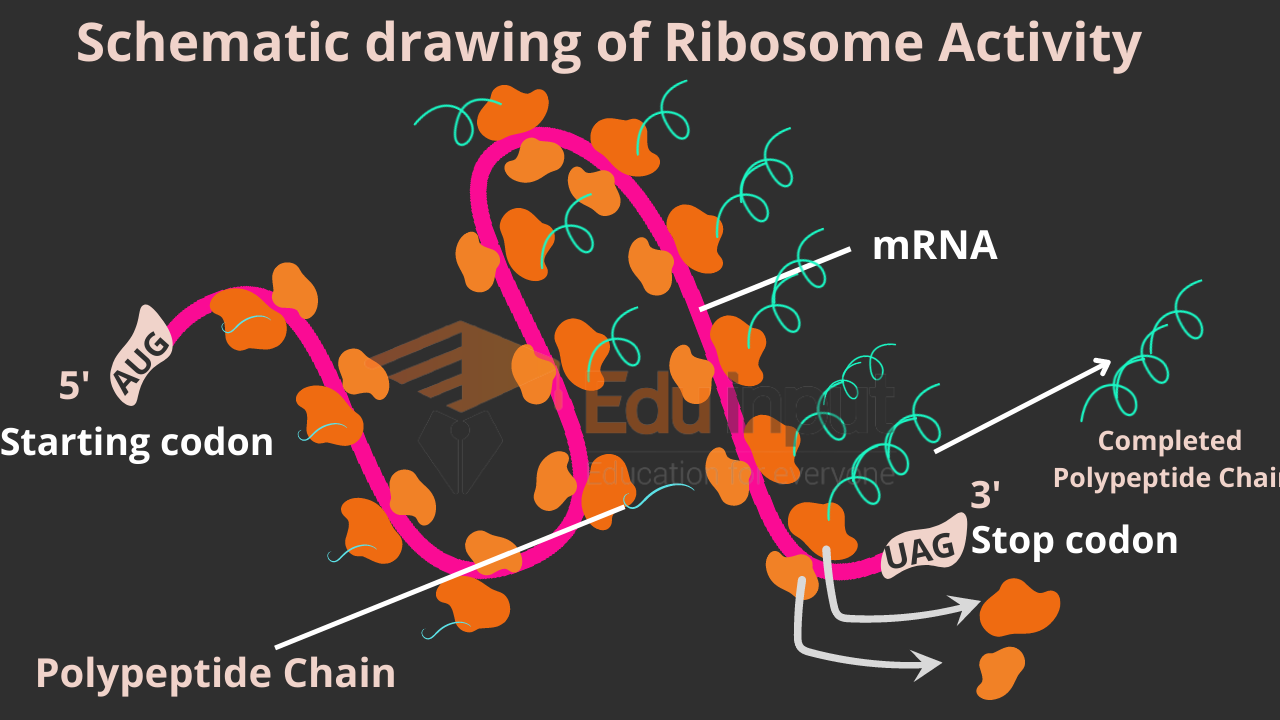


Leave a Reply