What is Diffusion? (Types, Examples, And Factors)
Diffusion in Biology refers to the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, which is caused by their random motion.
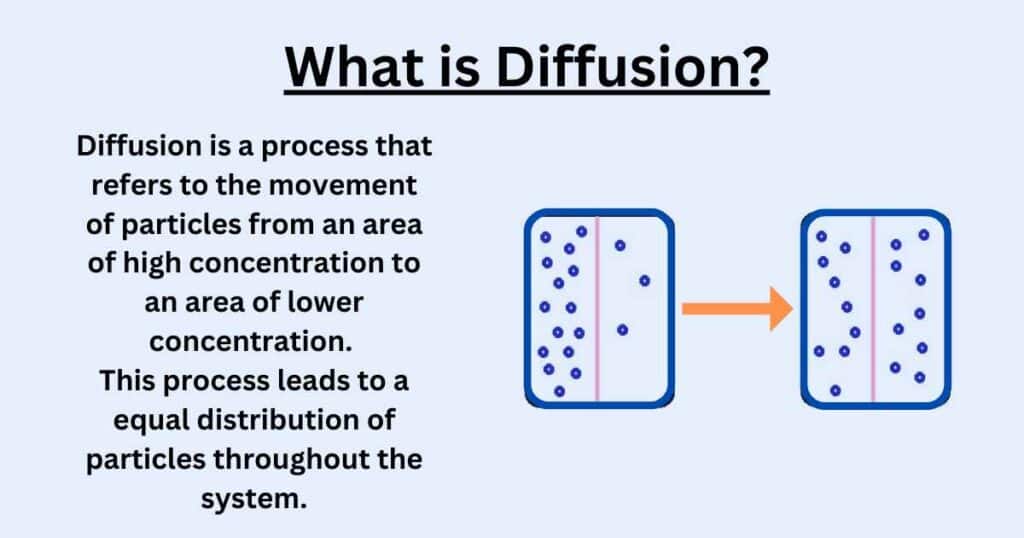
In humans, movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli in the lungs and the surrounding capillaries occurs through diffusion. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Learn Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis
Types of Diffusion
There are different types of diffusion that occur in biological systems:
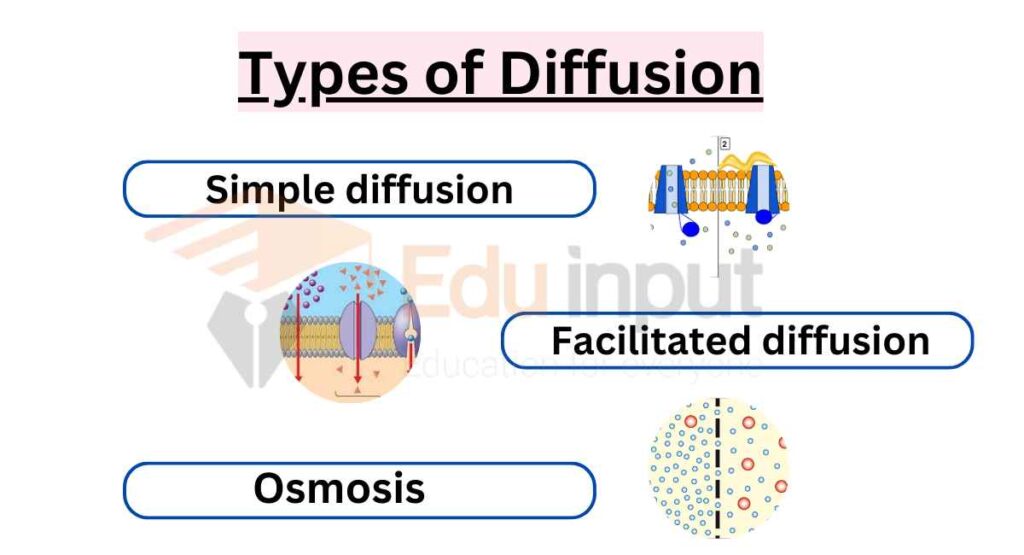
Simple diffusion
Simple diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration without the need for a membrane or carrier protein.
This type of diffusion is typically used for small nonpolar molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, which can diffuse easily through cell membranes via simple diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion involves the movement of molecules across a membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration, with the help of a membrane protein.
This process is used for larger or polar molecules, such as glucose and amino acids, which cannot diffuse across the membrane through simple diffusion.
Osmosis
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion that refers to the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
This process is important in maintaining the proper balance of water and solutes in biological systems, such as the kidneys and plants.
Diffusion Examples
Here are ew examples of process of mechanism describing how it happens:
Diffusion of Gases and Perfume
One common example of diffusion in chemistry is the movement of gases through a porous membrane.
For instance, when a balloon filled with helium is placed in a room filled with air, the helium molecules will diffuse out of the balloon and into the surrounding air until the concentration of helium is the same inside and outside the balloon.
Another example of diffusion can be seen when a person sprays perfume in one part of a room.
The scent molecules in the perfume move from an area of high concentration (near the spray) to an area of lower concentration (farther away from the spray) as they diffuse throughout the room.
This process can be observed over time as the scent gradually becomes more evenly distributed throughout the space.
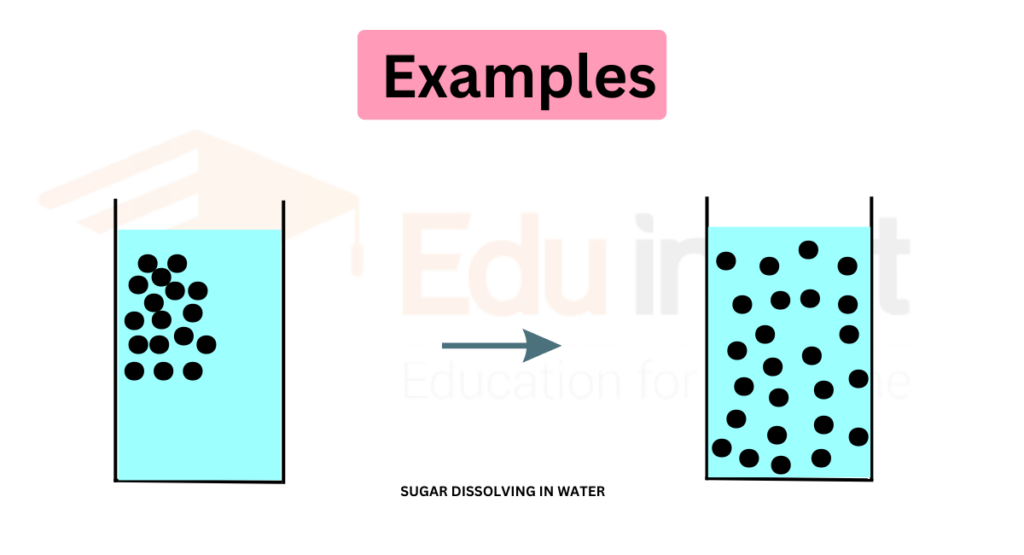
Diffusion of Sugar in Water
When a spoonful of sugar is added to a glass of water, the sugar particles initially cluster together at the bottom of the glass.
However, over time, the sugar particles begin to move and spread out throughout the water, resulting in a uniform concentration of sugar throughout the solution.
Examples of diffusion in chemical and biological processes
Here are the examples of diffusion in Biology and Chemistry:
- Movement of gases through a membrane (e.g., oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in the lungs)
- Mixing of solutions (e.g., sugar dissolving in water)
- Transport of nutrients in biological systems (e.g., glucose moving from the bloodstream into cells for energy production)
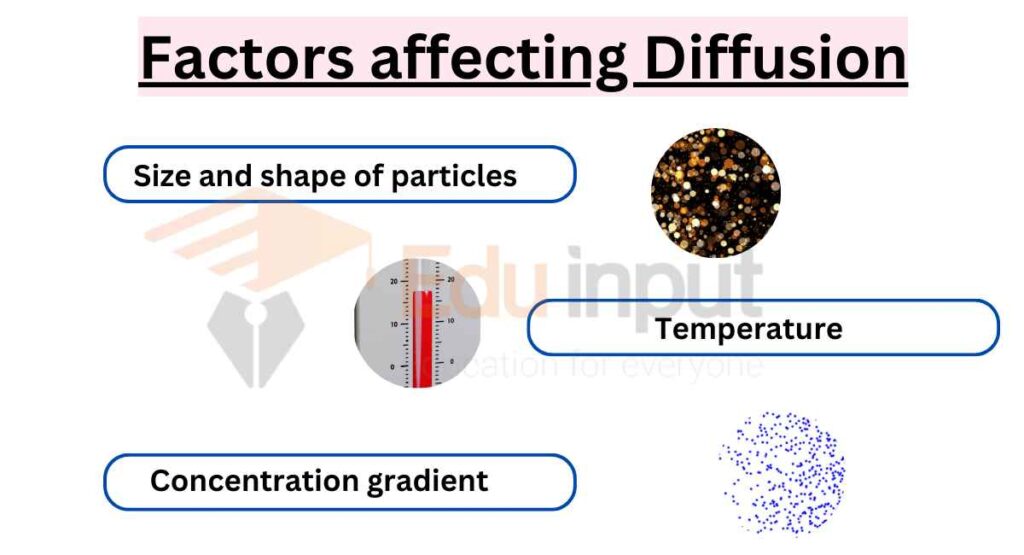
Factors affecting Diffusion
Factors affecting the rate of diffusion:
- Size and shape of particles
- Temperature
- Concentration gradient
Also Learn About:
FAQs
What is the definition of diffusion?
Diffusion is a process of movement of molecules (solids, liquids, gases) from higher concentration to lower concentration.
Why is it called diffusion?
The word “Diffusion” was derived from a Latin word “diffusionem, diffusio” meaning “to spread out/or pouring forth”. That’s why it is called diffusion as solute molecules spread out in solvent.
Who discovered diffusion?
Thomas Graham discovered the phenomenon of diffusion in gases for the first time.

 written by
written by 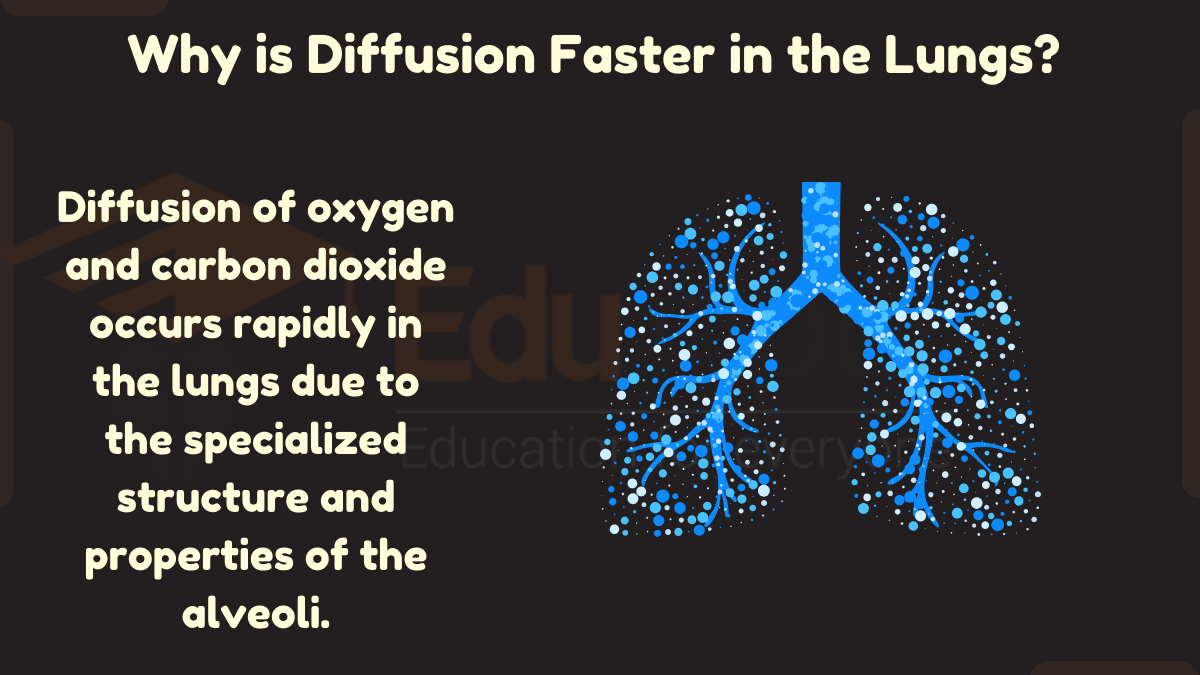


Leave a Reply