Manometer-Working, Types, And Applications
A manometer is an essential tool used for measuring pressure in various applications. Whether you’re working in an industrial setting, maintaining HVAC systems, or even in medical environments, manometers play a crucial role in accurate pressure measurement.
What is Manometer?
A manometer is a device used to measure pressure. It is an essential tool in various industries and applications where accurate pressure measurement is crucial. The word “manometer” is derived from the Greek words “manos” meaning “thin” and “metron” meaning “measure.”
The main purpose of a manometer is to compare the pressure of a fluid with a known reference pressure. It typically consists of a glass tube or a flexible diaphragm that reacts to pressure changes. The device can measure both positive and negative pressures, providing valuable information for different systems and processes.
Working Principle of Manometer
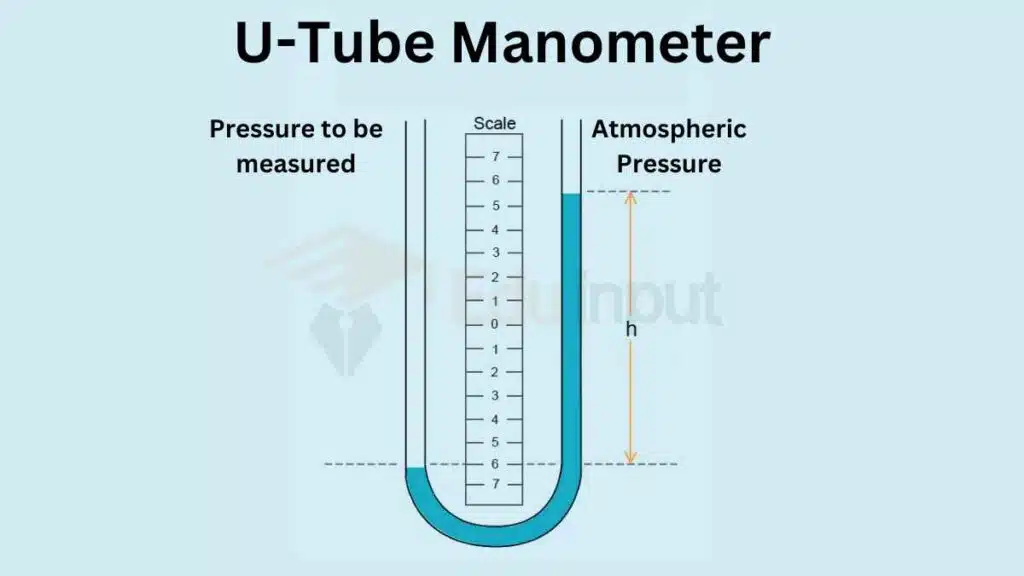
Manometers operate based on the principle that pressure exerted by a fluid is directly proportional to its height in a column. The most common manometer, known as the U-Tube Manometer consists of a U-shaped glass tube partially filled with a liquid usually mercury or water.
When pressure is applied to one end of the U-tube the liquid in the tube shifts and creates a difference in height between the two arms. The pressure can be determined by measuring this difference.
Types of Manometers
These are the main types of manometers.
U-Tube Manometer
This is the simplest and most commonly used type of manometer. It consists of a U-shaped tube partially filled with liquid. The pressure difference between the two arms of the tube determines the height difference of the liquid column, allowing pressure measurement.
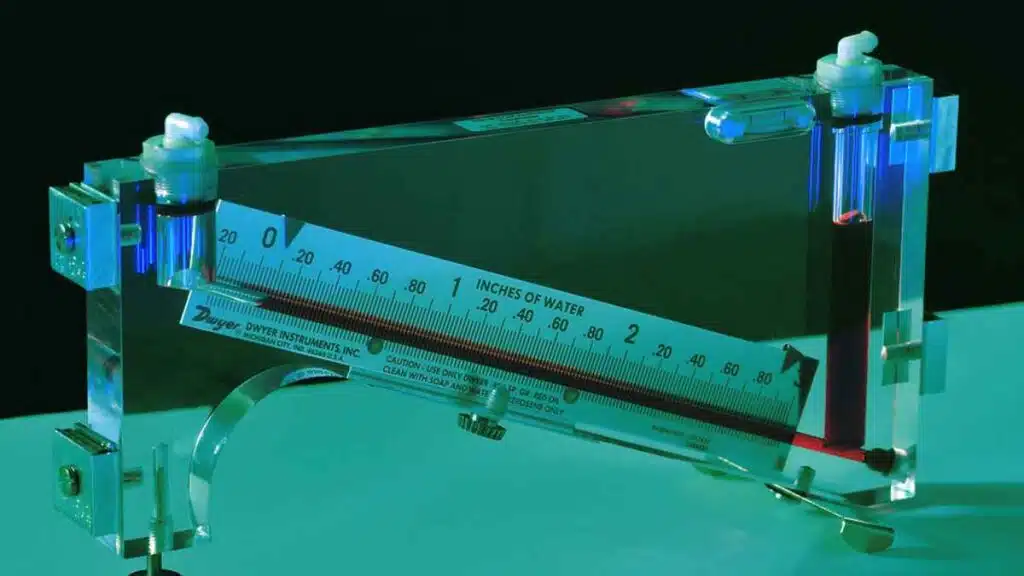
Inclined Manometer
Inclined manometers utilize an inclined tube instead of a U-shaped tube. The angle of inclination affects the sensitivity of the manometer, allowing for more precise pressure measurements in specific applications.

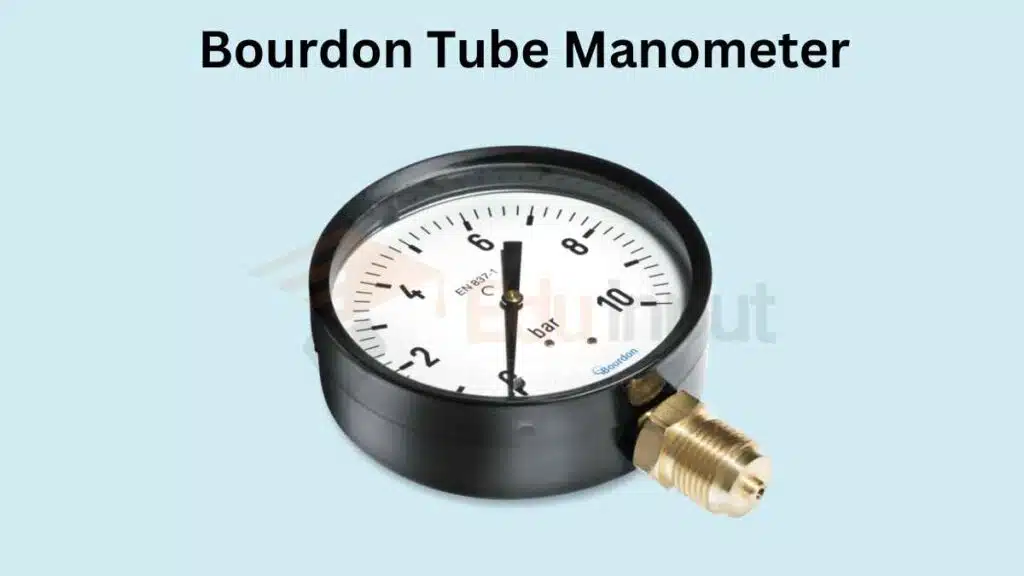
Bourdon Tube Manometer
Bourdon tube manometers use a flattened tube made of metal that is curved into a C-shape. As pressure is applied, the tube straightens, and the movement is translated into a corresponding pressure reading.

Digital Manometer
With advancements in technology, digital manometers have become popular due to their ease of use and accuracy. These manometers display pressure readings digitally, eliminating the need for visual interpretation.

Applications of Manometers
Manometers find applications in various industries and sectors. Some notable applications include:
- Industrial Applications: Manometers are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and oil and gas, where precise pressure control is crucial for operational efficiency and safety.
- HVAC Systems: Manometers are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to measure and balance air pressure in ducts, ensuring optimal performance and air quality.
- Medical Applications: Manometers are utilized in medical devices such as ventilators and anesthesia machines to monitor and control pressure, ensuring patient safety and effective treatment.
Advantages of Manometers
Manometers offer several advantages that make them indispensable in pressure measurement:
- Accuracy in Pressure Measurement: Manometers provide accurate and reliable pressure measurements, making them suitable for applications that require precise control and monitoring.
- Versatility and Wide Range of Applications: Manometers can be used in various industries and sectors due to their ability to measure a wide range of pressures, from low vacuum to high pressure.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other pressure-measuring instruments, manometers are relatively cost-effective while still maintaining accuracy and reliability.
Related FAQs
What is a manometer and how does it work?
A manometer is a device used to measure pressure. It works by comparing the height of a liquid column, such as mercury or water, with the pressure being measured. The pressure causes the liquid to rise or fall in a tube, allowing for pressure determination.
How does a manometer measure pressure?
A manometer measures pressure, which is the force applied per unit area. It provides readings in terms of the pressure exerted by a gas or liquid.
Where does a manometer measure?
A manometer measures pressure at a specific point or location in a system. The point of measurement depends on the application and the area of interest, such as within a pipe, duct, or device.





Leave a Reply