Difference Between Bus and Star Topology
The differences between bus and star topologies revolve around the setup you use in the network. Bus topology is a type of network topology. In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable. In star topology, different devices directly connect to the central device. These differences have implications for the network’s reliability, cost, and performance.
Bus Topology
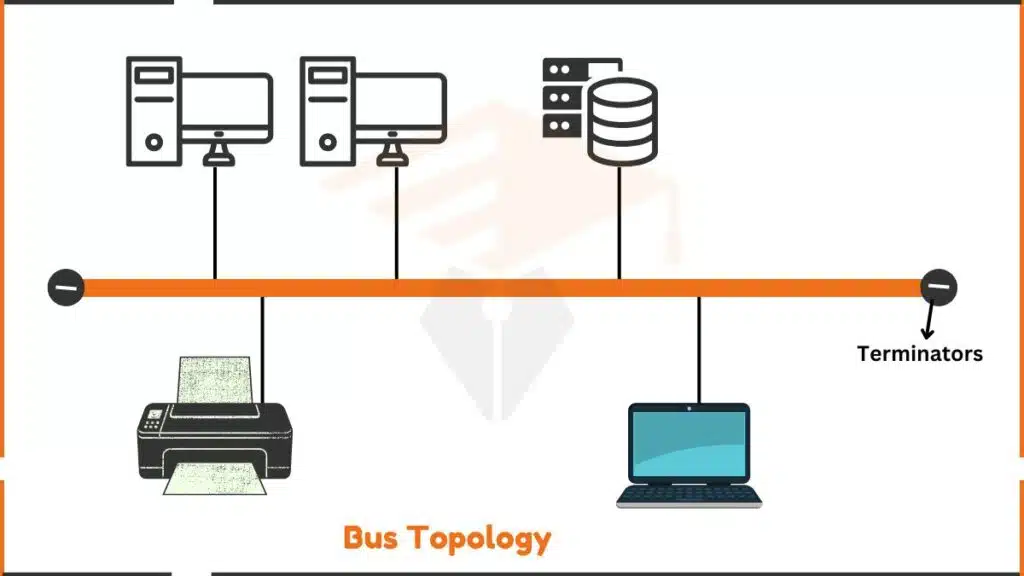
Bus topology uses one main cable to connect all network devices. Think of it like a long hallway with doors to different rooms. The main cable is the hallway, and each device connects through a door.
All devices connect directly to the main cable using connectors called taps or T-connectors. The cable ends have special plugs called terminators. These terminators prevent signal bouncing.
Star Topology
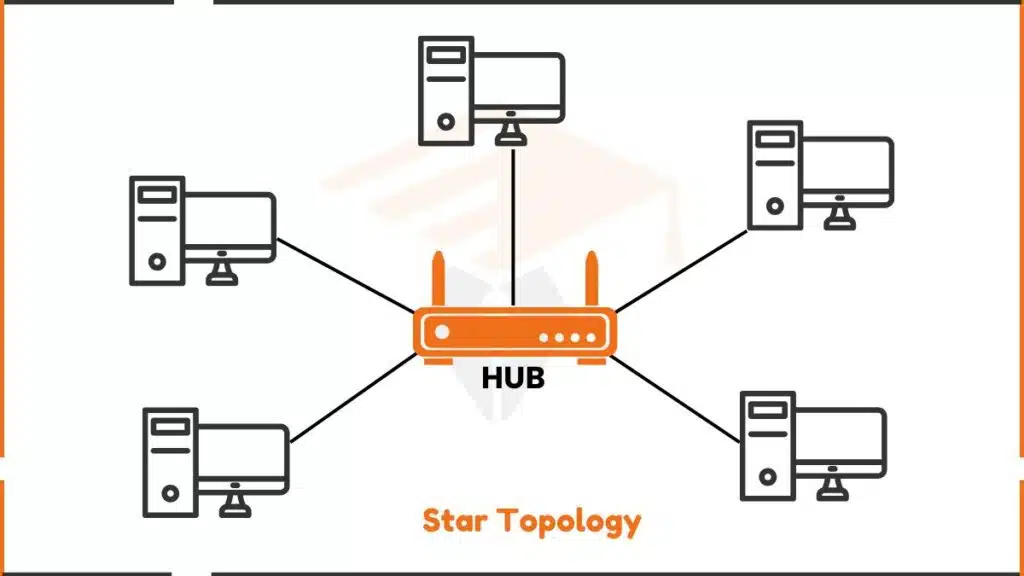
Star topology connects all devices to a central hub or switch. Picture a wheel with spokes the hub is the center, and each device connects via its cable (the spokes).
Each device has its dedicated connection to the central hub. No devices connect directly to each other. The hub manages all network traffic and connections.
Bus Topology Vs Star Topology
The following table highlights the key differences between Bus and Star Topology:
| Feature | Bus Topology | Star Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Method | Single backbone cable | Central hub |
| Data Transmission | Broadcasts to all devices | Point-to-point via hub |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher due to hub and cables |
| Fault Tolerance | The entire network fails if the main cable breaks | The entire network fails if main cable breaks |
| Scalability | Limited by cable length | Easy to add new devices |
| Data Collision | More common | Less common |
| Maintenance | Hard to troubleshoot | Easy to find problems |
Use Cases
Use cases of both bus and star topology:
Bus Topology Best For
- Small networks with few devices
- Simple network setups
- Limited budget installations
- Temporary networks
- Linear physical layouts
Star Topology Best For
- Large networks
- Office buildings
- Networks needing high reliability
- Easy maintenance requirements
- Future expansion plans
FAQs
What is the cheapest topology?
The cheapest topology is bus topology due to its simple design and minimal cable use.
Which topology is slow?
Bus topology is slow, especially with many devices, due to data congestion on a single cable.
Which topology is rarely used?
Bus topology is rarely used today, as it has limitations like slow speed, difficulty in troubleshooting, and vulnerability to network failure.






Leave a Reply